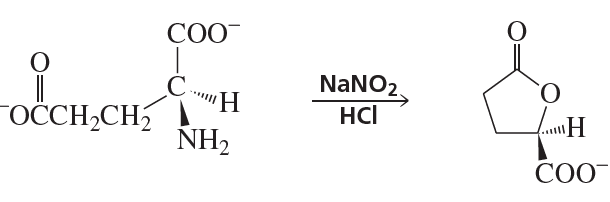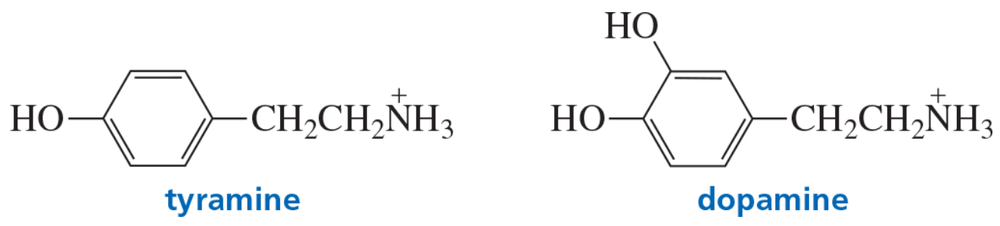Back
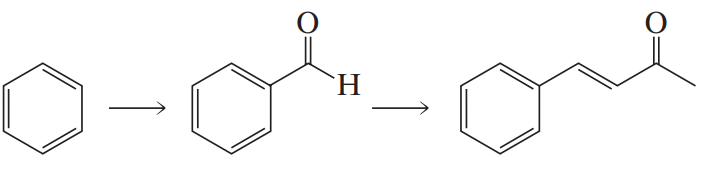
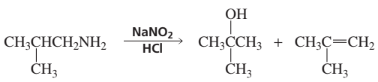
BackProblem 84a
What reagents are required to carry out the following synthesis?
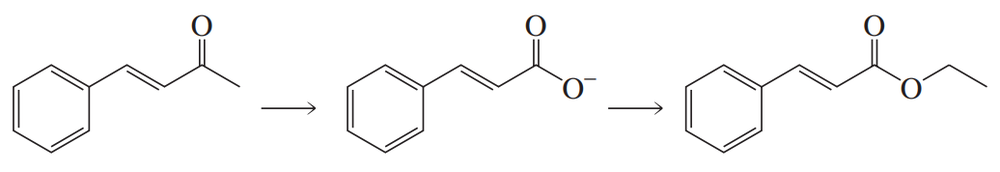
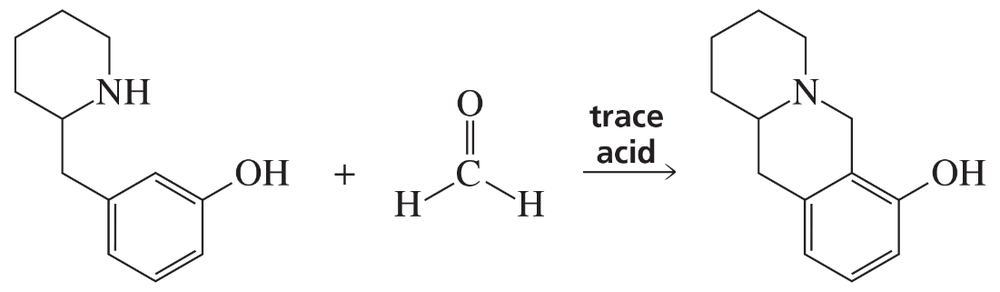
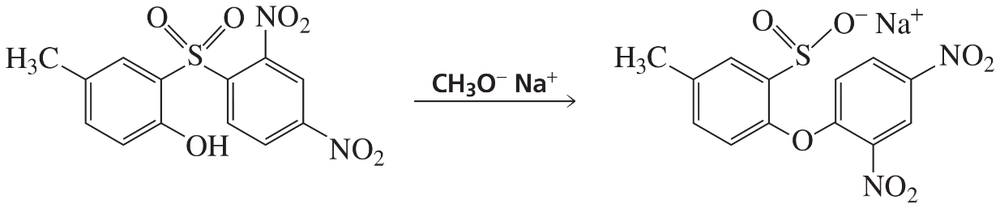
Problem 84b
What reagents are required to carry out the following synthesis?
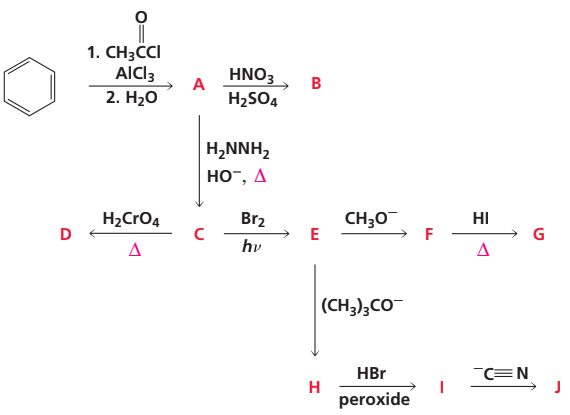
Problem 85a
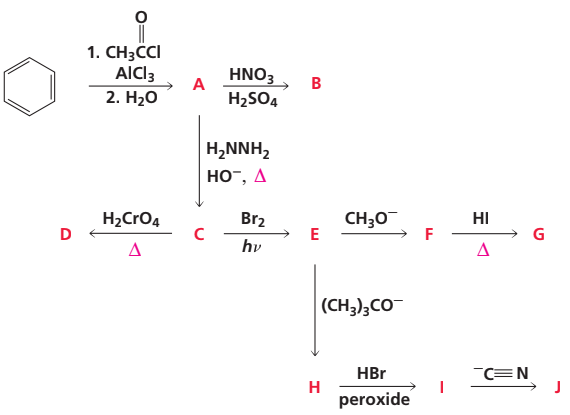
Identify A–J:
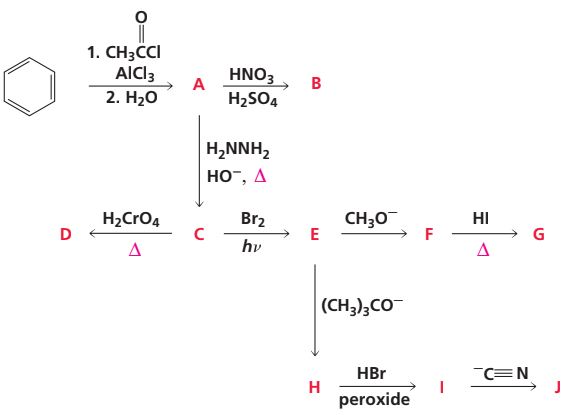
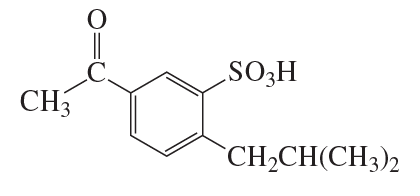
Problem 85b
Identify A–J:
Problem 85c
Identify A–J:
Problem 87a
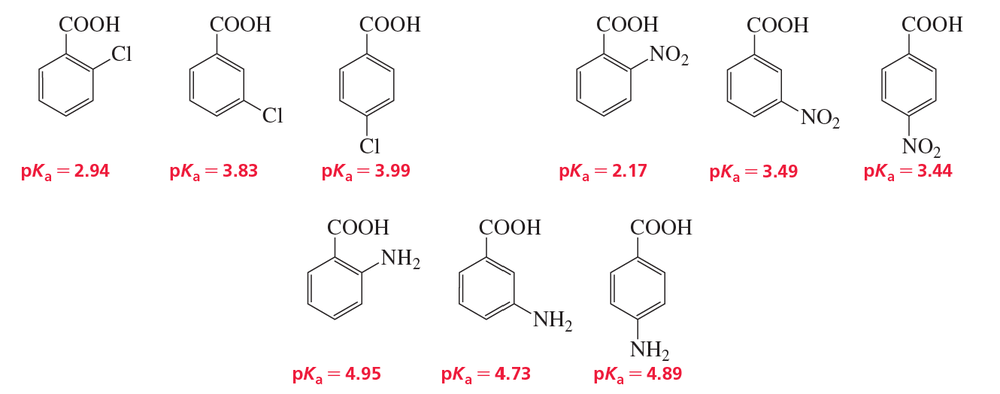
The pKa values of a few ortho-, meta-, and para-substituted benzoic acids are shown below:
The relative pKa values depend on the substituent. For chloro-substituted benzoic acids, the ortho isomer is the most acidic and the para isomer is the least acidic; for nitro-substituted benzoic acids, the ortho isomer is the most acidic and the meta isomer is the least acidic; and for amino-substituted benzoic acids, the meta isomer is the most acidic and the ortho isomer is the least acidic.
Explain these relative acidities.
a. Cl: ortho > meta > para
Problem 87c
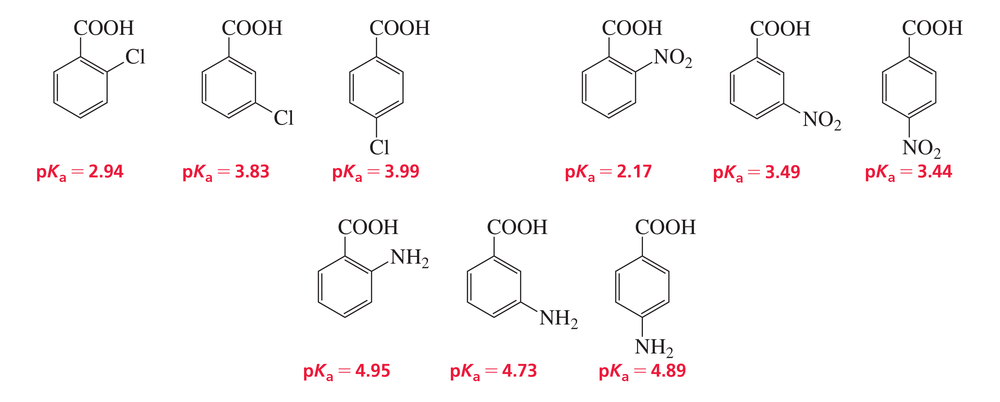
The pKa values of a few ortho-, meta-, and para-substituted benzoic acids are shown below:
The relative pKa values depend on the substituent. For chloro-substituted benzoic acids, the ortho isomer is the most acidic and the para isomer is the least acidic; for nitro-substituted benzoic acids, the ortho isomer is the most acidic and the meta isomer is the least acidic; and for amino-substituted benzoic acids, the meta isomer is the most acidic and the ortho isomer is the least acidic. Explain these relative acidities.
c. NH2: meta > para > ortho
Problem 88a
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
a.
Problem 88b
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
b.
Problem 90
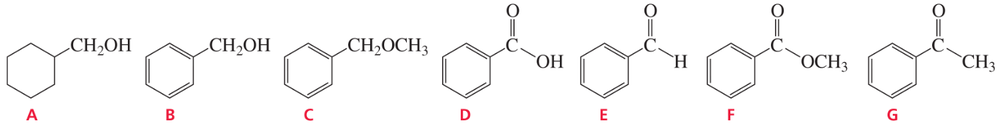
When heated with chromic acid, compound A forms benzoic acid. Identify compound A from its 1H NMR spectrum.
<IMAGE>
Problem 91c
Show how the following compounds can be prepared from benzene:
c.
Problem 92a
How can you distinguish the following compounds using: a. their infrared spectra?
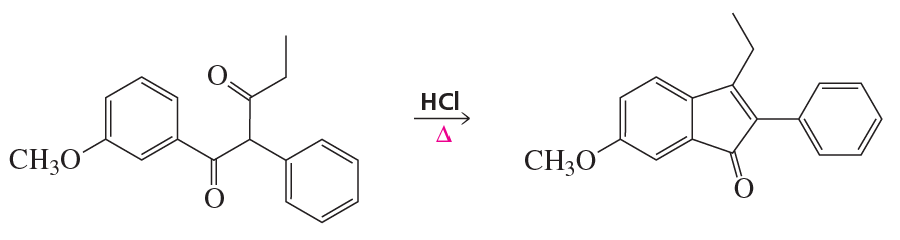
Problem 94
Propose a mechanism for the following reaction that explains why the configuration of the asymmetric center in the reactant is retained in the product:
Problem 95
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
b.
Problem 96
Describe how 3-methyl-1-phenyl-3-pentanol can be prepared from benzene. You can use any inorganic reagents and solvents, and any organic reagents provided they contain no more than two carbons.
Problem 98a
a. Explain why the following reaction leads to the products shown:
Problem 99
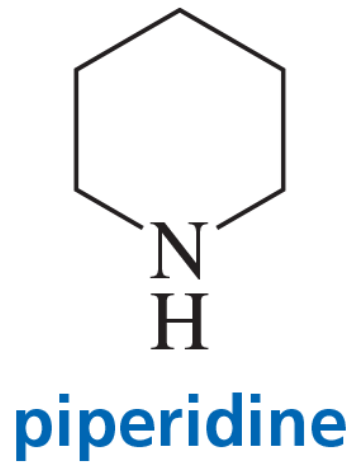
Explain why hydroxide ion catalyzes the reaction of piperidine with 2,4-dinitroanisole but has no effect on the reaction of piperidine with 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene.
Problem 101a
Tyramine is an alkaloid found in mistletoe and ripe cheese. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in the regulation of the central nervous system.
a. How can tyramine be prepared from b-phenylethylamine?
Problem 101b
Tyramine is an alkaloid found in mistletoe and ripe cheese. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in the regulation of the central nervous system.
b. How can dopamine be prepared from tyramine?
Problem 101c
Tyramine is an alkaloid found in mistletoe and ripe cheese. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in the regulation of the central nervous system.
c. Give two ways to prepare b-phenylethylamine from b-phenylethyl chloride.
Problem 101d
Tyramine is an alkaloid found in mistletoe and ripe cheese. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in the regulation of the central nervous system.
d. How can b-phenylethylamine be prepared from benzyl chloride?
Problem 101e
Tyramine is an alkaloid found in mistletoe and ripe cheese. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in the regulation of the central nervous system.
e. How can b-phenylethylamine be prepared from benzaldehyde?
Problem 102b
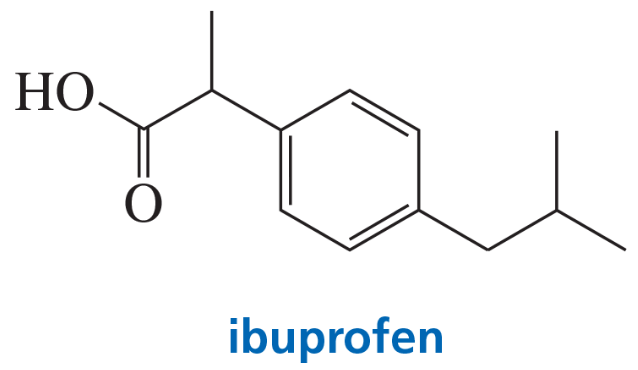
Ibuprofen is the active ingredient in pain relievers such as Advil, Motrin, and Nuprin. How can ibuprofen be synthesized from benzene?
Problem 102c
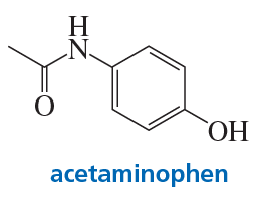
Acetaminophen is the active ingredient in Tylenol. How can acetominophen be synthesized from benzene?