25. The Urinary System
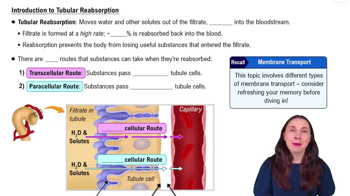
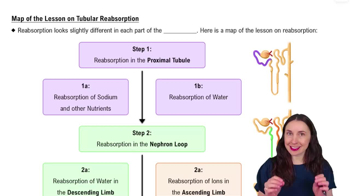
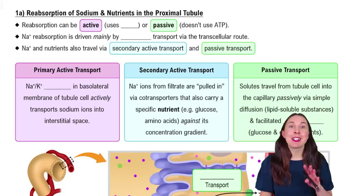
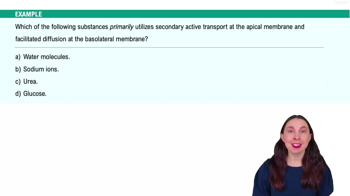
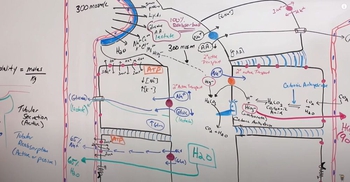
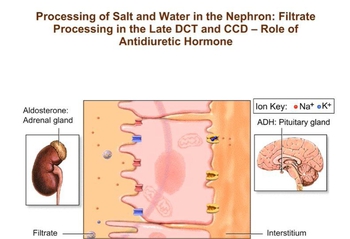
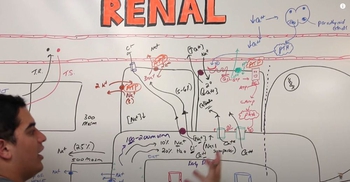
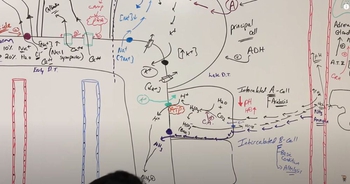
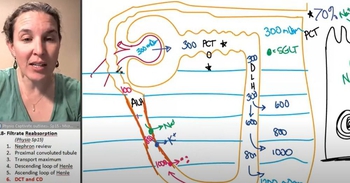
Renal Physiology Step 2: Tubular Reabsorption
25. The Urinary System
Renal Physiology Step 2: Tubular Reabsorption
Showing 15 of 15 videos
Additional 7 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 10 of 10 videos
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT a purpose of tubular reabsorption?
- Multiple Choice
Which of the following solutes are primarily reabsorbed by primary active transport?
- Multiple Choice
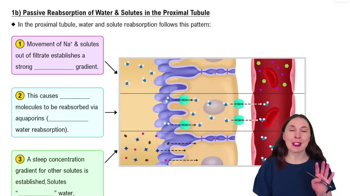
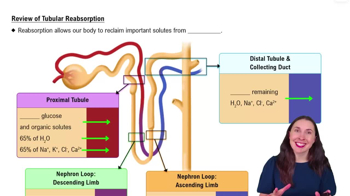
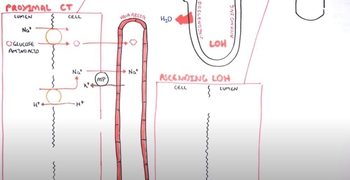
In the proximal tubule, _________ ions are pumped out of the tubule via ____________ transport. This creates an ____________ gradient, causing water to be reabsorbed through _______________.
- Multiple Choice
In the proximal tubule, _________ ions are pumped out of the tubule via ____________ transport. This creates an ____________ gradient, causing water to be reabsorbed through _______________.
- Open Question
Mark the following statements as true or false. If a statement is false, correct it to make a true statement.
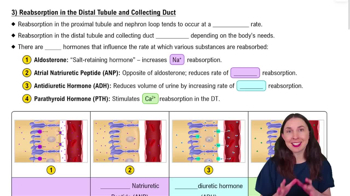
d. ADH triggers water reabsorption from the nephron loop.
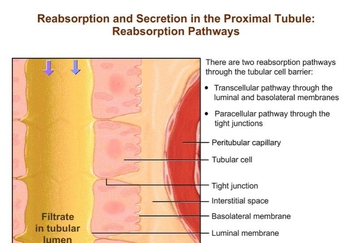
- Open QuestionExplain how the peritubular capillaries are adapted for receiving reabsorbed substances.
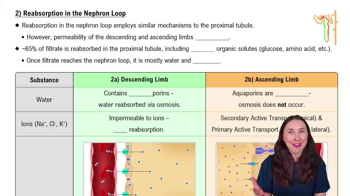
- Open QuestionDescribe what is involved in active and passive tubular reabsorption.
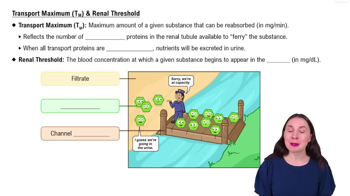
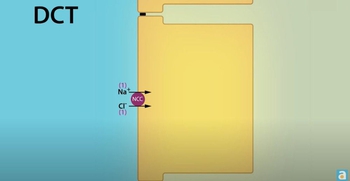
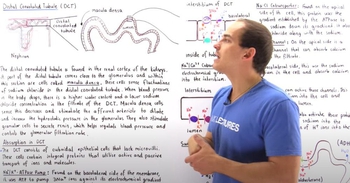
- Open QuestionTubular reabsorptiona. of glucose and many other substances is a Tₘ -limited active transport process,b. of chloride is always linked to the passive transport of Na⁺ ,c. is the movement of substances from the blood into the nephron,d. of sodium occurs only in the proximal tubule.