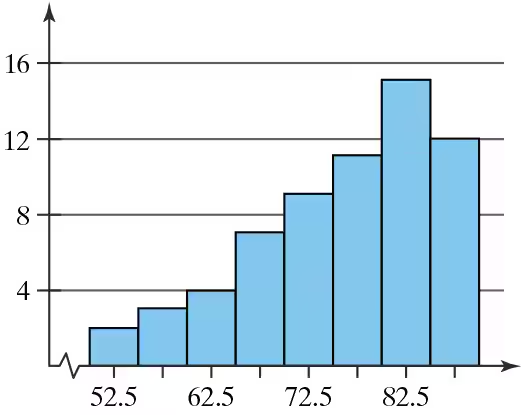
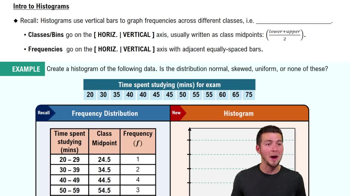
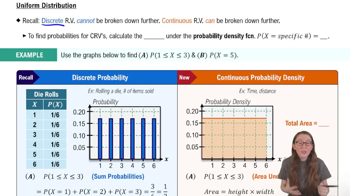
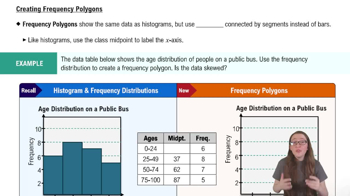
In Exercises 5 and 6, construct the dotplot.
Pulse Rates Listed below are pulse rates (beats per minute) of females selected from Data Set 1 “Body Data” in Appendix B. All of those pulse rates are even numbers. Is there a pulse rate that appears to be an outlier? What is its value?