7. Prokaryotic Cell Structures & Functions
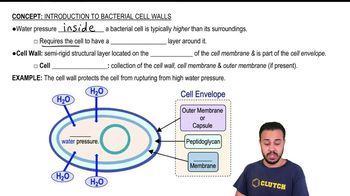
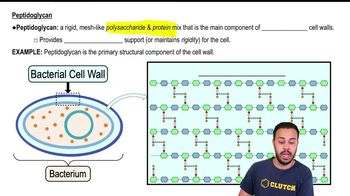
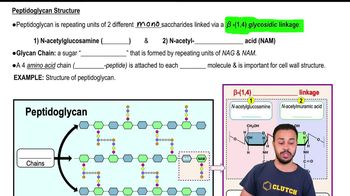
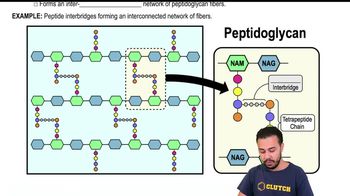
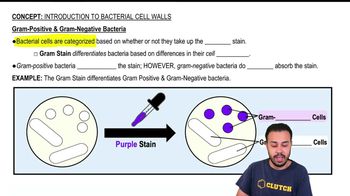
Introduction to Bacterial Cell Walls
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which is (are) true concerning the cell wall of prokaryotes?
- Multiple Choice
Peptidoglycan is made up of:
- Multiple Choice
The NAG and NAM molecules of peptidoglycan are connected by a:
- Multiple Choice
The glycan chains of adjacent peptidoglycan molecules are connected by:
- Open Question
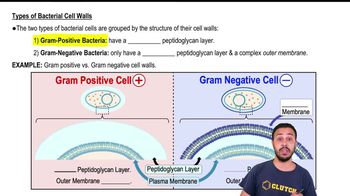
Answer the following questions using the diagrams provided, which represent cross sections of bacterial cell walls.
a. Which diagram represents a gram-positive bacterium? How can you tell? <IMAGE>
b. Explain how the Gram stain works to distinguish these two types of cell walls.
c. Why does penicillin have no effect on most gram-negative cells?
d. How do essential molecules enter cells through each wall?
e. Which cell wall is toxic to humans?
- Open Question
If you Gram-stained the bacteria that live in the human intestine, you would expect to find mostly
a. gram-positive cocci.
b. gram-negative rods.
c. gram-positive, endospore-forming rods.
d. gram-negative, nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
e. all of the above.
- Open Question
Bacteria cell walls tend to contain:
a. peptidoglycan.
b. lipid bilayers.
c. cholesterol.
d. pseudomurein.
e. flagellin.
- Open Question
Which of the following statements is true?
a. The cell walls of bacteria are composed of peptidoglycan.
b. Peptidoglycan is a fatty acid.
c. Gram-positive bacterial walls have a relatively thin layer of peptidoglycan anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane by teichoic acids.
d. Peptidoglycan is found mainly in the cell walls of fungi, algae, and plants.