Using the Kruskal-Wallis Test
In Exercises 5–8, use the Kruskal-Wallis test.
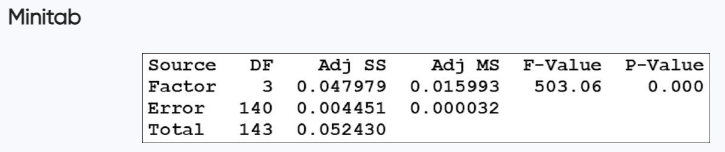
HIC Measurements Use the sample data from Exercise 1 with a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that small, midsize, large, and SUV vehicles have the same median HIC measurement in car crash tests.