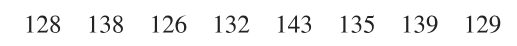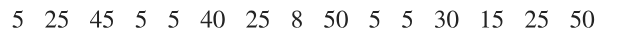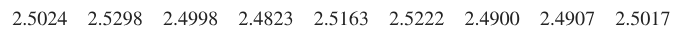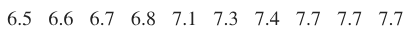Back
BackProblem 7.1.29
Heights of Presidents Refer to Data Set 22 “Presidents” in Appendix B. Treat the data as a sample and find the proportion of presidents who were taller than their opponents. Use that result to construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of the population percentage. Based on the result, does it appear that greater height is an advantage for presidential candidates? Why or why not?
Problem 7.1.13
Constructing and Interpreting Confidence Intervals. In Exercises 13–16, use the given sample data and confidence level. In each case, (a) find the best point estimate of the population proportion p; (b) identify the value of the margin of error E; (c) construct the confidence interval; (d) write a statement that correctly interprets the confidence interval.
Tennis Challenges In a recent U.S. Open tennis tournament, men playing singles matches used challenges on 240 calls made by the line judges. Among those challenges, 88 were found to be successful with the call overturned. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the proportion of successful challenges.
Problem 7.4.6
Seating Choice In a 3M Privacy Filters poll, respondents were asked to identify their favorite seat when they fly, and the results include these responses: window, window, other, other. Letting “window” and letting “other”, those four responses can be represented as {1, 1, 0, 0}. Here are ten bootstrap samples for those responses: [Image]
Using only the ten given bootstrap samples, construct an 80% confidence interval estimate of the proportion of respondents who indicated their favorite seat is “window.”
Problem 7.1.22
"Critical Thinking. In Exercises 17–28, use the data and confidence level to construct a confidence interval estimate of p, then address the given question.
Internet Use A random sample of 5005 adults in the United States includes 751 who do not use the Internet (based on three Pew Research Center polls). Construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of the percentage of U.S. adults who do not use the Internet. Based on the result, does it appear that the percentage of U.S. adults who do not use the Internet is different from 48%, which was the percentage in the year 2000?"
Problem 7.2.22
Mean IQ of Data Scientists See the preceding exercise, in which we can assume that sigma=15 for the IQ scores. Data scientists are a group with IQ scores that vary less than the IQ scores of the general population. Find the sample size needed to estimate the mean IQ of data scientists, given that we want 98% confidence that the sample mean is within 2 IQ points of the population mean. Does the sample size appear to be practical?
Problem 7.2.17
Genes Samples of DNA are collected, and the four DNA bases of A, G, C, and T are coded as 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively. The results are listed below. Construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of the mean. What is the practical use of the confidence interval?
2 2 1 4 3 3 3 3 4 1
Problem 7.4.28
Estimating the Median Use the sample data listed in Exercise 1 “Bootstrap Requirements” to generate 1000 bootstrap samples, and find the median in each of those samples. After obtaining the 1000 sample medians, find the 95% confidence interval estimate of the population median by evaluating p2.5 and p97.5 from the sorted 1000 medians. Given that the sample times in Exercise 1 are from the 50 times in Data Set 20 “Alcohol and Tobacco in Movies” and those 50 times have a median of 5.5, how well did the bootstrap method work to create a “good” confidence interval?
Problem 7.2.13
Archeology Archeologists have studied sizes of Egyptian skulls in an attempt to determine whether breeding occurred between different cultures. Listed below are the widths (mm) of skulls from 150 A.D. (based on data from Ancient Races of the Thebaid by Thomson and Randall-Maciver). Construct a 99% confidence interval estimate of the mean skull width.
Problem 7.1.5
Finding Critical Values.
In Exercises 5–8, find the critical value z=a/2 that corresponds to the given confidence level.
90%
Problem 7.2.19
Mercury in Sushi An FDA guideline is that the mercury in fish should be below 1 part per million (ppm). Listed below are the amounts of mercury (ppm) found in tuna sushi sampled at different stores in New York City. The study was sponsored by the New York Times, and the stores (in order) are D’Agostino, Eli’s Manhattan, Fairway, Food Emporium, Gourmet Garage, Grace’s Marketplace, and Whole Foods. Construct a 98% confidence interval estimate of the mean amount of mercury in the population. Does it appear that there is too much mercury in tuna sushi?
0.56 0.75 0.10 0.95 1.25 0.54 0.88
Problem 7.2.15
Los Angeles Commute Time Listed below are 15 Los Angeles commute times (based on a sample from Data Set 31 “Commute Times” in Appendix B). Construct a 99% confidence interval estimate of the population mean. Is the confidence interval a good estimate of the population mean?
Problem 7.1.40
One-Sided Confidence Interval A one-sided claim about a population proportion is a claim that the proportion is less than (or greater than) some specific value. Such a claim can be formally addressed using a one-sided confidence interval for p, which can be expressed as p<p+E or p>p-E, where the margin of error E is modified by replacing za/2 with za. (Instead of dividing between two tails of the standard normal distribution, put all of it in one tail.) The Chapter Problem refers to a Sallie Mae survey of 950 undergraduate students, and 53% of the survey subjects take online courses. Use that data to construct a one-sided 95% confidence interval that would be suitable for helping to determine whether the percentage of all undergraduates who take online courses is greater than 50%.
Problem 7.1.17
Critical Thinking. In Exercises 17–28, use the data and confidence level to construct a confidence interval estimate of p, then address the given question.
Births A random sample of 860 births in New York State included 426 boys. Construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of the proportion of boys in all births. It is believed that among all births, the proportion of boys is 0.512. Do these sample results provide strong evidence against that belief?
Problem 7.3.5
Use the given information to find the number of degrees of freedom, the critical values X2L and X2R, and the confidence interval estimate of σ. It is reasonable to assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a population with a normal distribution:
Nicotine in Menthol Cigarettes 95% confidence; n = 25, s = 0.24 mg
Problem 7.2.33
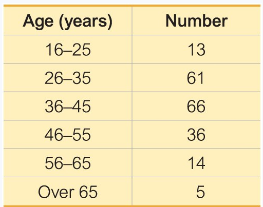
Ages of Prisoners The accompanying frequency distribution summarizes sample data consisting of ages of randomly selected inmates in federal prisons (based on data from the Federal Bureau of Prisons). Use the data to construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of the mean age of all inmates in federal prisons.
Problem 7.3.21
Large Data Sets from Appendix B. In Exercises 21 and 22, use the data set in Appendix B. Assume that each sample is a simple random sample obtained from a population with a normal distribution.
Comparing Waiting Lines Refer to Data Set 30 “Queues” in Appendix B. Construct separate 95% confidence interval estimates of using the two-line wait times and the single-line wait times. Do the results support the expectation that the single line has less variation? Do the wait times from both line configurations satisfy the requirements for confidence interval estimates of sigma
Problem 7.2.23
Ages of Moviegoers Find the sample size needed to estimate the mean age of movie patrons, given that we want 98% confidence that the sample mean is within 1.5 years of the population mean. Assume that sigma=19.6 years, based on a previous report from the Motion Picture Association of America. Could the sample be obtained from one movie at one theater?
Problem 7.3.14
Mint Specs Listed below are weights (grams) from a simple random sample of pennies produced after 1983 (from Data Set 40 “Coin Weights” in Appendix B). Construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of for the population of such pennies. What does the confidence interval suggest about the U.S. Mint specifications that now require a standard deviation of 0.0230 g for weights of pennies?
Problem 7.C.3
Cell Phone Radiation. Listed below are amounts of cell phone radiation (W/kg) measured from randomly selected cell phones (based on data from the Federal Communications Commission). Use these values for Exercises 1–6.
[Image]
Level of Measurement What is the level of measurement of these data (nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio)? Are the original unrounded amounts of radiation continuous data or discrete data?
Problem 7.CQQ.7
Requirements A construction quality control analyst has collected a random sample of six concrete road barriers, and she plans to weigh each of them and construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of the mean weight of all such barriers. What requirements must be satisfied in order to construct the confidence interval with the method from Section 7-2 that uses the t distribution?
Problem 7.CQQ.8
Degrees of Freedom In general, what does “degrees of freedom” refer to? For the sample data described in Exercise 7 “Requirements,” find the number of degrees of freedom, assuming that you want to construct a confidence interval estimate of u using the t distribution.
Problem 7.CR.8b
Controversial Song The song “Baby It’s Cold Outside” generated much controversy because of its lyrics and tone. CBS New York conducted a survey by asking viewers to use the Internet to respond to a question asking whether that song was really too offensive to play. Among 1043 Internet users who chose to respond, 986 said that the song was not too offensive, and 57 of the respondents said that the song was too offensive.
b. Based on the result from part (a), is it safe to say that the majority of the population does not feel that the song is too offensive.
Problem 7.CR.8c
Controversial Song The song “Baby It’s Cold Outside” generated much controversy because of its lyrics and tone. CBS New York conducted a survey by asking viewers to use the Internet to respond to a question asking whether that song was really too offensive to play. Among 1043 Internet users who chose to respond, 986 said that the song was not too offensive, and 57 of the respondents said that the song was too offensive.
.
c. What is wrong with this survey? Based on this survey, what do we really know about the population?
Problem 7.RE.4
Space Mountain Use the following wait times (minutes) for the Space Mountain ride at Disney World (from Data Set 33 “Disney World Wait Times” in Appendix B). Construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of the mean of all wait times. Write a brief statement that interprets that confidence interval.
40 35 40 40 25 80 50 30 35 40
Problem 7.RE.5a
Distributions Identify the distribution (normal, Student t, chi-square) that should be used in each of the following situations. If none of the three distributions can be used, what other method could be used?
a. In constructing a confidence interval of , you have 75 sample values and they appear to be from a population with a skewed distribution. The population standard deviation is not known.
Problem 7.RE.10b
Arm Circumferences Listed below are arm circumferences (cm) of randomly selected women (based on Data Set 1 “Body Data” from Appendix B). Also shown is the normal quantile plot of those measurements.
b. Are the requirements for constructing a 95% confidence interval estimate of the population standard deviation satisfied? If so, construct that confidence interval.
Problem 7.8a
Controversial Song The song “Baby It’s Cold Outside” generated much controversy because of its lyrics and tone. CBS New York conducted a survey by asking viewers to use the Internet to respond to a question asking whether that song was really too offensive to play. Among 1043 Internet users who chose to respond, 986 said that the song was not too offensive, and 57 of the respondents said that the song was too offensive.
a. Construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of the proportion of the population having the belief that the song is not too offensive.
Problem 7.4.15a
15. HEIGHTS OF FEMALE SOCCER PLAYERS Listed below are the heights (in.) of players on the U.S. Women’s National Soccer Team (at the time of this writing). Use those heights as a sample of the heights of all professional women soccer players.
a. Use 1000 bootstrap samples to construct a 95% confidence interval estimate of σ.
Problem 7.4.23a
Analysis of Last Digits Weights of respondents were recorded as part of the California Health Interview Survey. The last digits of weights from 50 randomly selected respondents are listed below.
a. Use the bootstrap method with 1000 bootstrap samples to find a 95% confidence interval estimate of .
Problem 7.3.16a
Comparing Waiting Lines
The values listed below are waiting times (in minutes) of customers at the Jefferson Valley Bank, where customers enter a single waiting line that feeds three teller windows. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the population standard deviation sigma.