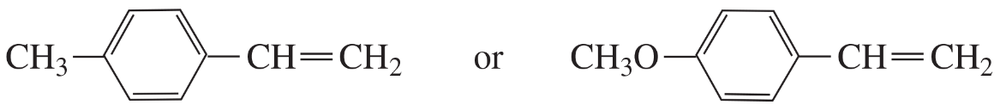Back
BackProblem 58a,b
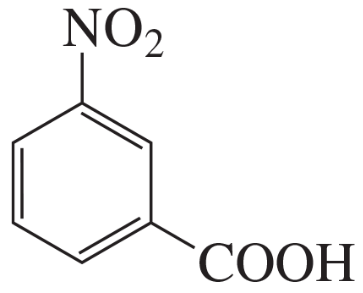
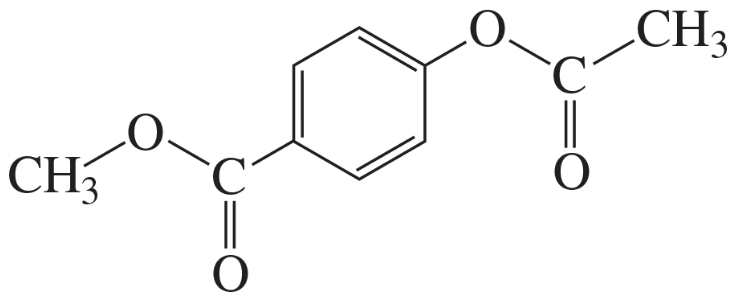
For each of the following compounds, indicate the ring carbon(s) that is/are nitrated when the compound is treated with HNO3/H2SO4:
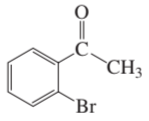
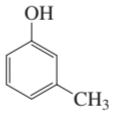
a.
b.
Problem 58c,d
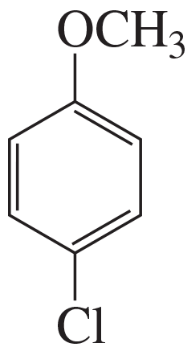
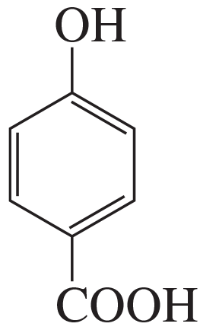
For each of the following compounds, indicate the ring carbon(s) that is/are nitrated when the compound is treated with HNO3/H2SO4:
c.
d.
Problem 58e,f
For each of the following compounds, indicate the ring carbon(s) that is/are nitrated when the compound is treated with HNO3/H2SO4:
e.
f.
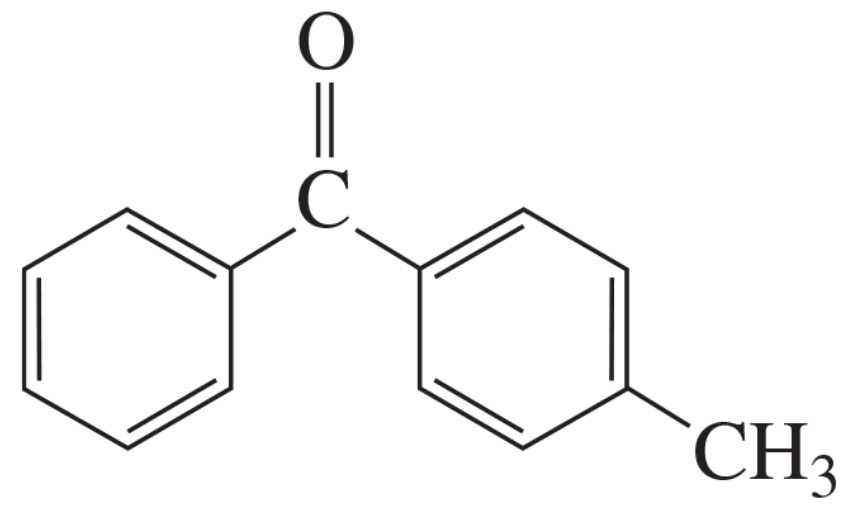
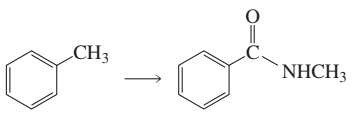
Problem 59
Show two pairs of reagents that would each result in formation of the following compound:
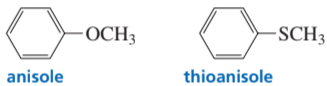
Problem 60
Why is anisole nitrated more rapidly than thioanisole under the same conditions?
Problem 61
Describe two ways to prepare anisole from benzene.
Problem 62
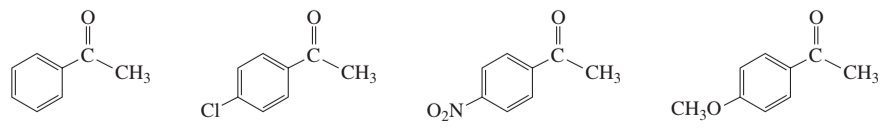
Which of the following compounds reacts with HBr more rapidly?
Problem 64
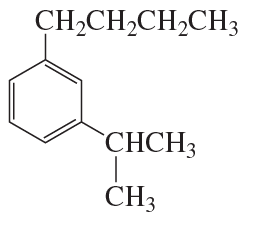
An aromatic hydrocarbon with a molecular formula of C13H20 has an 1H NMR spectrum with a signal at ~7 ppm that integrates to 5H. It also has two singlets; one of the singlets has 1.5 times the area of the second. What is the structure of the aromatic hydrocarbon?
Problem 65a
Show how the following compounds can be synthesized from benzene:
a. N,N,N-trimethylanilinium iodide
Problem 65g
Show how the following compounds can be synthesized from benzene:
g. p-dideuteriobenzene
Problem 65h
Show how the following compounds can be synthesized from benzene:
h. p-nitro-N-methylaniline
Problem 66a
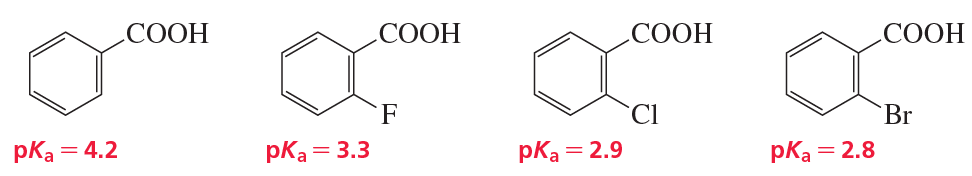
Use the four compounds shown below to answer the following questions:
a. Why are the ortho-halo-substituted benzoic acids stronger acids than benzoic acid?
Problem 66b
Use the four compounds shown below to answer the following questions:
b. Why is o-fluorobenzoic acid the weakest of the ortho-halo-substituted benzoic acids?
Problem 67a
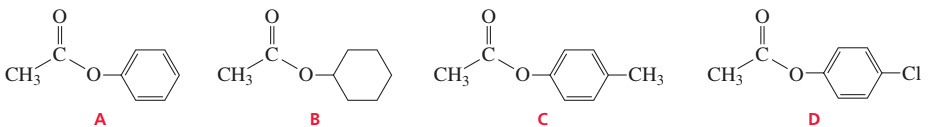
a. Rank the following esters from most reactive to least reactive in the first slow step of a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction (formation of the tetrahedral intermediate):
Problem 67b
b. Rank the same esters from most reactive to least reactive in the second slow step of a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction (collapse of the tetrahedral intermediate).
Problem 68b
A mixture of 0.10 mol benzene and 0.10 mol p-xylene was allowed to react with 0.10 mol nitronium ion until all the nitronium ion was gone. Two products were obtained: 0.002 mol of one and 0.098 mol of the other.
b. Why was more of one product obtained than of the other?
Problem 69
Does m-xylene or p-xylene react more rapidly with Cl2 + FeCl3? Explain your answer.
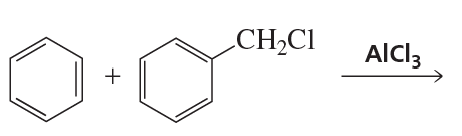
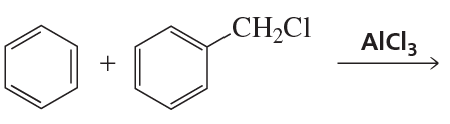
Problem 70(c)
What are the products of the following reactions?
c.
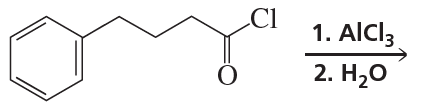
Problem 70(a)
What are the products of the following reactions?
a.
Problem 70a
What are the products of the following reactions?
a.
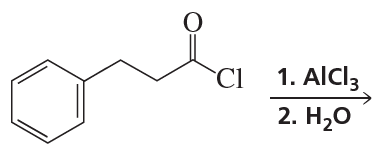
Problem 70b
What are the products of the following reactions?
b.
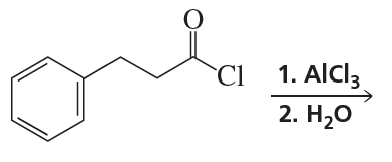
Problem 70c
What are the products of the following reactions?
c.
Problem 71
Benzene underwent a Friedel–Crafts acylation followed by a Wolff–Kishner reduction. The product gave the following 1H NMR spectrum. What acyl chloride was used in the Friedel–Crafts acylation?
<IMAGE>
Problem 72b
What products are obtained from the reaction of the following compounds with H2CrO4 + ∆?
b.
Problem 73
Which set of underlined hydrogens has its 1H NMR signal at a higher frequency?
a. CH3CH2CH3 or CH3OCH2CH3
b. CH3CH=CH2 or CH3OCH=CH2
Problem 75a
Show how the following compounds can be prepared from the given starting materials. You can use any necessary organic or inorganic reagents.
a.
Problem 76
Rank the following compounds from largest Keq to smallest Keq for hydrate formation:
Problem 78a
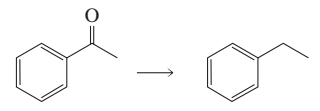
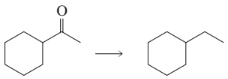
a. Describe three ways the following reaction can be carried out:
Problem 78b
b. Describe two ways the following reaction can be carried out:
Problem 79a
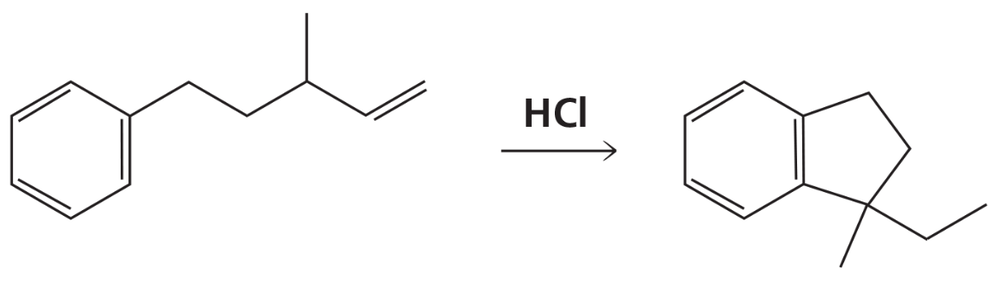
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
a.