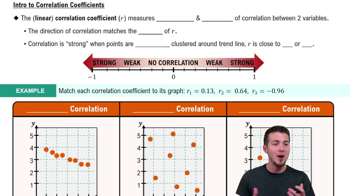
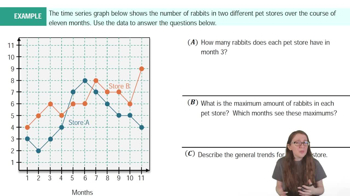
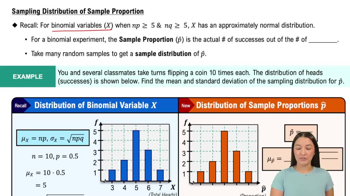
V and Digital Ads Listed below are amounts (billions of dollars) spent on TV and digital advertising. The amounts are listed in order by year ending with the year 2022. The last few years are projected amounts (based on data from Magna Global). Construct a graph that reveals the story that the data are trying to tell. What story does the graph depict?
TV Ads:
[Image]