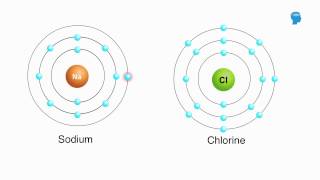
2. Cell Chemistry & Cell Components
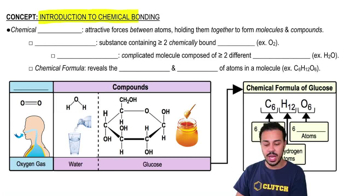
Introduction to Chemical Bonding
2. Cell Chemistry & Cell Components
Introduction to Chemical Bonding
Additional 3 creators.
Learn with other creators
Showing 6 of 6 videos
Practice this topic
- Open Question
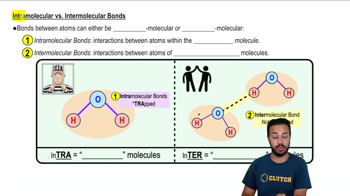
Appropriately label all of the chemical bonds in this image as either intramolecular or intermolecular.
- Multiple Choice
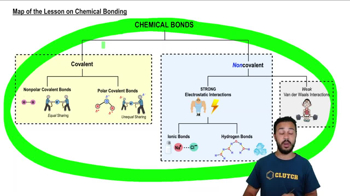
Map of the Lesson on Chemical Bonding
According to the map above, which of the following are types of covalent bonds?
a) Polar.
b) Van der Waals.
c) Ionic.
d) Hydrogen.
e) None of the above.
- Multiple ChoiceHow would you respond to this reasoning? Oxygen is not a greenhouse gas; therefore, gases containing oxygen—such as ozone, nitrous oxide, and carbon dioxide—are not greenhouse gases either.
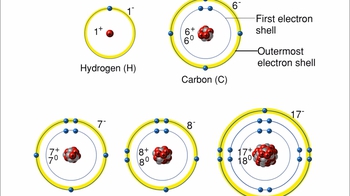
- Multiple ChoiceAn atom that normally has __________ in its outer shell would not tend to form chemical bonds with other atoms.
- Multiple ChoiceThe chemical characteristics or reactivity of an element depend mostly on the __________.
- Open QuestionWhat are the defining characteristics of a condensation reaction?a. Two monomers are covalently bonded together and a water molecule is produced.b. Two monomers are covalently bonded together and a water molecule is used up.c. A polymer is broken down into monomers and a water molecule is produced.d. A polymer is broken down into monomers and a water molecule is used up.1views
- Open QuestionWhat are the defining characteristics of a condensation reaction?a. Two monomers are covalently bonded together and a water molecule is produced.b. Two monomers are covalently bonded together and a water molecule is used up.c. A polymer is broken down into monomers and a water molecule is produced.d. A polymer is broken down into monomers and a water molecule is used up.
- Open QuestionWhat is chemically nonsensical about this structure?1views