12. Microbial Metabolism
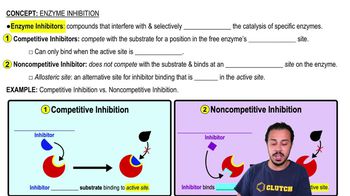
Enzyme Inhibition
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes competitive inhibition?
a) A competitive inhibitor binds to the substrate and inhibits it from binding to the active site of the enzyme.
b) A competitive inhibitor binds to a site other than the active site and inhibits the substrate from binding.
c) A competitive inhibitor binds to the active site and degrades the enzyme.
d) A competitive inhibitor binds to the active site of an enzyme and inhibits the substrate to bind.
- Multiple Choice
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
a) By binding to the active site of the enzyme, thus preventing binding of the normal substrate.
b) By binding to an allosteric site, thus changing the shape of the active site of the enzyme.
c) By decreasing the free-energy change of the reaction catalyzed by the enzyme.
d) By binding to the substrate, thus changing its shape so that it no longer binds to the active site of the enzyme.
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of enzyme inhibition is overcome by increasing the substrate concentration?
a) The need for a coenzyme.
b) Noncompetitive inhibition.
c) Competitive inhibition.
d) None of the above.
- Open Question
DRAW IT Using the following diagrams, show each of the following:
a. where the substrate will bind
b. where the competitive inhibitor will bind
c. where the noncompetitive inhibitor will bind
d. which of the four elements could be the inhibitor in feedback inhibition
e. What effect will the reactions in (a), (b), and (c) have?
<IMAGE>
- Open Question
How do organisms control the rate of metabolic activities in their cells?
- Open Question
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor at a single allosteric site affect a whole pathway of enzymatic reactions?