Back
BackProblem 54e
Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with the following reagents.
(e) propane-1,3-diol, H+
Problem 54f
Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with the following reagents.
(f) zinc amalgam and dilute hydrochloric acid
Problem 55a
Show how you would synthesize octan-2-one from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(a) heptanal
Problem 55b
Show how you would synthesize octan-2-one from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(b) oct-1-yne
Problem 55c
Show how you would synthesize octan-2-one from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(c) 2,3-dimethylnon-2-ene
Problem 55e
Show how you would synthesize octan-2-one from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(e) heptanoic acid
Problem 55f
Show how you would synthesize octan-2-one from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(f) CH3(CH2)5CN
Problem 56a
Show how you would synthesize octanal from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(a) octan-1-ol
Problem 56b
Show how you would synthesize octanal from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(b) non-1-ene
Problem 56c
Show how you would synthesize octanal from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(c) oct-1-yne
Problem 56d
Show how you would synthesize octanal from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(d) 1-bromoheptane
Problem 56e
Show how you would synthesize octanal from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(e) 1-bromohexane
Problem 56f
Show how you would synthesize octanal from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(f) octanoic acid
Problem 56g
Show how you would synthesize octanal from each compound. You may use any necessary reagents.
(g) ethyl octanoate
Problem 57a
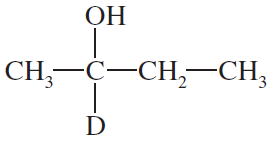
Both NaBH4 and NaBD4 are commercially available, and D2O is common and inexpensive. Show how you would synthesize the following labeled compounds, starting with butan-2-one.
(a)
Problem 58
When LiAlH4 reduces 3-methylcyclopentanone, the product mixture contains 60% cis-3-methylcyclopentanol and 40% trans-3-methylcyclopentanol. Use your models, and make three-dimensional drawings to explain this preference for the cis isomer.
Problem 59
The Wittig reaction is useful for placing double bonds in less stable positions. For example, the following transformation is easily accomplished using a Wittig reaction.
(a) Show how you would use a Wittig reaction to do this.
(b) Show how you might do this without using a Wittig reaction, and then explain why the Wittig reaction is a much better synthesis.
Problem 60a
Show how you would accomplish the following syntheses.
(a) benzene → n-butylbenzene
Problem 60b
Show how you would accomplish the following syntheses.
(b) benzonitrile → propiophenone
Problem 60c
Show how you would accomplish the following syntheses.
(c) benzene → p-methoxybenzaldehyde
Problem 60d
Show how you would accomplish the following syntheses.
(d)
Problem 61a
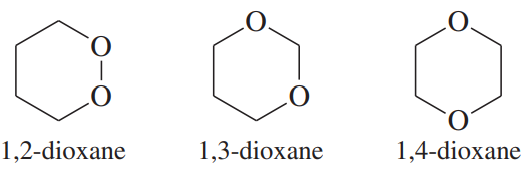
There are three dioxane isomers: 1,2-dioxane, 1,3-dioxane, and 1,4-dioxane. One of these acts like an ether and is an excellent solvent for Grignard reactions. Another one is potentially explosive when heated. The third one quickly hydrolyzes in dilute acid. Show which isomer acts like a simple ether, and then explain why one of them is potentially explosive.
Problem 61b
There are three dioxane isomers: 1,2-dioxane, 1,3-dioxane, and 1,4-dioxane. One of these acts like an ether and is an excellent solvent for Grignard reactions. Another one is potentially explosive when heated. The third one quickly hydrolyzes in dilute acid. Propose a mechanism for the acid hydrolysis of the third isomer.
Problem 62a
Two structures for the sugar glucose are shown on page 914. Interconversion of the open-chain and cyclic hemiacetal forms is catalyzed by either acid or base.
(a) Propose a mechanism for the cyclization, assuming a trace of acid is present.
Problem 62b
Two structures for the sugar glucose are shown on page 914. Interconversion of the open-chain and cyclic hemiacetal forms is catalyzed by either acid or base.
(b) The cyclic hemiacetal is more stable than the open-chain form, so very little of the open-chain form is present at equilibrium. Will an aqueous solution of glucose reduce Tollens reagent and give a positive Tollens test? Explain.
Problem 63
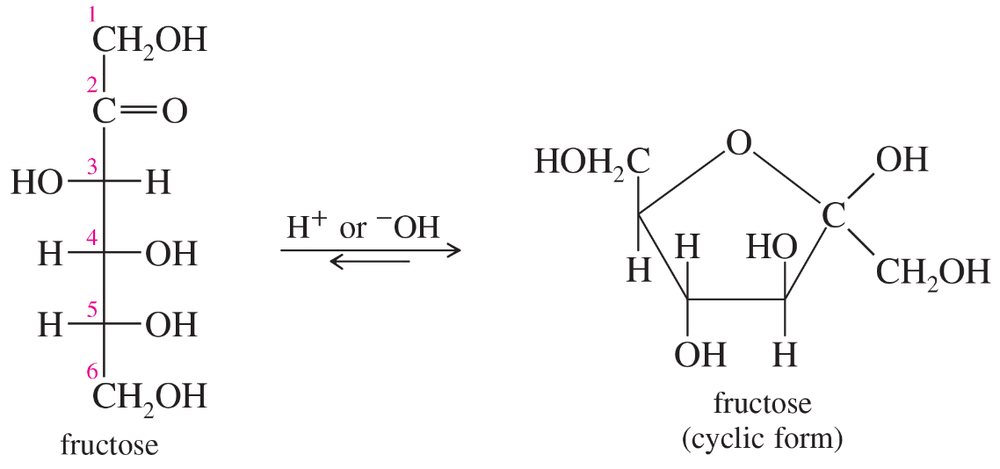
Two structures of the sugar fructose are shown next. The cyclic structure predominates in aqueous solution.
(a) Number the carbon atoms in the cyclic structure. What is the functional group at C2 in the cyclic form?
(b) Propose a mechanism for the cyclization, assuming a trace of acid is present.
Problem 64a
Hydration of alkynes (via oxymercuration) gives good yields of single compounds only with symmetrical or terminal alkynes. Show what the products would be from hydration of each compound.
a. hex-3-yne
Problem 64b
Hydration of alkynes (via oxymercuration) gives good yields of single compounds only with symmetrical or terminal alkynes. Show what the products would be from hydration of each compound.
b. hex-2-yne
Problem 64c
Hydration of alkynes (via oxymercuration) gives good yields of single compounds only with symmetrical or terminal alkynes. Show what the products would be from hydration of each compound.
c. hex-1-yne
Problem 64d
Hydration of alkynes (via oxymercuration) gives good yields of single compounds only with symmetrical or terminal alkynes. Show what the products would be from hydration of each compound.
d. cyclodecyne