- 1. Introduction to Microbiology
- Introduction to Microbiology
- Introduction to Taxonomy
- Scientific Naming of Organisms
- Members of the Bacterial World
- Introduction to Bacteria
- Introduction to Archaea
- Introduction to Eukarya
- Acellular Infectious Agents: Viruses, Viroids & Prions
- Importance of Microorganisms
- Scientific Method
- Experimental Design
- 2. Disproving Spontaneous Generation
- 3. Chemical Principles of Microbiology
- 4. Water
- 5. Molecules of Microbiology
- 6. Cell Membrane & Transport
- Cell Envelope & Biological Membranes
- Bacterial & Eukaryotic Cell Membranes
- Archaeal Cell Membranes
- Types of Membrane Proteins
- Concentration Gradients and Diffusion
- Introduction to Membrane Transport
- Passive vs. Active Transport
- Osmosis
- Simple and Facilitated Diffusion
- Active Transport
- ABC Transporters
- Group Translocation
- Types of Small Molecule Transport Review
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis
- 7. Prokaryotic Cell Structures & Functions
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells
- Binary Fission
- Generation Times
- Bacterial Cell Morphology & Arrangements
- Overview of Prokaryotic Cell Structure
- Introduction to Bacterial Cell Walls
- Gram-Positive Cell Walls
- Gram-Negative Cell Walls
- Gram-Positive vs. Gram-Negative Cell Walls
- The Glycocalyx: Capsules & Slime Layers
- Introduction to Biofilms
- Pili
- Fimbriae & Hami
- Introduction to Prokaryotic Flagella
- Prokaryotic Flagellar Structure
- Prokaryotic Flagellar Movement
- Proton Motive Force Drives Flagellar Motility
- Chemotaxis
- Review of Prokaryotic Surface Structures
- Prokaryotic Ribosomes
- Introduction to Bacterial Plasmids
- Cell Inclusions
- Endospores
- Sporulation
- Germination
- 8. Eukaryotic Cell Structures & Functions
- 9. Microscopes
- Introduction to Microscopes
- Magnification, Resolution, & Contrast
- Introduction to Light Microscopy
- Light Microscopy: Bright-Field Microscopes
- Light Microscopes that Increase Contrast
- Light Microscopes that Detect Fluorescence
- Electron Microscopes
- Reviewing the Different Types of Microscopes
- Introduction to Staining
- Simple Staining
- Differential Staining
- Other Types of Staining
- Reviewing the Types of Staining
- Gram Stain
- 10. Dynamics of Microbial Growth
- Biofilms
- Growing a Pure Culture
- Microbial Growth Curves in a Closed System
- Temperature Requirements for Microbial Growth
- Oxygen Requirements for Microbial Growth
- pH Requirements for Microbial Growth
- Osmolarity Factors for Microbial Growth
- Reviewing the Environmental Factors of Microbial Growth
- Nutritional Factors of Microbial Growth
- Growth Factors
- Introduction to Cultivating Microbial Growth
- Types of Solid Culture Media
- Plating Methods
- Measuring Growth by Direct Cell Counts
- Measuring Growth by Plate Counts
- Measuring Growth by Membrane Filtration
- Measuring Growth by Biomass
- Introduction to the Types of Culture Media
- Chemically Defined Media
- Complex Media
- Selective Media
- Differential Media
- Reducing Media
- Enrichment Media
- Reviewing the Types of Culture Media
- 11. Controlling Microbial Growth
- Introduction to Controlling Microbial Growth
- Selecting a Method to Control Microbial Growth
- Physical Methods to Control Microbial Growth
- Review of Physical Methods to Control Microbial Growth
- Chemical Methods to Control Microbial Growth
- Chemicals Used to Control Microbial Growth
- Liquid Chemicals: Alcohols, Aldehydes, & Biguanides
- Liquid Chemicals: Halogens
- Liquid Chemicals: Surface-Active Agents
- Other Types of Liquid Chemicals
- Chemical Gases: Ethylene Oxide, Ozone, & Formaldehyde
- Review of Chemicals Used to Control Microbial Growth
- Chemical Preservation of Perishable Products
- 12. Microbial Metabolism
- Introduction to Energy
- Laws of Thermodynamics
- Chemical Reactions
- ATP
- Enzymes
- Enzyme Activation Energy
- Enzyme Binding Factors
- Enzyme Inhibition
- Introduction to Metabolism
- Negative & Positive Feedback
- Redox Reactions
- Introduction to Aerobic Cellular Respiration
- Types of Phosphorylation
- Glycolysis
- Entner-Doudoroff Pathway
- Pentose-Phosphate Pathway
- Pyruvate Oxidation
- Krebs Cycle
- Electron Transport Chain
- Chemiosmosis
- Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration
- Fermentation & Anaerobic Respiration
- 13. Photosynthesis
- 14. DNA Replication
- 15. Central Dogma & Gene Regulation
- Central Dogma
- Introduction to Transcription
- Steps of Transcription
- Transcription Termination in Prokaryotes
- Eukaryotic RNA Processing and Splicing
- Introduction to Types of RNA
- Genetic Code
- Introduction to Translation
- Steps of Translation
- Review of Transcription vs. Translation
- Prokaryotic Gene Expression
- Review of Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Gene Expression
- Introduction to Regulation of Gene Expression
- Prokaryotic Gene Regulation via Operons
- The Lac Operon
- Glucose's Impact on Lac Operon
- The Trp Operon
- Review of the Lac Operon & Trp Operon
- Introduction to Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
- Eukaryotic Chromatin Modifications
- Eukaryotic Transcriptional Control
- Eukaryotic Post-Transcriptional Regulation
- Post-Translational Modification
- Eukaryotic Post-Translational Regulation
- 16. Microbial Genetics
- Introduction to Microbial Genetics
- Introduction to Mutations
- Methods of Inducing Mutations
- Prototrophs vs. Auxotrophs
- Mutant Detection
- The Ames Test
- Introduction to DNA Repair
- DNA Repair Mechanisms
- Horizontal Gene Transfer
- Bacterial Transformation
- Transduction
- Introduction to Conjugation
- Conjugation: F Plasmids
- Conjugation: Hfr & F' Cells
- Genome Variability
- CRISPR CAS
- 17. Biotechnology
- 18. Viruses, Viroids, & Prions
- Introduction to Viruses
- Introduction to Bacteriophage Infections
- Bacteriophage: Lytic Phage Infections
- Bacteriophage: Lysogenic Phage Infections
- Bacteriophage: Filamentous Phage Infections
- Plaque Assays
- Introduction to Animal Virus Infections
- Animal Viruses: 1. Attachment to the Host Cell
- Animal Viruses: 2. Entry & Uncoating in the Host Cell
- Animal Viruses: 3. Synthesis & Replication
- Animal Viruses: DNA Virus Synthesis & Replication
- Animal Viruses: RNA Virus Synthesis & Replication
- Animal Viruses: Antigenic Drift vs. Antigenic Shift
- Animal Viruses: Reverse-Transcribing Virus Synthesis & Replication
- Animal Viruses: 4. Assembly Inside Host Cell
- Animal Viruses: 5. Release from Host Cell
- Acute vs. Persistent Viral Infections
- COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2)
- Plant Viruses
- Viroids
- Prions
- 19. Innate Immunity
- Introduction to Immunity
- Introduction to Innate Immunity
- Introduction to First-Line Defenses
- Physical Barriers in First-Line Defenses: Skin
- Physical Barriers in First-Line Defenses: Mucous Membrane
- First-Line Defenses: Chemical Barriers
- First-Line Defenses: Normal Microflora
- Introduction to Cells of the Immune System
- Cells of the Immune System: Granulocytes
- Cells of the Immune System: Agranulocytes
- Introduction to Cell Communication
- Cell Communication: Surface Receptors & Adhesion Molecules
- Cell Communication: Cytokines
- Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)
- Introduction to the Complement System
- Activation Pathways of the Complement System
- Effects of the Complement System
- Review of the Complement System
- Phagoctytosis
- Introduction to Inflammation
- Steps of the Inflammatory Response
- Fever
- Interferon Response
- 20. Adaptive Immunity
- Introduction to Adaptive Immunity
- Antigens
- Introduction to T Lymphocytes
- Major Histocompatibility Complex Molecules
- Activation of T Lymphocytes
- Functions of T Lymphocytes
- Review of Cytotoxic vs Helper T Cells
- Introduction to B Lymphocytes
- Antibodies
- Classes of Antibodies
- Outcomes of Antibody Binding to Antigen
- T Dependent & T Independent Antigens
- Clonal Selection
- Antibody Class Switching
- Affinity Maturation
- Primary and Secondary Response of Adaptive Immunity
- Immune Tolerance
- Regulatory T Cells
- Natural Killer Cells
- Review of Adaptive Immunity
- 21. Principles of Disease
- Symbiotic Relationships
- The Human Microbiome
- Characteristics of Infectious Disease
- Stages of Infectious Disease Progression
- Koch's Postulates
- Molecular Koch's Postulates
- Bacterial Pathogenesis
- Introduction to Pathogenic Toxins
- Exotoxins Cause Damage to the Host
- Endotoxin Causes Damage to the Host
- Exotoxins vs. Endotoxin Review
- Immune Response Damage to the Host
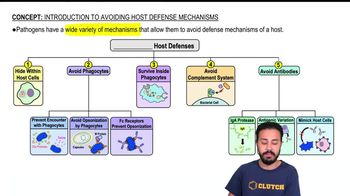
- Introduction to Avoiding Host Defense Mechanisms
- 1) Hide Within Host Cells
- 2) Avoiding Phagocytosis
- 3) Surviving Inside Phagocytic Cells
- 4) Avoiding Complement System
- 5) Avoiding Antibodies
- Viruses Evade the Immune Response
- 25. Epidemiology
- 26. Applications of the Immune Response
- 27. Immunological Disorders
- 28. Antimicrobial Drugs
- Introduction to Antimicrobial Drugs
- How Antimicrobial Drugs Work
- Broad vs Narrow Spectrum Drugs
- Superinfections
- Drug Interactions: Synergism and Antagonism
- Therapeutic Window & Therapeutic Index
- Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis: Beta-lactam & Penicillin
- Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis: Polypeptide Antibiotics & Isoniazid
- Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis
- Disruptors of Cell Membranes
- Inhibitors of Nucleic Acid Synthesis
- Competitive Inhibitors of Metabolic Pathways
- Antifungal Drugs
- Antiviral Drugs
- Tests to Guide Antimicrobial Use
- Antimicrobial Resistance
- 29. Microbial Infections - Skin and Eyes
- 30. Microbial Infections - Respiratory System
- 31. Microbial Infections - Digestive System
21. Principles of Disease
Introduction to Avoiding Host Defense Mechanisms
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
All of the following are methods that pathogens use to avoid phagocytosis by immune cells except which of these answers?
- Multiple Choice
Certain pathogens, like Staphylococcus aureus, hide within host cells to avoid being phagocytosed by immune cells. What other advantageous reasons would a pathogen have for hiding within host cells?
- Open Question
Which of the following does not represent the same mechanism for avoiding host defenses as the others?
a. Rabies virus attaches to the receptor for the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
b. Salmonella attaches to the receptor for epidermal growth factor.
c. Lymphocryptovirus (mononucleosis) virus binds to the host receptor for complement protein.
d. Surface protein genes in N. gonorrhoeae mutate frequently.
e. none of the above
- Open Question
A 12-year-old child hospitalized for Guillain-Barré syndrome had a 4-day history of headache, dizziness, fever, sore throat, and weakness of legs. Seizures began 2 weeks later. Bacterial cultures were negative. The child died 3 weeks after hospitalization. An autopsy revealed inclusions in brain cells that tested positive in an immunofluorescence test. This patient probably had
a. rabies.
b. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
c. botulism.
d. tetanus.
e. leprosy.
- Open Question
After receiving a corneal transplant, a patient developed dementia and loss of motor function, then became comatose and died. Cultures were negative. Serological tests were negative. Autopsy revealed spongiform degeneration of brain tissue. The patient most likely had
a. rabies.
b. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
c. botulism.
d. tetanus.
e. leprosy.