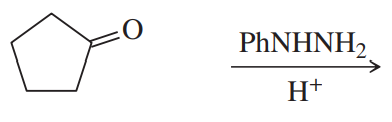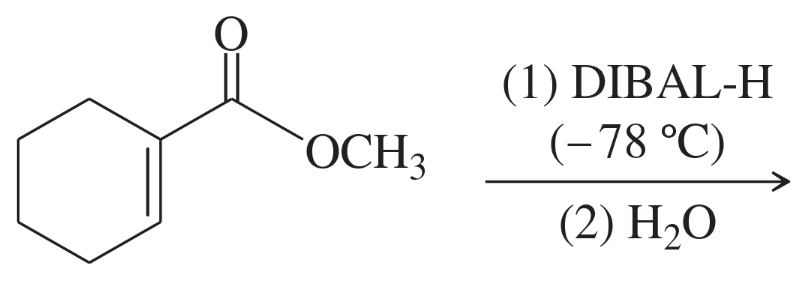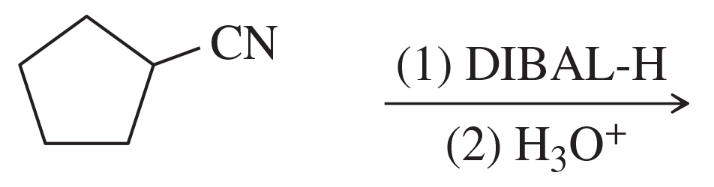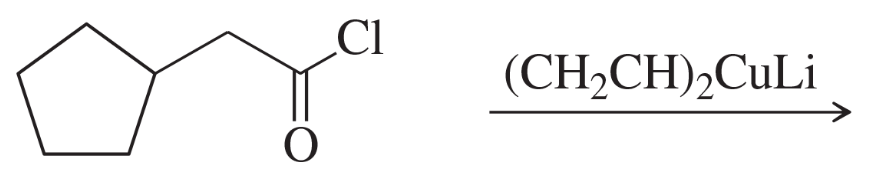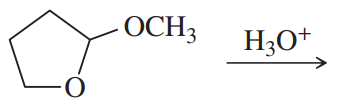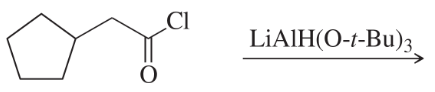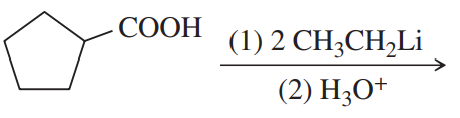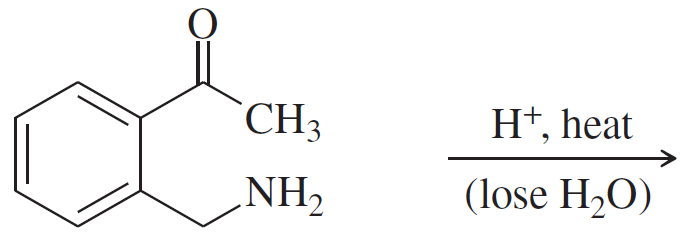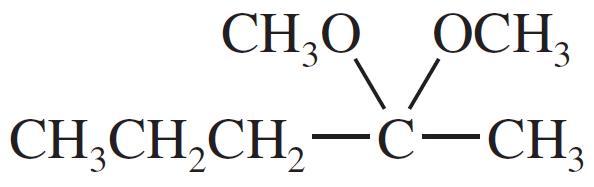Back
BackProblem 39a
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
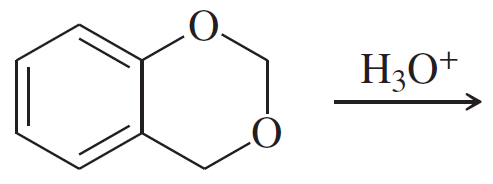
(a)
Problem 39b
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(b)
Problem 39c
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(c)
Problem 39d
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(d)
Problem 39e
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(e)
Problem 39f
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(f)
Problem 39g
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(g)
Problem 39h
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(h)
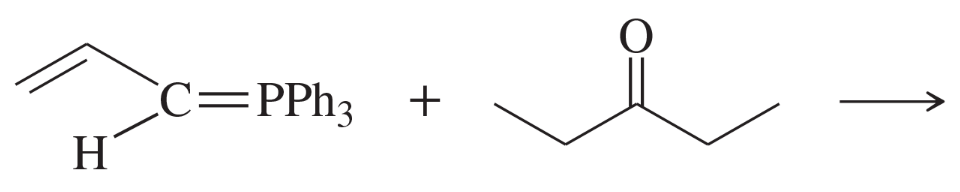
Problem 39i
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(i)
Problem 39j
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(j)
Problem 40
Rank the following carbonyl compounds in order of increasing equilibrium constant for hydration:
CH3COCH2Cl ClCH2CHO CH2O CH3COCH3 CH3CHO
Problem 41a
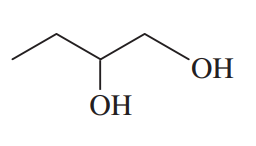
Acetals can serve as protecting groups for 1,2-diols, as well as for aldehydes and ketones. When the acetal is formed from acetone plus the diol, the acetal is called an acetonide. Show the acetonides formed from these diols with acetone under acid catalysis.
Problem 41b
Acetals can serve as protecting groups for 1,2-diols, as well as for aldehydes and ketones. When the acetal is formed from acetone plus the diol, the acetal is called an acetonide. Show the acetonides formed from these diols with acetone under acid catalysis.
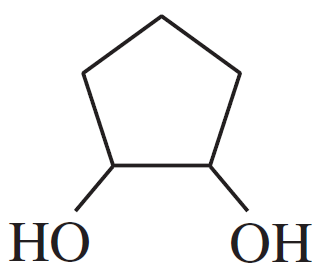
Problem 41c
Acetals can serve as protecting groups for 1,2-diols, as well as for aldehydes and ketones. When the acetal is formed from acetone plus the diol, the acetal is called an acetonide. Show the acetonides formed from these diols with acetone under acid catalysis.
Problem 45b
The following compounds undergo McLafferty rearrangement in the mass spectrometer. Predict the masses of the resulting charged fragments.
(b) 3-methylhexan-2-one
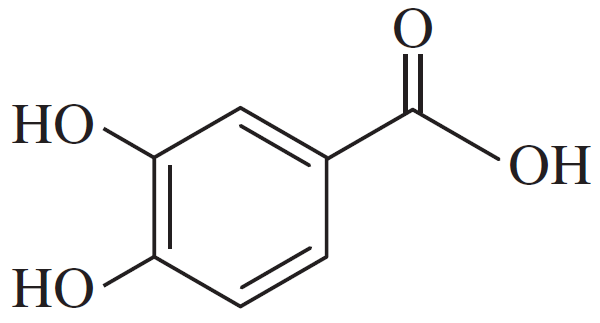
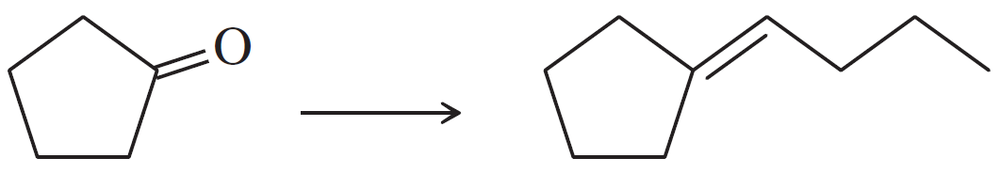
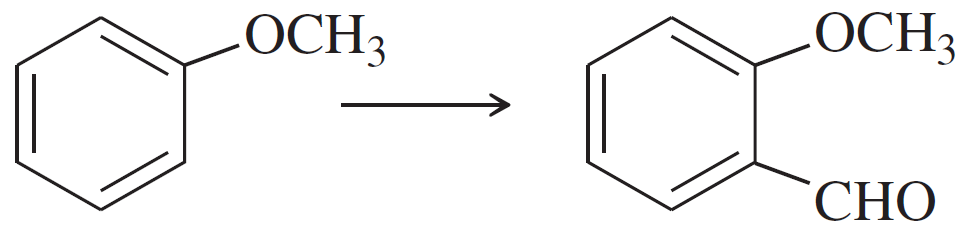
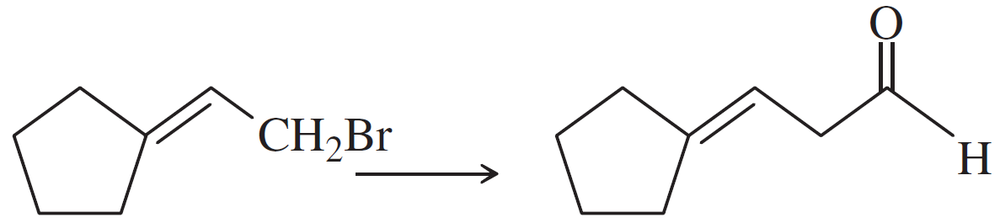
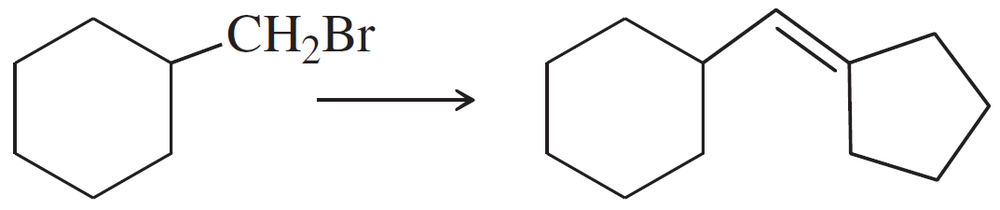
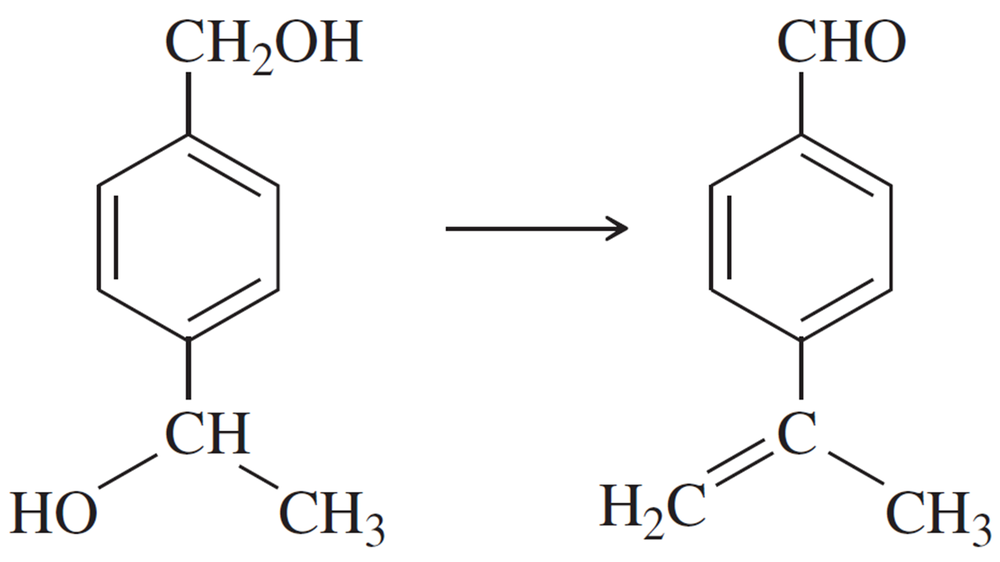
Problem 47a
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions efficiently and in good yield. You may use any necessary additional reagents and solvents.
(a)
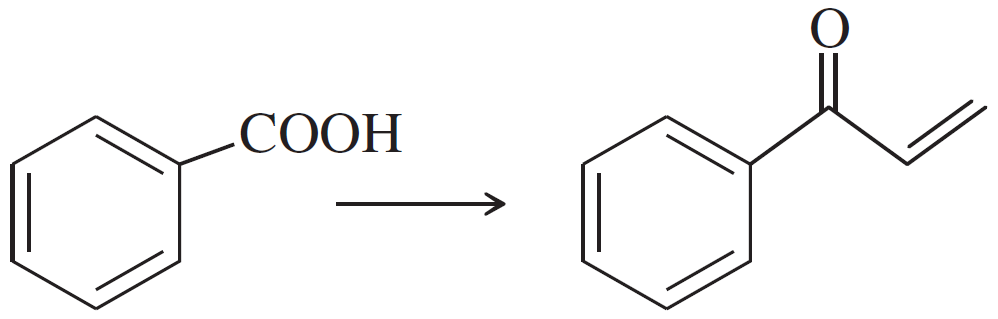
Problem 47b
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions efficiently and in good yield. You may use any necessary additional reagents and solvents.
(b)
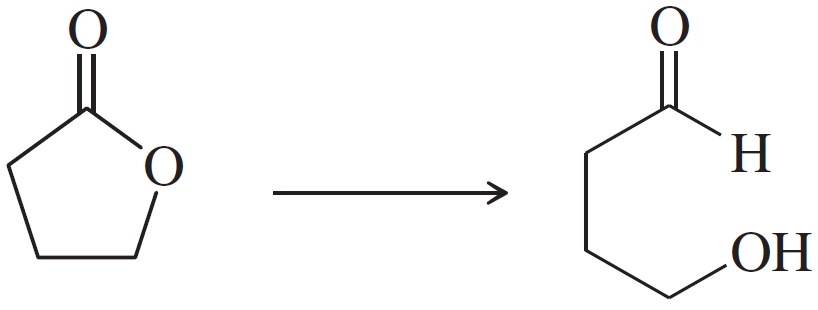
Problem 47c
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions efficiently and in good yield. You may use any necessary additional reagents and solvents.
(c)
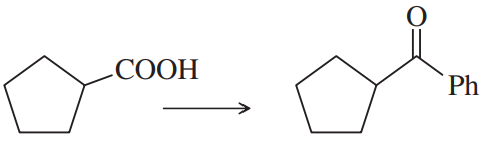
Problem 47d
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions efficiently and in good yield. You may use any necessary additional reagents and solvents.
(d)
Problem 47e
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions efficiently and in good yield. You may use any necessary additional reagents and solvents.
(e)
Problem 47f
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions efficiently and in good yield. You may use any necessary additional reagents and solvents.
(f)
Problem 47g
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions efficiently and in good yield. You may use any necessary additional reagents and solvents.
(g)
Problem 47h
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions efficiently and in good yield. You may use any necessary additional reagents and solvents.
(h)
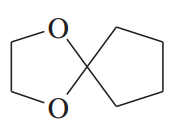
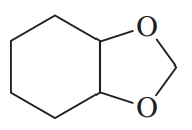
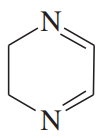
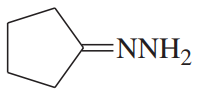
Problem 49a
For each compound,
1. name the functional group.
2. show what compound(s) result from complete hydrolysis.
(a)
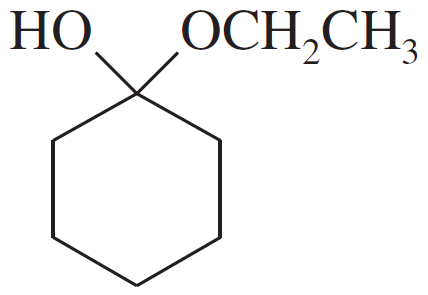
Problem 49b
For each compound,
1. name the functional group.
2. show what compound(s) result from complete hydrolysis.
(b)
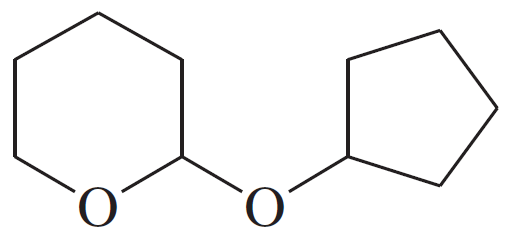
Problem 49c
For each compound,
1. name the functional group.
2. show what compound(s) result from complete hydrolysis.
(c)
Problem 49d
For each compound,
1. name the functional group.
2. show what compound(s) result from complete hydrolysis.
(d)
Problem 49e
For each compound,
1. name the functional group.
2. show what compound(s) result from complete hydrolysis.
(e)
Problem 49g
For each compound,
1. name the functional group.
2. show what compound(s) result from complete hydrolysis.
(g)
Problem 49h
For each compound,
1. name the functional group.
2. show what compound(s) result from complete hydrolysis.
(h)