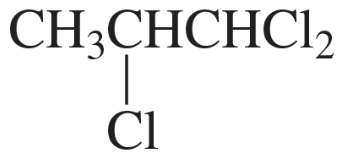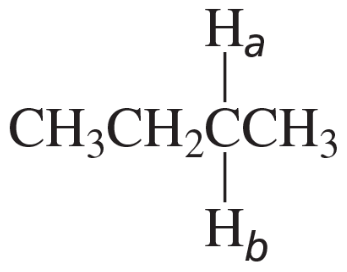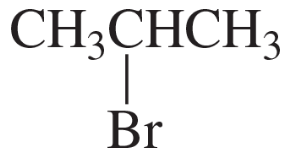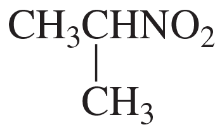Back
BackProblem 28f
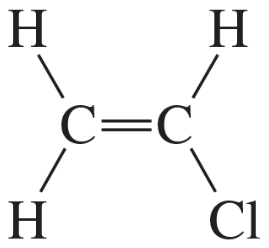
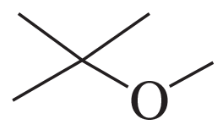
Describe the 1H NMR spectrum you would expect for each of the following compounds, indicating the relative positions of the signals:
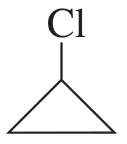
f.
Problem 28g
Describe the 1H NMR spectrum you would expect for each of the following compounds, indicating the relative positions of the signals:
g. CH3CH2OCH2CH3
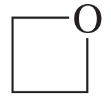
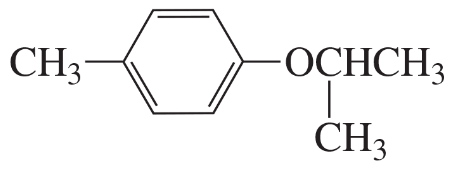
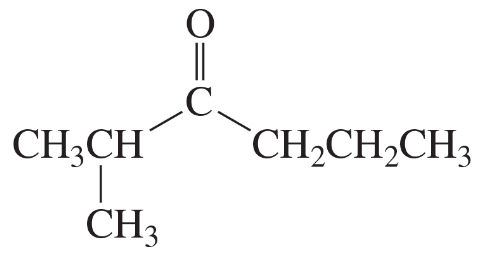
Problem 28i
Describe the 1H NMR spectrum you would expect for each of the following compounds, indicating the relative positions of the signals:
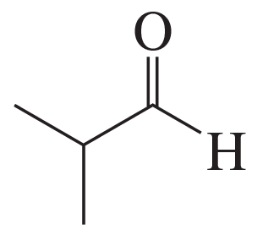
i.
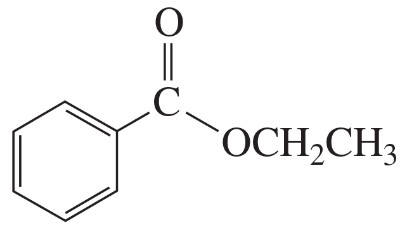
Problem 28k
Describe the 1H NMR spectrum you would expect for each of the following compounds, indicating the relative positions of the signals:
k.
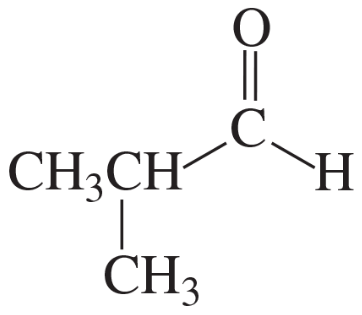
Problem 28n
Describe the 1H NMR spectrum you would expect for each of the following compounds, indicating the relative positions of the signals:
n.
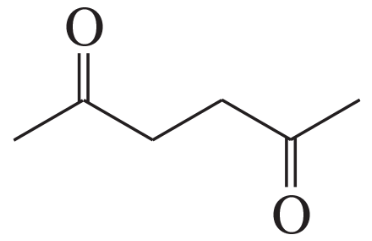
Problem 29b
Propose structures that are consistent with the following spectra. (Integral ratios are given from left to right across the spectrum.)
b. The 1H NMR spectrum of a compound with molecular formula C6H10O2 has two singlets with integral ratios of 2 : 3.
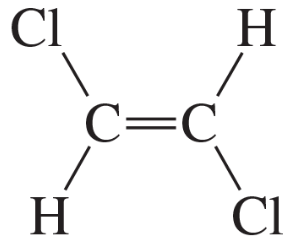
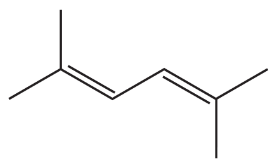
Problem 30
Why is there no coupling between the a and c protons or between the b and c protons in the cis and trans alkenes shown in Figure 14.20?
<IMAGE>
Problem 32a
Draw a splitting diagram for Hb, where
a. Jba = 12 Hz and Jbc = 6 Hz.
Problem 33a(1)
For the following compounds, which pairs of hydrogens (Ha and Hb) are enantiotopic hydrogens?
1.
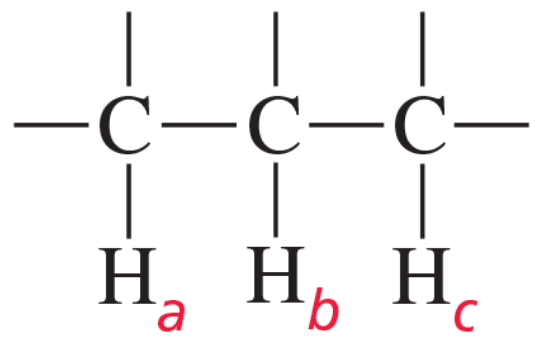
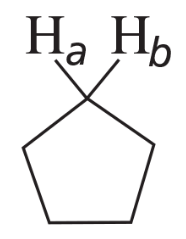
Problem 33a(c)
For the following compounds, which pairs of hydrogens (Ha and Hb) are enantiotopic hydrogens?
Problem 33b
Which pairs are diastereotopic hydrogens?
Problem 35
How would the 1H NMR spectra for the four compounds with molecular formula C3H6Br2 differ?
Problem 37
Explain why the chemical shift of the OH proton of a carboxylic acid is at a higher frequency than the chemical shift of an OH proton of an alcohol.
Problem 39
Propose a mechanism for proton exchange of an alcohol in aqueous base.
Problem 41(9)
Answer the following questions for each compound:
a. How many signals are in its 13C NMR spectrum?
b. Which signal is at the lowest frequency?
9. CH2=CHBr
Problem 41(8)
Answer the following questions for each compound:
a. How many signals are in its 13C NMR spectrum?
b. Which signal is at the lowest frequency?
8.
Problem 41a(7)
Answer the following questions for each compound:
a. How many signals are in its 13C NMR spectrum? b. Which signal is at the lowest frequency?
7.
Problem 42(5)
Describe the proton-coupled 13C NMR spectra for compound 5 in Problem 41, indicating the relative positions of the signals.
5.
Problem 42(1)
Describe the proton-coupled 13C NMR spectra for compound 1 in Problem 41, indicating the relative positions of the signals.
1. CH3CH2CH2Br
Problem 42(3)
Describe the proton-coupled 13C NMR spectra for compound 3 in Problem 41, indicating the relative positions of the signals.
3.
Problem 43a
How can 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dinitrobenzene be distinguished by
a. 1H NMR spectroscopy?
Problem 43b
How can 1,2-, 1,3-, and 1,4-dinitrobenzene be distinguished by
b. 13C NMR spectroscopy?
Problem 44a
Identify each compound below from its molecular formula and its 13C NMR spectrum.
a. C11H22O
<IMAGE>
Problem 45
Identify pairs of coupled protons in the compound whose COSY spectrum is shown below.
<IMAGE>
Problem 46
What does cross peak X in Figure 14.34 tell you?
<IMAGE>
Problem 47a(4,5,6)
How many signals are produced by each of the following compounds in its
a. 1H NMR spectrum?
4.
5.
6.
Problem 47b(1)
How many signals are produced by each of the following compounds in its
b. 13C NMR spectrum?
1.
Problem 47b(2)
How many signals are produced by each of the following compounds in its
b. 13C NMR spectrum?
2.
Problem 49a
Label each set of chemically equivalent protons, using a for the set that will be at the lowest frequency in the 1H NMR spectrum, b for the next lowest, and so on. Indicate the multiplicity of each signal.
a.
Problem 49c
Label each set of chemically equivalent protons, using a for the set that will be at the lowest frequency in the 1H NMR spectrum, b for the next lowest, and so on. Indicate the multiplicity of each signal.
c.