12. Microbial Metabolism
Redox Reactions
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
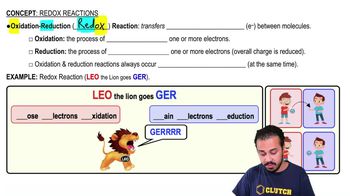
Oxidation is the _________________________, and reduction is the _________________________.
a) Gain of electrons; Loss of electrons.
b) Gain of protons; Loss of protons.
c) Loss of electrons; Gain of electrons.
d) Gain of oxygen; Loss of oxygen.
- Multiple Choice
When glucose donates electrons to NAD+ creating NADH, the glucose molecule becomes:
a) Hydrolyzed.
b) Oxidized.
c) Neutral.
d) Reduced.
- Multiple Choice
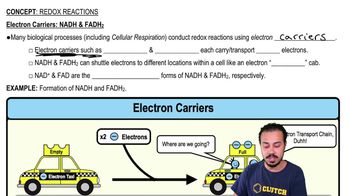
An electron carrier before it harvests energy from glucose molecules in a series of gradual steps is:
a) Pyruvate.
b) AMP.
c) ATP.
d) NAD+.
e) NADH.
- Multiple Choice
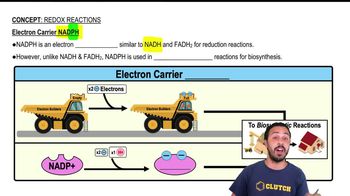
NADH is commonly used as an electron carrier during the breaking down of complex molecules like glucose in cellular respiration. NADPH is also a common electron carrier. However, NADPH is used to build complex molecules like glucose in a process called:
- Open Question
Define oxidation-reduction, and differentiate the following terms:
a. aerobic and anaerobic respiration
b. respiration and fermentation
c. cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation
- Open Question
Why must NADH be reoxidized? How does this happen in an organism that uses respiration? Fermentation?
- Open Question
Which substance in the following reaction is being reduced?
<IMAGE>
a. acetaldehyde
b. NADH
c. ethanol
d. NAD⁺
- Open Question
In the sulfur cycle, microbes degrade organic sulfur compounds, such as (a) _________________, to release H₂S, which can be oxidized by Acidithiobacillus to (b) _________________. This ion can be assimilated into amino acids by (c) _________________ or reduced by Desulfovibrio to (d) _________________. H₂S is used by photoautotrophic bacteria as an electron donor to synthesize (e) _________________. The sulfur-containing by-product of this metabolism is (f) _________________.