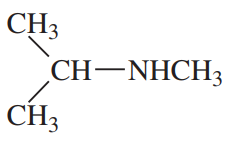Back
BackProblem 23c
Predict the products from the reactions of the following amines with sodium nitrite in dilute HCl.
(c) piperidine
Problem 23d
Predict the products from the reactions of the following amines with sodium nitrite in dilute HCl.
(d) aniline
Problem 24
Propose a mechanism for the synthesis of methyl orange.
Problem 25a,b,c
Give the expected products of lithium aluminum hydride reduction of the following compounds (followed by hydrolysis).
(a) butyronitrile
(b) N-cyclohexylacetamide
(c) ε-caprolactam
Problem 25a,b
Show how you would convert aniline to the following compounds.
(a) fluorobenzene
(b) chlorobenzene
Problem 25c
Show how you would convert aniline to the following compounds.
(c) 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene
Problem 25d,e
Show how you would convert aniline to the following compounds.
(d) bromobenzene
(e) iodobenzene
Problem 25f
Show how you would convert aniline to the following compounds.
(f) benzonitrile
Problem 25g
Show how you would convert aniline to the following compounds.
(g) phenol
Problem 26a,b,c
Show how to synthesize the following amines from the indicated starting materials by reductive amination.
(a) benzylmethylamine from benzaldehyde
(b) N-benzylpiperidine from piperidine
(c) N-cyclohexylaniline from cyclohexanone
Problem 26e
Show how to synthesize the following amines from the indicated starting materials by reductive amination.
(e)
Problem 27
Show how to synthesize the following amines from the indicated starting materials by acylation–reduction.
(a) N-butylpiperidine from piperidine
(b) N-benzylaniline from aniline
Problem 28
Addition of one equivalent of ammonia to 1-bromoheptane gives a mixture of heptan-1-amine, some dialkylamine, some trialkylamine, and even some tetraalkylammonium bromide.
(a) Give a mechanism to show how this reaction takes place, as far as the dialkylamine.
(b) How would you modify the procedure to get an acceptable yield of heptan-1-amine?
Problem 29a,b,c
Show how Gabriel syntheses are used to prepare the following amines.
(a) benzylamine
(b) hexan-1-amine
(c) γ-aminobutyric acid
Problem 30a
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions.
(a) benzyl bromide → benzylamine
Problem 30b
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions.
(b) 1-bromo-2-phenylethane → 3-phenylpropan-1-amine
Problem 30c
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions.
(c) pentanoic acid → pentan-1-amine
Problem 30d
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions.
(d) pentanoic acid → hexan-1-amine
Problem 30e
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions.
(e) (R)-2-bromobutane → (S)-butan-2-amine
Problem 30f
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions.
(f) (R)-2-bromobutane → (S)-2-methylbutan-1-amine
Problem 31a
Show how to prepare the following aromatic amines by aromatic nitration, followed by reduction. You may use benzene and toluene as your aromatic starting materials.
(a) aniline
Problem 31d
Show how to prepare the following aromatic amines by aromatic nitration, followed by reduction. You may use benzene and toluene as your aromatic starting materials.
(d) m-aminobenzoic acid
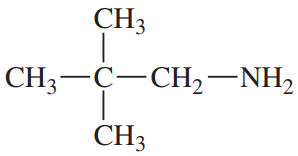
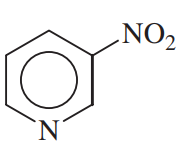
Problem 32a,b,c
For each compound,
(1) classify the nitrogen-containing functional groups.
(2) provide an acceptable name.
(a)
(b)
(c)
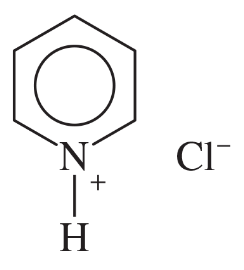
Problem 32g,h
For each compound,
(1) classify the nitrogen-containing functional groups.
(2) provide an acceptable name.
(g)
(h)
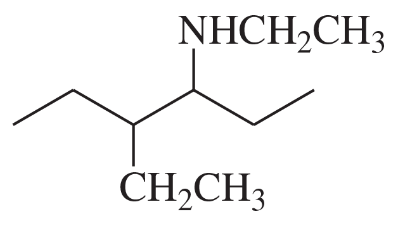
Problem 33a
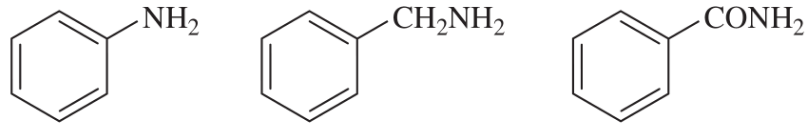
Rank the amines in each set in order of increasing basicity.
(a)
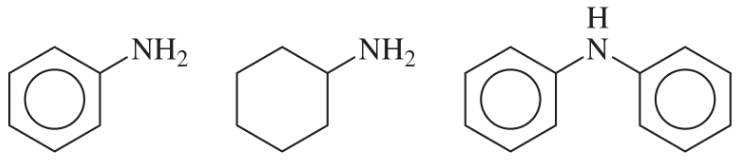
Problem 33c
Rank the amines in each set in order of increasing basicity.
(c)
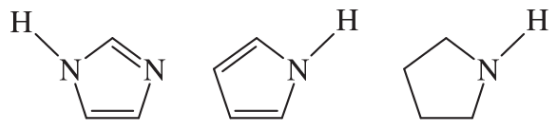
Problem 33d
Rank the amines in each set in order of increasing basicity.
(d)
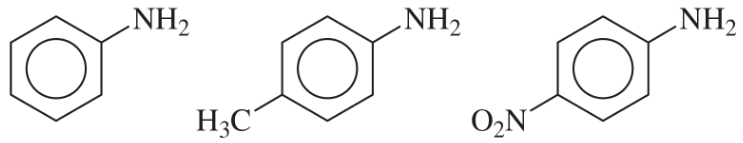
Problem 33e
Rank the amines in each set in order of increasing basicity.
(e)
Problem 34a,b
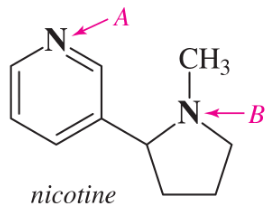
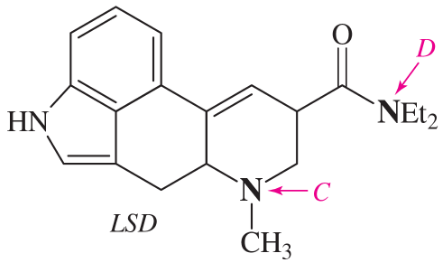
Within each structure, rank the indicated nitrogens by increasing basicity.
(a)
(b)
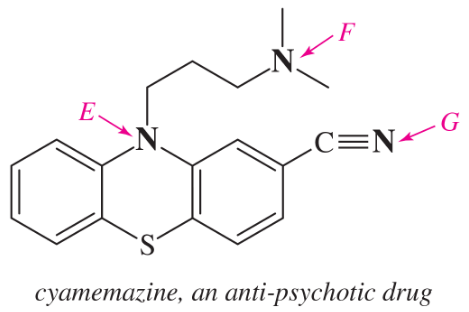
Problem 34c
Within each structure, rank the indicated nitrogens by increasing basicity.
(c)