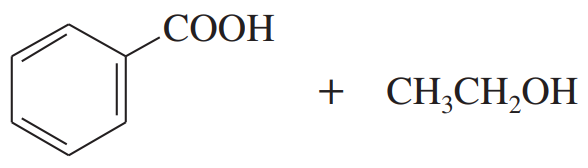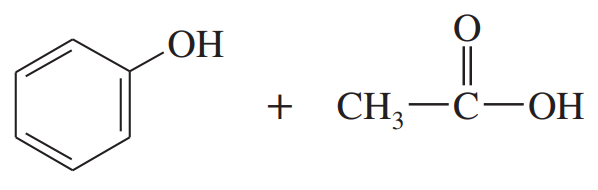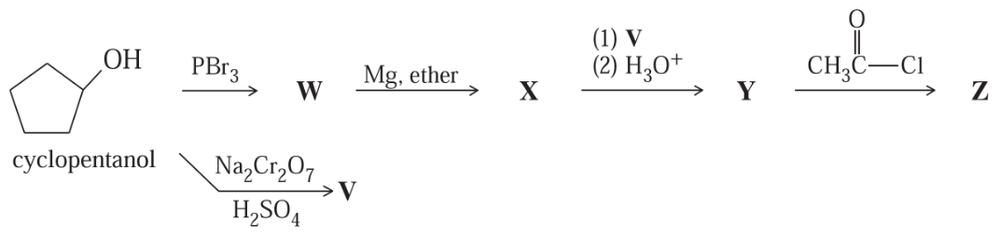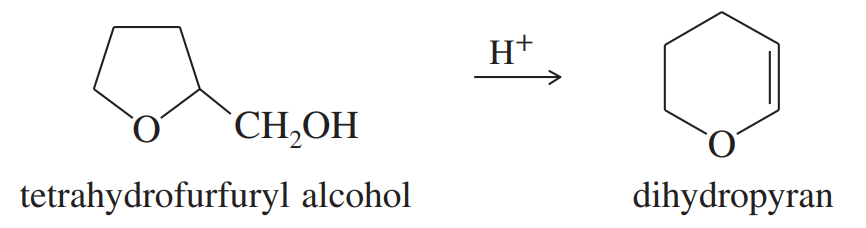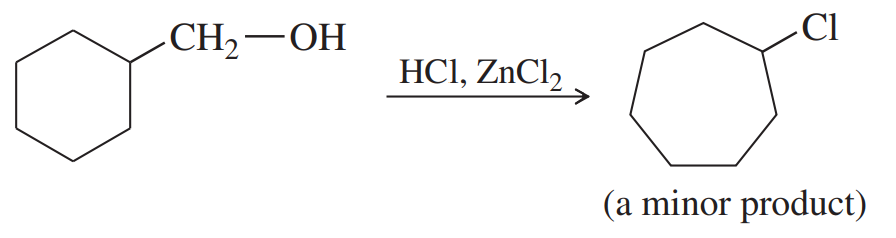Back
BackProblem 38f
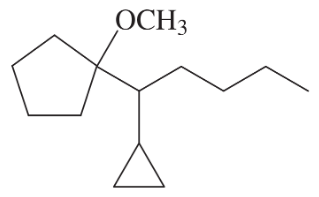
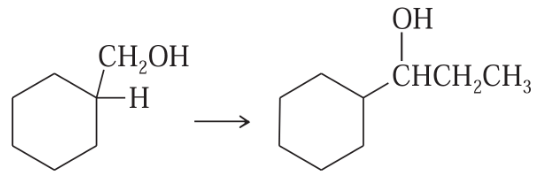
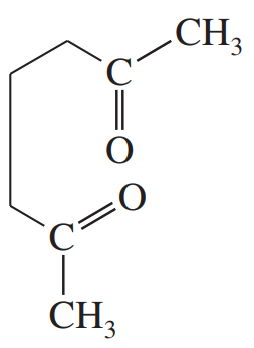
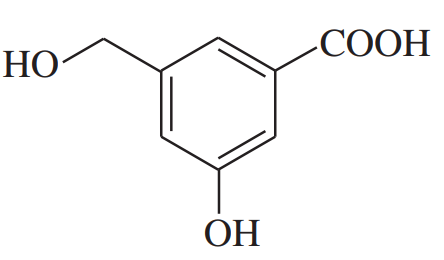
Develop syntheses for the following compounds. As starting materials, you may use cyclopentanol, alcohols containing no more than four carbon atoms, and any common reagents and solvents.
(f)
Problem 39a,b
Predict the major products of the following reactions, including stereochemistry where appropriate.
(a) (R)-butan-2-ol + TsCl in pyridine
(b) (S)-2-butyl tosylate + NaBr
Problem 39c,d
Predict the major products of the following reactions, including stereochemistry where appropriate.
(c) cyclooctanol + NaOCl/HOAC
(d) cyclopentylmethanol + CrO3·pyridine·HCl
Problem 39e,f,g
Predict the major products of the following reactions, including stereochemistry where appropriate.
(e) cyclopentylmethanol + Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4
(f) cyclopentanol + HCl/ZnCl2
(g) n-butanol + HBr
Problem 39h,i,j
Predict the major products of the following reactions, including stereochemistry where appropriate.
(h) cyclooctylmethanol + CH3CH2MgBr
(i) potassium tert-butoxide + methyl iodide
(j) sodium methoxide + tert-butyl iodide
Problem 39k,l,m
Predict the major products of the following reactions, including stereochemistry where appropriate.
(k) cyclopentanol + H2SO4/heat
(l) product from (k) + OsO4/H2O2, then HIO4
(m) sodium ethoxide + 1-bromobutane
Problem 39n,o,p
Predict the major products of the following reactions, including stereochemistry where appropriate.
(n) sodium ethoxide + 2-methyl-2-bromobutane
(o) octan-1-ol + DMSO + oxalyl chloride
(p) 4-cyclopentylhexan-1-ol + DMP reagent
Problem 40a,b,c
Show how you would convert 2-methylcyclopentanol to the following products. Any of these products may be used as the reactant in any subsequent part of this problem.
a. 1-methylcyclopentene
b. 2-methylcyclopentyl tosylate
c. 2-methylcyclopentanone
Problem 40d
Show how you would convert 2-methylcyclopentanol to the following products. Any of these products may be used as the reactant in any subsequent part of this problem.
d. 1-methylcyclopentanol
Problem 40g,h
Show how you would convert 2-methylcyclopentanol to the following products. Any of these products may be used as the reactant in any subsequent part of this problem.
(g) 2-methylcyclopentyl acetate
(h) 1-bromo-1-methylcyclopentane
Problem 41a,b
In each case, show how you would synthesize the chloride, bromide, and iodide from the corresponding alcohol.
(a) 1-halobutane (halo = chloro, bromo, iodo)
(b) halocyclopentane
Problem 42a,b
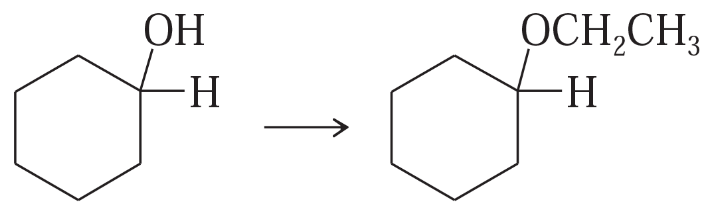
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions.
(a)
(b)
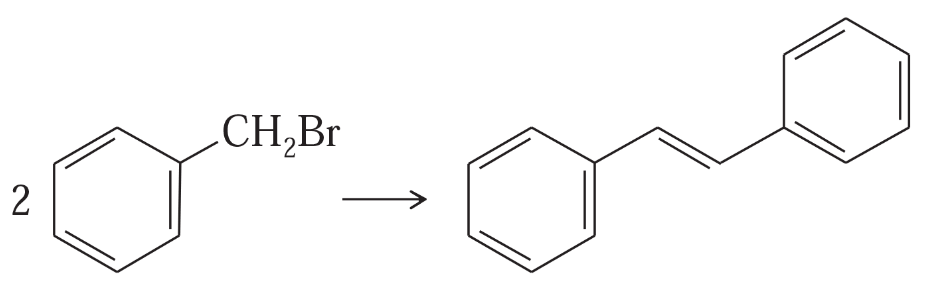
Problem 42c
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions.
(c)
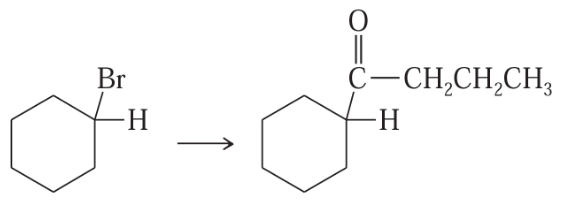
Problem 42d
Show how you would accomplish the following synthetic conversions.
(d)
Problem 43a,b,c
Predict the major products of dehydration catalyzed by sulfuric acid.
(a) hexan-1-ol
(b) hexan-2-ol
(c) pentan-3-ol
Problem 44a,b,c
Predict the esterification products of the following acid/alcohol pairs.
(a) CH3CH2CH2COOH + CH3OH
(b) CH3OH + HNO3
(c) 2 CH3CH2OH + H3PO4
Problem 44d,e
Predict the esterification products of the following acid/alcohol pairs.
(d)
(e)
Problem 45
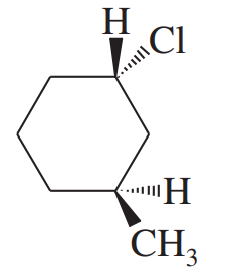
Both cis- and trans-2-methylcyclohexanol undergo dehydration in warm sulfuric acid to give 1-methylcyclohexene as the major alkene product. These alcohols can also be converted to alkenes by tosylation using TsCl and pyridine, followed by elimination using KOC(CH3)3 as a strong base. Under these basic conditions, the tosylate of cis-2-methylcyclohexanol eliminates to give mostly 1-methylcyclohexene, but the tosylate of trans-2-methylcyclohexanol eliminates to give only 3-methylcyclohexene. Explain how this stereochemical difference in reactants controls a regiochemical difference in the products of the basic elimination, but not in the acid-catalyzed elimination.
Problem 46a,b,c
Show how you would convert (S)-hexan-2-ol to
(a) (S)-2-chlorohexane.
(b) (R)-2-bromohexane.
(c) (R)-hexan-2-ol.
Problem 48d,e,f
Show how you would make each compound, beginning with an alcohol of your choice.
(d)
(e)
(f)
Problem 48g,h
Show how you would make each compound, beginning with an alcohol of your choice.
(g)
(h)
Problem 49a,b,c
Predict the major products (including stereochemistry) when cis-3-methylcyclohexanol reacts with the following reagents.
(a) PBr3
(b) SOCl2
(c) Lucas reagent
Problem 49d,e
Predict the major products (including stereochemistry) when cis-3-methylcyclohexanol reacts with the following reagents.
(d) concentrated HBr
(e) TsCl/pyridine, then NaBr
Problem 51
The compound shown below has three different types of OH groups, all with different acidities. Show the structure produced after this compound is treated with different amounts of NaH followed by a methylating reagent. Add a brief explanation.
(a) 1 equivalent of NaH, followed by 1 equivalent of CH3I and heat
(b) 2 equivalents of NaH, followed by 2 equivalents of CH3I and heat
(c) 3 equivalents of NaH, followed by 3 equivalents of CH3I and heat
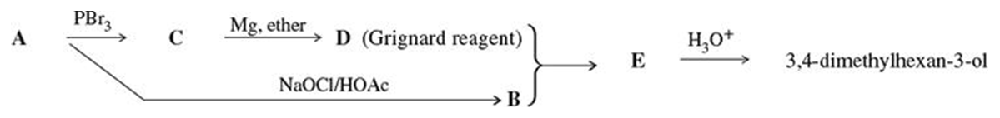
Problem 52
Compound A is an optically active alcohol. Treatment with chromic acid converts A into a ketone, B. In a separate reaction, A is treated with PBr3, converting A into compound C. Compound C is purified, and then it is allowed to react with magnesium in ether to give a Grignard reagent, D. Compound B is added to the resulting solution of the Grignard reagent. After hydrolysis of the initial product (E), this solution is found to contain 3,4-dimethylhexan-3-ol. Propose structures for compounds A, B, C, D, and E.
Problem 53
Give the structures of the intermediates and products V through Z.
Problem 54
Under acid catalysis, tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol reacts to give surprisingly good yields of dihydropyran. Propose a mechanism to explain this useful synthesis.
Problem 55a
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions. In most cases, more products are formed than are shown here. You only need to explain the formation of the products shown, however.
(a)
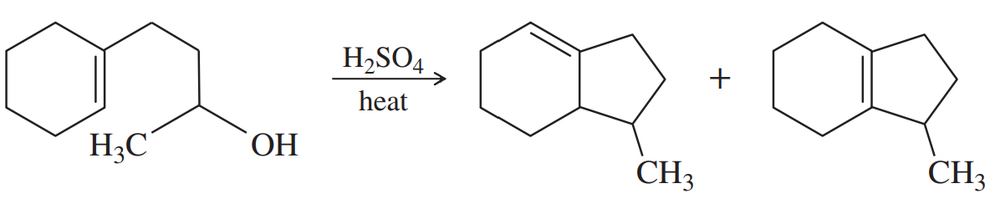
Problem 55b
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions. In most cases, more products are formed than are shown here. You only need to explain the formation of the products shown, however.
(b)
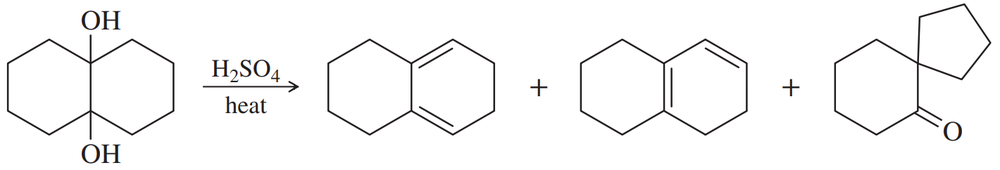
Problem 55c
Propose mechanisms for the following reactions. In most cases, more products are formed than are shown here. You only need to explain the formation of the products shown, however.
(c)