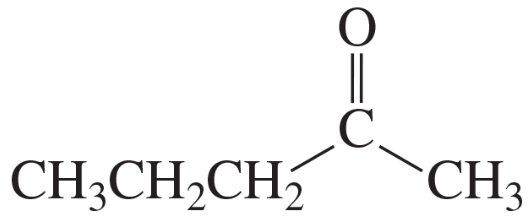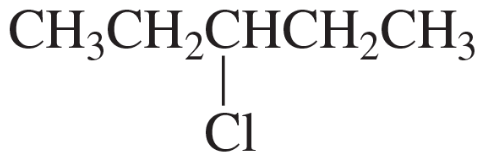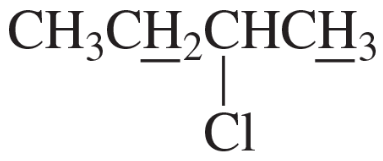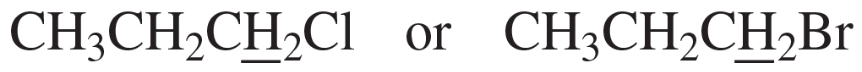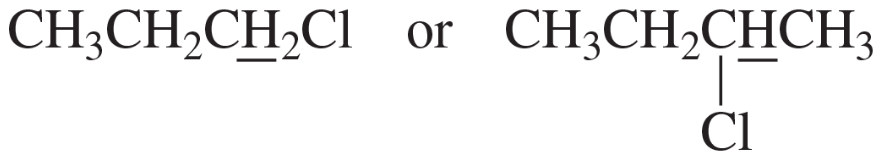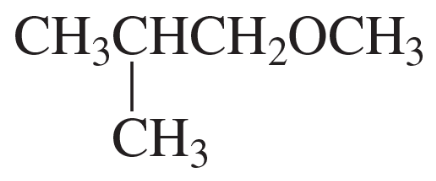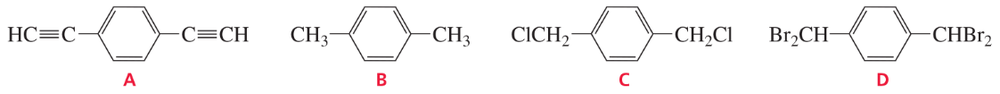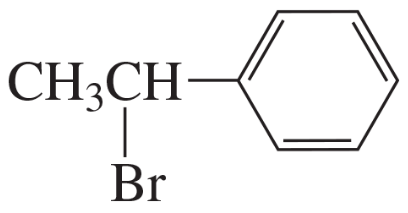Back
BackProblem 2b
What strength magnetic field is required when a 500-MHz instrument is used for 1H NMR?
Problem 3
How many signals would you expect to see in the 1H NMR spectrum of each of the five compounds with molecular formula C6H14?
Problem 4a,b
How many signals would you expect to see in the 1H NMR spectrum of each of the following compounds?
a. CH3CH2CH2CH3
b. BrCH2CH2Br
Problem 4e,f
How many signals would you expect to see in the 1H NMR spectrum of each of the following compounds?
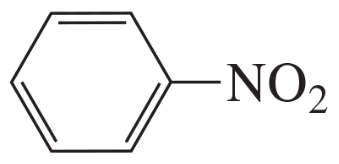
e.
f.
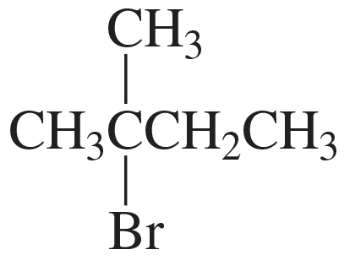
Problem 4g,h
How many signals would you expect to see in the 1H NMR spectrum of each of the following compounds?
g.
h.
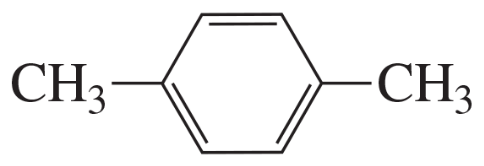
Problem 4m,n,o
How many signals would you expect to see in the 1H NMR spectrum of each of the following compounds?
m.
n.
o.
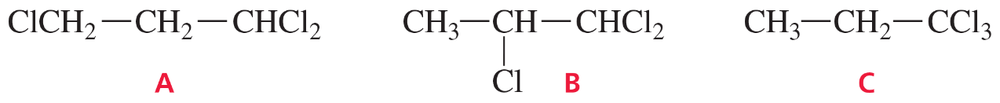
Problem 6c
Draw an isomer of dichlorocyclopropane that gives an 1H NMR spectrum
c. with three signals
Problem 9a
If two signals differ by 1.5 ppm in a 300 MHz spectrometer, by how much do they differ in a 500 MHz spectrometer?
Problem 9b
If two signals differ by 90 Hz in a 300 MHz spectrometer, by how much do they differ in a 500 MHz spectrometer
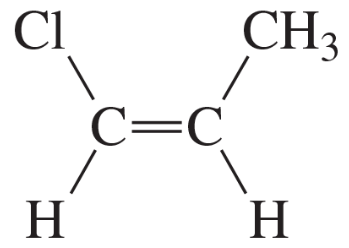
Problem 12c,d
Which underlined proton (or sets of protons) has the greater chemical shift (that is, the higher frequency signal)?
c.
d.
Problem 13a,b
Which underlined proton (or sets of protons) has the greater chemical shift (that is, the higher frequency signal)?
a.
b.
Problem 14c
Without referring to Table 14.1, label the proton or set of protons in each compound that gives the signal at the lowest frequency a, at the next lowest b, and so on.
c. ClCH2CH2CH2Cl
Problem 14e
Without referring to Table 14.1, label the proton or set of protons in each compound that gives the signal at the lowest frequency a, at the next lowest b, and so on.
e.
Problem 14h
Without referring to Table 14.1, label the proton or set of protons in each compound that gives the signal at the lowest frequency a, at the next lowest b, and so on.
h.
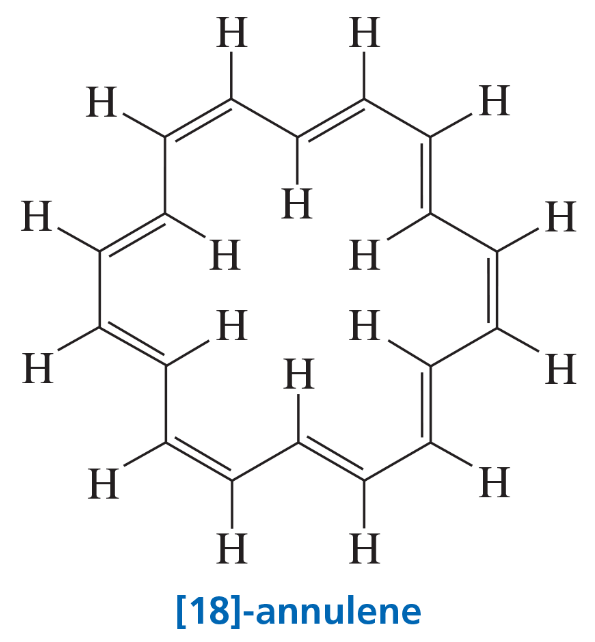
Problem 15a
[18]-Annulene shows two signals in its 1H NMR spectrum: one at 9.25 ppm and the other to the right of the TMS signal at –2.88 ppm. What hydrogens are responsible for each of the signals? (Hint: Look at the direction of the induced magnetic field outside and inside the benzene ring in Figure 14.6.)
Problem 16
How would integration distinguish the 1H NMR spectra of the following compounds?
Problem 18
Which of the following compounds is responsible for the 1H NMR spectrum shown below?
<IMAGE>
Problem 20
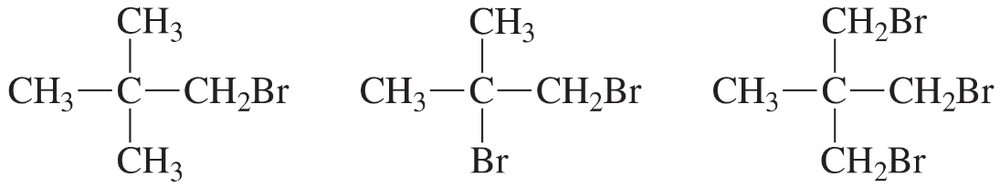
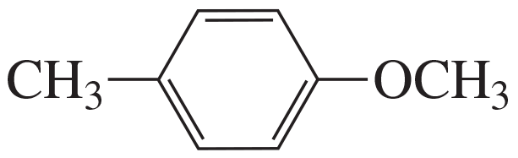
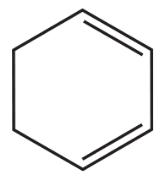
Explain how the following compounds, each with the same molecular formula, could be distinguished by their 1H NMR spectra.
Problem 22a
Draw a diagram like the one shown in Figure 14.12 to predict
a. the relative intensities of the peaks in a triplet.
<IMAGE>
Problem 22b
Draw a diagram like the one shown in Figure 14.12 to predict
b. the relative intensities of the peaks in a quintet.
<IMAGE>
Problem 23a
Indicate the number of signals and the multiplicity of each signal in the 1H NMR spectrum of each of the following compounds:
a. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3
Problem 23c
Indicate the number of signals and the multiplicity of each signal in the 1H NMR spectrum of each of the following compounds:
c. ClCH2CH2CH2Cl
Problem 24
Explain the relative chemical shifts of the benzene ring protons in Figure 14.18.
<IMAGE>
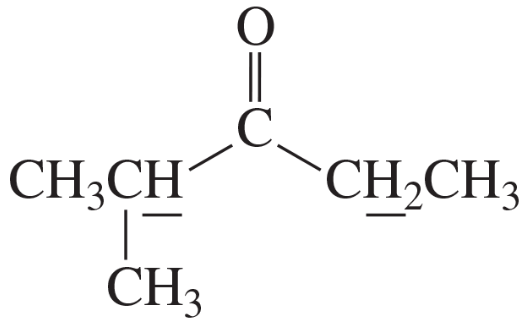
Problem 26b
Identify each compound from its molecular formula and its 1H NMR spectrum:
b. C5H10O
<IMAGE>
Problem 27c
Predict the splitting patterns for the signals given by the compounds in Problem 4.
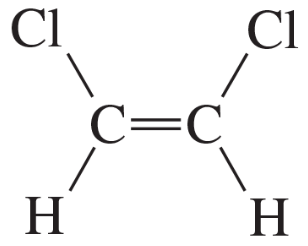
c. CH2=CCl2
Problem 27d
Predict the splitting patterns for the signals given by the compounds in Problem 4.
d.
Problem 27i
Predict the splitting patterns for the signals given by the compounds in Problem 4.
i.
Problem 27j
Predict the splitting patterns for the signals given by the compounds in Problem 4.
j.
Problem 28b
Describe the 1H NMR spectrum you would expect for each of the following compounds, indicating the relative positions of the signals:
b. CH3OCH2CH2CH2Br
Problem 28d
Describe the 1H NMR spectrum you would expect for each of the following compounds, indicating the relative positions of the signals:
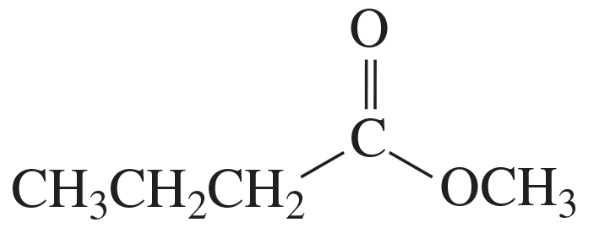
d.