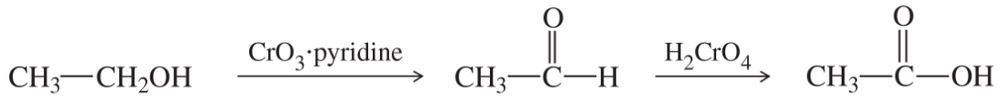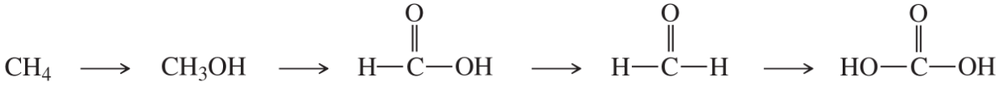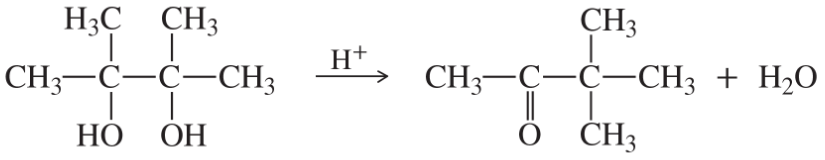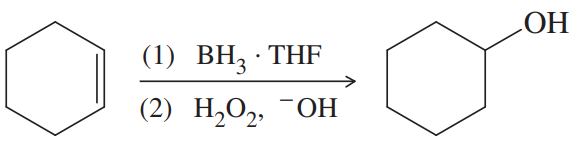Back
BackProblem 1a,b,c
Classify each reaction as an oxidation, a reduction, or neither.
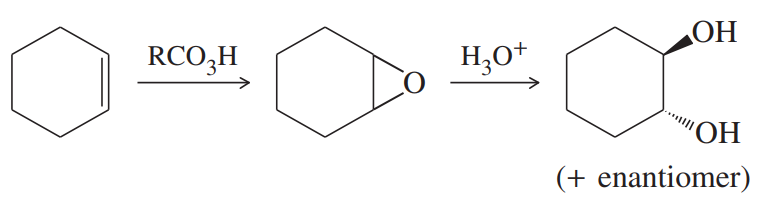
(a)
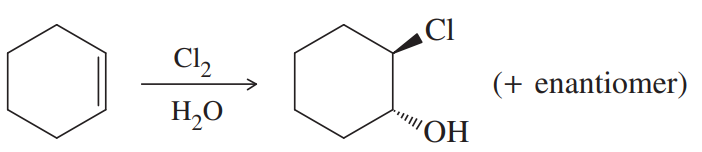
(b)
(c)
Problem 1d,e,f
Classify each reaction as an oxidation, a reduction, or neither.
(d)
(e)
(f)
Problem 1g,h,i
Classify each reaction as an oxidation, a reduction, or neither.
(g)
(h)
(i)
Problem 1j,k,l
Classify each reaction as an oxidation, a reduction, or neither.
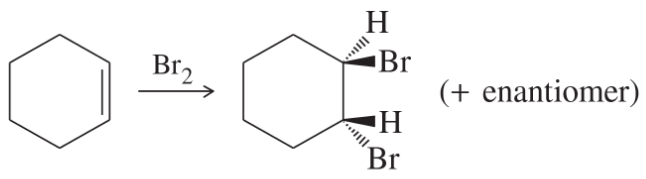
(j)
(k)
(l)
Problem 2a,b,c
Predict the products of the reactions of the following compounds with:
1. chromic acid or excess sodium hypochlorite with acetic acid.
2. PCC or NaOCl (1 equivalent) with TEMPO.
a. cyclohexanol
b. 1-methylcyclohexanol
c. cyclopentylmethanol
Problem 2d
Predict the products of the reactions of the following compounds with:
1. chromic acid or excess sodium hypochlorite with acetic acid.
2. PCC or NaOCl (1 equivalent) with TEMPO.
d. cyclohexanone
Problem 2e
Predict the products of the reactions of the following compounds with:
1. chromic acid or excess sodium hypochlorite with acetic acid.
2. PCC or NaOCl (1 equivalent) with TEMPO.
e. cyclohexane
Problem 2f
Predict the products of the reactions of the following compounds with:
1. chromic acid or excess sodium hypochlorite with acetic acid.
2. PCC or NaOCl (1 equivalent) with TEMPO.
f. 1-phenylpropan-1-ol
Problem 2g,h
Predict the products of the reactions of the following compounds with:
1. chromic acid or excess sodium hypochlorite with acetic acid.
2. PCC or NaOCl (1 equivalent) with TEMPO.
g. hexan-1-ol
h. acetaldehyde, CH3CHO
Problem 3a,b,c
We have covered several oxidants that use a multi-valent atom (Cr, Cl, S, or I) as their active species, going from a higher oxidation state before the oxidation to a lower oxidation state after oxidizing the alcohol. Draw the Lewis structures of the following atoms, before and after the oxidation of an alcohol to a ketone or aldehyde. How many bonds to oxygen does each atom have before and after the oxidation?
a. the Cr in chromic acid
b. the Cl in sodium hypochlorite
c. the S in the Swern oxidation
Problem 4a,b
Give the structure of the principal product(s) when each of the following alcohols reacts with (1) Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4, (2) PCC, (3) DMP, and (4) 1 equiv NaOCl-TEMPO.
a. octan-1-ol
b. octan-3-ol
Problem 4c(3,4)
Give the structure of the principal product(s) when each of the following alcohols reacts with (3) DMP, and (4) 1 equiv NaOCl-TEMPO.
c. 4-hydroxydecanal
Problem 4c(1,2)
Give the structure of the principal product(s) when each of the following alcohols reacts with (1) Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4, (2) PCC
c. 4-hydroxydecanal
Problem 4d(1,2)
Give the structure of the principal product(s) when each of the following alcohols reacts with (1) Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4, (2) PCC
d. 1-methylcyclohexan-1,4-diol
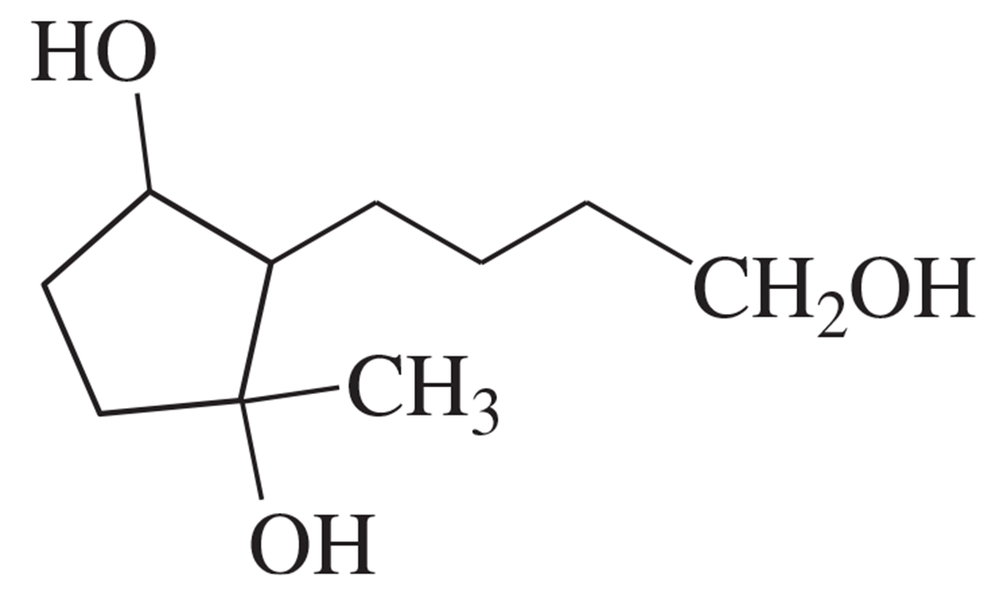
Problem 5a,b,c
Predict the products you expect when the following starting material undergoes oxidation with an excess of each of the reagents shown below.
a. chromic acid
b. PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate)
c. sodium hypochlorite/acetic acid
Problem 5d,e
Predict the products you expect when the following starting material undergoes oxidation with an excess of each of the reagents shown below.
d. DMSO and oxalyl chloride
e. DMP (periodinane) reagent
Problem 6a,b,c
Suggest the most appropriate method for each of the following laboratory syntheses. In each case, suggest both a chromium reagent and a chromium-free reagent.
(a) butan-1-ol → butanal, CH3CH2CH2CHO
(b) but-2-en-1-ol → but-2-enoic acid, CH3CH=CH–COOH
(c) butan-2-ol → butan-2-one, CH3COCH2CH3
Problem 6d,e
Suggest the most appropriate method for each of the following laboratory syntheses. In each case, suggest both a chromium reagent and a chromium-free reagent.
(d) cyclopentanol → 1-ethylcyclopentanol (two steps)
(e) cyclopentylmethanol → 1-cyclopentylpropan-1-ol (two steps)
Problem 6f
Suggest the most appropriate method for each of the following laboratory syntheses. In each case, suggest both a chromium reagent and a chromium-free reagent.
(f) 1-methylcyclohexanol → 2-methylcyclohexanone (several steps)
Problem 7
A chronic alcoholic requires a much larger dose of ethanol as an antidote to methanol poisoning than does a nonalcoholic patient. Suggest a reason why a larger dose of the competitive inhibitor is required for an alcoholic.
Problem 9a,b,c
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(a) ethyl tosylate + potassium tert-butoxide
(b) isobutyl tosylate + NaI
(c) (R)-2-hexyl tosylate + NaCN
Problem 9d,e
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(d) the tosylate of cyclohexylmethanol + excess NH3
(e) n-butyl tosylate + sodium acetylide, H–C≡C:– +Na
Problem 10a,b
Show how you would convert propan-1-ol to the following compounds using tosylate intermediates. You may use whatever additional reagents are needed.
a. 1-bromopropane
b. propan-1-amine, CH3CH2CH2NH2
Problem 10c,d
Show how you would convert propan-1-ol to the following compounds using tosylate intermediates. You may use whatever additional reagents are needed.
c. CH3CH2CH2OCH2CH3, ethyl proyl ether
d. CH3CH2CH2CN, butyronitrile
Problem 11a,b
Predict the products of the following reactions.
(a) cyclohexylmethanol + TsCl/pyridine
(b) product of (a) + LiAlH4
Problem 11c,d
Predict the products of the following reactions.
(c) 1-methylcyclohexanol + H2SO4, heat
(d) product of (c) + H2, Pt
Problem 12a
Propose a mechanism for the reaction of
(a) 1-methylcyclohexanol with HBr to form 1-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane.
Problem 13
The reaction of tert-butyl alcohol with concentrated HCl goes by the SN1 mechanism. Write a mechanism for this reaction.
Problem 14d,e
Show how you would use a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds. Tell what you would observe with each compound.
(d) allyl alcohol and propan-1-ol
(e) butan-2-one and tert-butyl alcohol
Problem 15
Neopentyl alcohol, (CH3)3CCH2OH, reacts with concentrated HBr to give 2-bromo-2-methylbutane, a rearranged product. Propose a mechanism for the formation of this product.