8. Eukaryotic Cell Structures & Functions
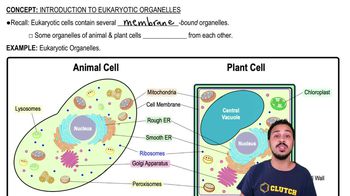
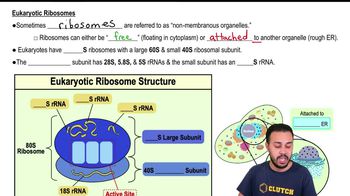
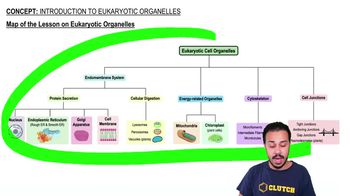
Introduction to Eukaryotic Organelles
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
What biomolecule does a ribosome synthesize in all types of cells?
- Multiple Choice
Using the map above, which of the following is NOT a component of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells?
- Multiple Choice
Using the map above, what two organelles produce cellular energy in eukaryotic cells?
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT part of the Eukaryotic endomembrane system?
- Open Question
Use the following choices to answer questions 8–10:
a. Apicomplexa
b. ciliates
c. dinoflagellates
d. Microsporidia
These are nonmotile parasites with special organelles for penetrating host tissue.
- Open Question
The presence of which of the following would be helpful in distinguishing a prokaryote from a eukaryote? Select all that apply. (NCLEX/HESI/TEAS)
a. Peptidoglycan
b. Phospholipids
c. A cell wall
d. A nucleus
e. Chloroplasts
f. Ribosomes
g. Ability to carry out active transport
h. DNA
- Open Question
Match the organelle to the function <IMAGE>
- Open Question
Match the terms with their descriptions following. Only one description is intended for each term.
____ Ribosome
____ Cytoskeleton
____ Centriole
____ Nucleus
____ Mitochondrion
____ Chloroplast
____ ER
____ Golgi body
____ Peroxisome
A. Site of protein synthesis
B. Contains enzymes to neutralize hydrogen peroxide
C. Functions as the transport system within a eukaryotic cell
D. Allows contraction of the cell
E. Site of most DNA in eukaryotes
F. Contains microtubules in "9 + 0" arrangement
G. Light-harvesting organelle
H. Packages large molecules for export from a cell
I. Its internal membranes are sites for ATP production