Notation For the data given in Exercise 1, identify the values of n1, n2, n3 and N.
Table of contents
- 1. Intro to Stats and Collecting Data1h 14m
- 2. Describing Data with Tables and Graphs1h 56m
- 3. Describing Data Numerically2h 5m
- 4. Probability2h 16m
- 5. Binomial Distribution & Discrete Random Variables3h 6m
- 6. Normal Distribution and Continuous Random Variables2h 11m
- 7. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Mean3h 23m
- Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean and Central Limit Theorem19m
- Distribution of Sample Mean - Excel23m
- Introduction to Confidence Intervals15m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Mean1h 18m
- Determining the Minimum Sample Size Required12m
- Finding Probabilities and T Critical Values - Excel28m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Means - Excel25m
- 8. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Proportion2h 10m
- 9. Hypothesis Testing for One Sample5h 8m
- Steps in Hypothesis Testing1h 6m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Means1h 4m
- Hypothesis Testing: Means - Excel42m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Proportions37m
- Hypothesis Testing: Proportions - Excel27m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Variance12m
- Critical Values and Rejection Regions28m
- Link Between Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Testing12m
- Type I & Type II Errors16m
- 10. Hypothesis Testing for Two Samples5h 37m
- Two Proportions1h 13m
- Two Proportions Hypothesis Test - Excel28m
- Two Means - Unknown, Unequal Variance1h 3m
- Two Means - Unknown Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variance15m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel9m
- Two Means - Known Variance12m
- Two Means - Sigma Known Hypothesis Test - Excel21m
- Two Means - Matched Pairs (Dependent Samples)42m
- Matched Pairs Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Variances and F Distribution29m
- Two Variances - Graphing Calculator16m
- 11. Correlation1h 24m
- 12. Regression3h 33m
- Linear Regression & Least Squares Method26m
- Residuals12m
- Coefficient of Determination12m
- Regression Line Equation and Coefficient of Determination - Excel8m
- Finding Residuals and Creating Residual Plots - Excel11m
- Inferences for Slope31m
- Enabling Data Analysis Toolpak1m
- Regression Readout of the Data Analysis Toolpak - Excel21m
- Prediction Intervals13m
- Prediction Intervals - Excel19m
- Multiple Regression - Excel29m
- Quadratic Regression15m
- Quadratic Regression - Excel10m
- 13. Chi-Square Tests & Goodness of Fit2h 21m
- 14. ANOVA2h 28m
9. Hypothesis Testing for One Sample
Steps in Hypothesis Testing
Problem 13.5.7
Textbook Question
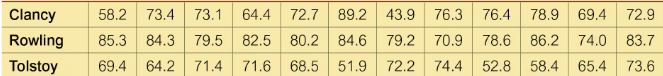
Clancy, Rowling, and Tolstoy Ease of Reading Pages were randomly selected from three books: The Bear and the Dragon by Tom Clancy, Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone by J. K. Rowling, and War and Peace by Leo Tolstoy. Listed below are Flesch Reading Ease Scores for those pages. Higher scores correspond to pages that are easier to read. Use a 0.01 significance level to test the claim that pages from books by those three authors have the same median Flesch Reading Ease score.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Organize the data into three groups based on the authors: Clancy, Rowling, and Tolstoy. Each group contains the Flesch Reading Ease scores provided in the table.
Step 2: Since the problem involves testing the claim about medians, use a non-parametric test suitable for comparing medians across multiple groups. The Kruskal-Wallis test is appropriate for this scenario.
Step 3: Calculate the ranks of all the scores combined, regardless of the group they belong to. Assign ranks to the scores, with the smallest score receiving rank 1, the next smallest rank 2, and so on. If there are tied scores, assign the average rank to the tied values.
Step 4: Compute the test statistic for the Kruskal-Wallis test using the formula: , where N is the total number of observations, R is the sum of ranks for each group, and n is the number of observations in each group.
Step 5: Compare the calculated test statistic (H) to the critical value from the chi-square distribution table with degrees of freedom equal to the number of groups minus 1 (df = 3 - 1 = 2) at the 0.01 significance level. If H exceeds the critical value, reject the null hypothesis that the medians are the same; otherwise, fail to reject the null hypothesis.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
6mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Flesch Reading Ease Score
The Flesch Reading Ease Score is a numerical measure that indicates how easy a text is to read. Scores range from 0 to 100, with higher scores signifying easier readability. This metric is calculated based on the average number of syllables per word and the average number of words per sentence, making it a useful tool for assessing the complexity of written material.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Z-Scores From Given Probability - TI-84 (CE) Calculator
Median
The median is a statistical measure that represents the middle value in a data set when the values are arranged in ascending order. It is particularly useful for understanding the central tendency of a distribution, especially when the data may contain outliers that could skew the mean. In this context, comparing the medians of Flesch Reading Ease Scores across different authors helps determine if their writing styles differ significantly in readability.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Calculating the Median
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to determine whether there is enough evidence to reject a null hypothesis in favor of an alternative hypothesis. In this scenario, the null hypothesis posits that the median Flesch Reading Ease scores for the three authors are equal. By applying a significance level (0.01 in this case), researchers can assess the likelihood of observing the data if the null hypothesis is true, guiding them in making informed conclusions about the authors' writing styles.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Step 1: Write Hypotheses

 6:21m
6:21mWatch next
Master Step 1: Write Hypotheses with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
