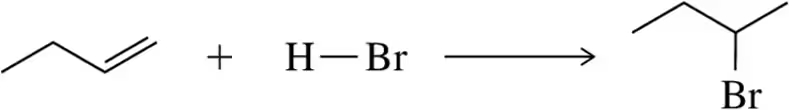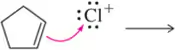Back
BackProblem 1b(i)
(i) Using bond dissociation energies, calculate ∆H° for the following reactions. [BDE for O―H = 110 kcal /mol.]
(b)
Problem 2
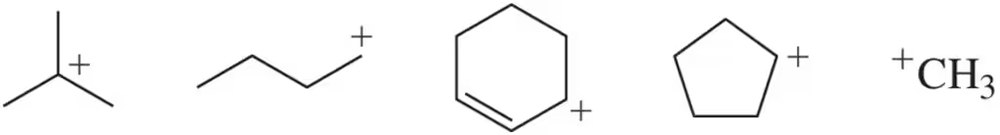
(a) Rank the following carbocations from least stable to most stable. (b) Which would you expect to form first? (c) Which would you expect to react most quickly with a bromide ion (Br⁻) ? [Carbocations, like radicals, are electron deficient.]
Problem 3
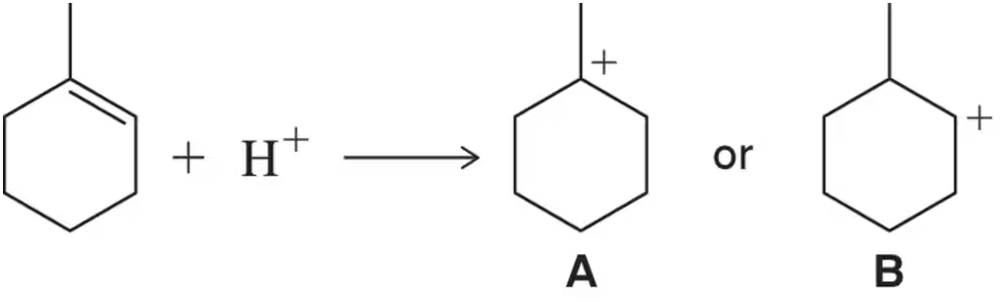
Given that A is more stable than B, draw a reaction coordinate diagram that rationalizes the fact that A forms more quickly than B in the following reaction.
Problem 4
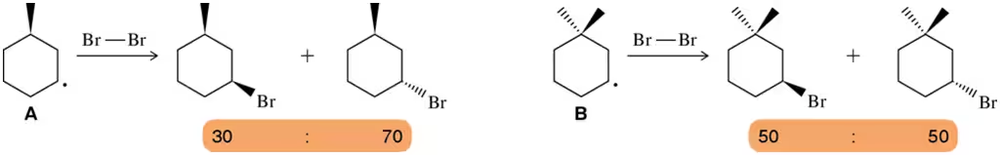
Rationalize the fact that reaction A results in an unequal mixture of products, but reaction B yields an equal mixture of two products.
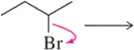
Problem 5a
Predict the product that results from the following 'pushed electrons.'
(a)
Problem 5c
Predict the product that results from the following 'pushed electrons.'
(c)
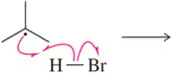
Problem 5f
Predict the product that results from the following 'pushed electrons.'
(f)
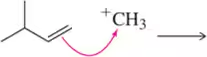
Problem 5i
Predict the product that results from the following 'pushed electrons.'
(i)
Problem 6a
Given the structure, calculate the index of hydrogen deficiency (degrees of unsaturation) of the following molecules.
(a)
Problem 7a
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency for each of the following molecular formulas?
(a) C6H12O6
Problem 7b
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency for each of the following molecular formulas?
(b) C12H11NO3
Problem 7c
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency for each of the following molecular formulas?
(c) C8H14Cl2
Problem 7d
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency for each of the following molecular formulas?
(d) C9H12N2O2
Problem 7e
What is the index of hydrogen deficiency for each of the following molecular formulas?
(e) C6H12O2
Problem 8
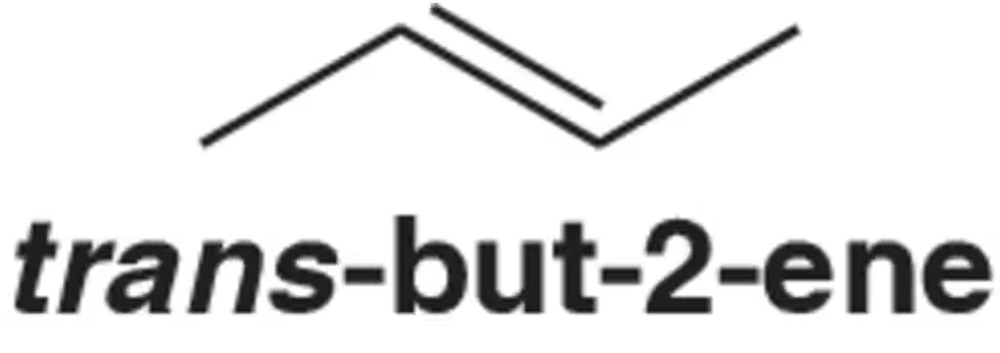
Draw the molecular orbital picture of trans-but-2-ene.
Problem 8.55b
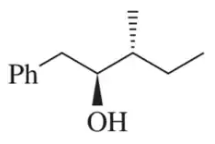
Suggest an alkene to undergo hydroboration–oxidation (1. BH3 2. NaOH, H2O2) to give exclusively the alcohols shown. Pay close attention to the relative (but not absolute) stereochemical outcome.
(b)
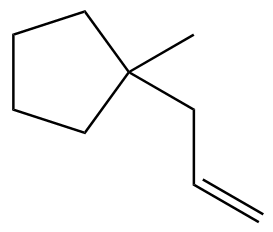
Problem 8.39d
Provide the expected product for the reaction of each of the following alkenes with H₂SO₄ and H₂O.
(d)
Problem 9a
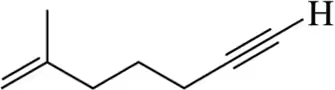
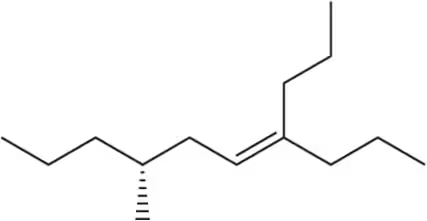
Provide the IUPAC names for the following alkenes.
(a)
Problem 10a
Given the following IUPAC names, draw the corresponding structures.
(a) (R)-3-isopropyl-6-methylnon-1-ene
Problem 10c
Given the following IUPAC names, draw the corresponding structures.
(c) (S)-3-fluoropent-1-ene
Problem 11a
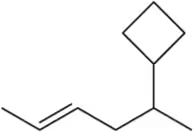
Name the following alkenes, being sure to specify whether they are cis or trans.
(a)
Problem 11c
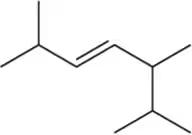
Name the following alkenes, being sure to specify whether they are cis or trans.
(c)
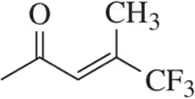
Problem 12a
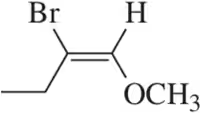
Which of the following alkenes are E and which are Z?
(a)
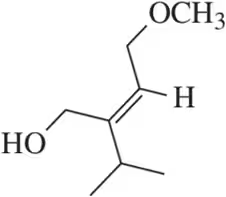
Problem 12b
Which of the following alkenes are E and which are Z?
(b)
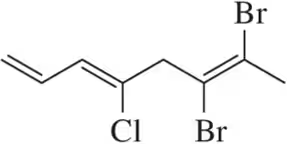
Problem 12c
Which of the following alkenes are E and which are Z?
(c)
Problem 13a
Given the name, draw the structure of the following alkenes.
(a) (E)-4-ethyl-5-methyloct-3-ene
Problem 13b
Given the name, draw the structure of the following alkenes.
(b) ((Z)-1-cyclohexyl-2-methylhept-2-ene
Problem 13c
Given the name, draw the structure of the following alkenes.
(c) (Z)-3-isopropylhept-3-ene
Problem 15b
Name the following alkenes.
(b)
Problem 16
How many stereoisomers are possible (a) for 4-methylnona-2,7-diene? (b) For 6-chloronona-2,4,7-triene?