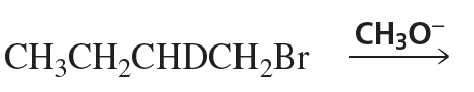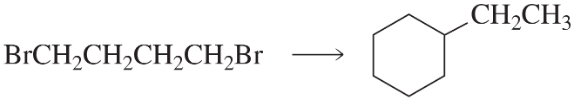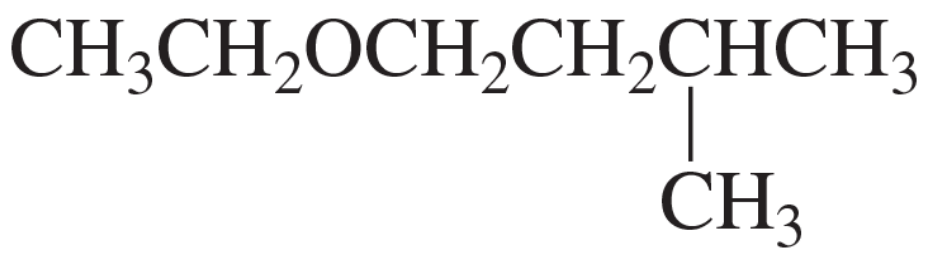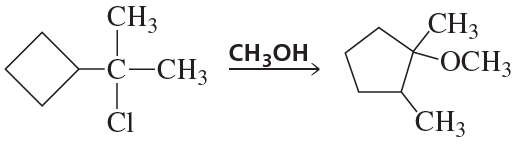Back
BackProblem 110a,b
Draw the substitution products for each of the following SN2 reactions. If the products can exist as stereoisomers, show which stereoisomers are formed:
a. (3S,4S)-3-bromo-4-methylhexane + CH3O-
b. (3S,4R)-3-bromo-4-methylhexane + CH3O-
Problem 110c,d
Draw the substitution products for each of the following SN2 reactions. If the products can exist as stereoisomers, show which stereoisomers are formed:
c. (3R,4R)-3-bromo-4-methylhexane + CH3O-
d. (3R,4S)-3-bromo-4-methylhexane + CH3O-
Problem 111a,b
Draw the elimination products for each of the following E2 reactions; if the products can exist as stereoisomers, indicate which stereoisomers are obtained.
a. (2S,3S)-2-chloro-3-methylpentane + high concentration of CH3O−
b. (2S,3R)-2-chloro-3-methylpentane + high concentration of CH3O−
Problem 111c
Draw the elimination products for each of the following E2 reactions; if the products can exist as stereoisomers, indicate which stereoisomers are obtained.
c. (2R,3S)-2-chloro-3-methylpentane + high concentration of CH3O-
Problem 111d
Draw the elimination products for each of the following E2 reactions; if the products can exist as stereoisomers, indicate which stereoisomers are obtained.
d. (2R,3R)-2-chloro-3-methylpentane + high concentration of CH3O-
Problem 111e
Draw the elimination products for each of the following E2 reactions; if the products can exist as stereoisomers, indicate which stereoisomers are obtained.
e. 3-chloro-3-ethyl-2,2-dimethylpentane + high concentration of CH3CH2O-
Problem 112a
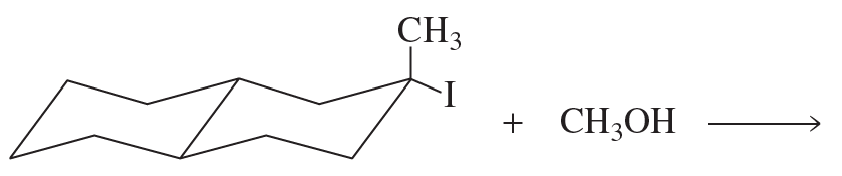
Draw the major elimination product that would be obtained from each of the following reactants with a strong base and with a weak base:
a.
Problem 114
Explain why the rate of the reaction of 1-bromo-2-butene with ethanol is increased if silver nitrate is added to the reaction mixture.
Problem 115a
Draw the products of each of the following SN2/E2 reactions. If the products can exist as stereoisomers, show which stereoisomers are formed.
a. (3S,4S)-3-bromo-4-methylhexane + CH3O−
Problem 115b
Draw the products of each of the following SN2/E2 reactions. If the products can exist as stereoisomers, show which stereoisomers are formed.
b. (3R,4R)-3-bromo-4-methylhexane + CH3O−
Problem 115c
Draw the products of each of the following SN2/E2 reactions. If the products can exist as stereoisomers, show which stereoisomers are formed.
c. (3S,4R)-3-bromo-4-methylhexane + CH3O−
Problem 116
Two elimination products are obtained from the following E2 reaction:
a. What are the elimination products?
b. Which is formed in greater yield?
Problem 117
Draw the structures of the products obtained from the following reaction:
Problem 118b
How could you prepare the following compounds from the given starting materials?
b.
Problem 119a
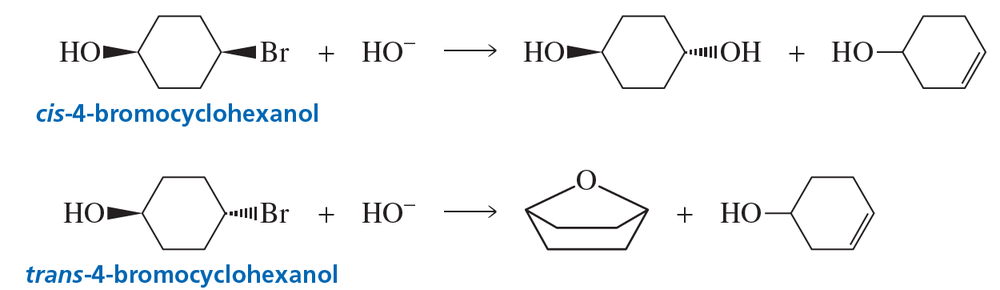
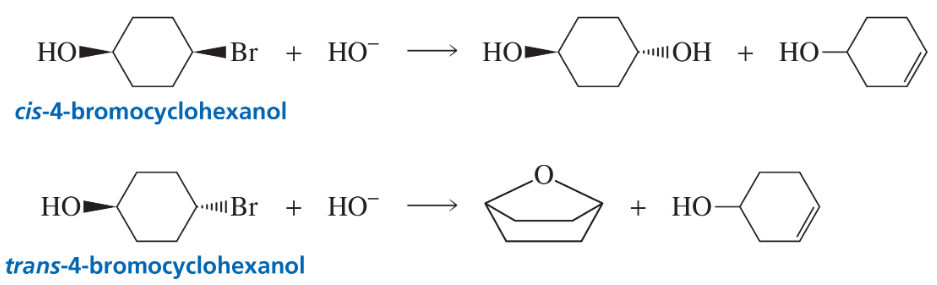
cis-4-Bromocyclohexanol and trans-4-bromocyclohexanol form the same elimination product but a different substitution product when they react with HO−.
a. Why do they form the same elimination product?
Problem 119b
cis-4-Bromocyclohexanol and trans-4-bromocyclohexanol form the same elimination product but a different substitution product when they react with HO−.
b. Explain, by showing the mechanisms, why different substitution products are obtained.
Problem 119c
cis-4-Bromocyclohexanol and trans-4-bromocyclohexanol form the same elimination product but a different substitution product when they react with HO−.
c. How many stereoisomers does each of the elimination and substitution reactions form?
Problem 120a(2)
Draw the product of each of the following reactions:
2.
Problem 120a(1)
Draw the product of each of the following reactions:
1.
Problem 120b
Give two sets of reactants (each set including an alkyl halide and a nucleophile) that could be used to synthesize the following alkyne:
CH3CH2C≡CCH2CH2CH2CH3
Problem 120c
Give two sets of reactants (each set including an alkyl halide and a nucleophile) that could be used to synthesize the following ether:
Problem 121
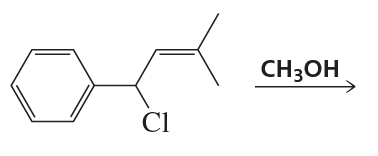
Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:
Problem 122
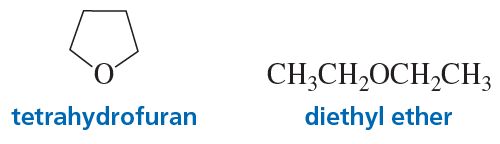
Explain why tetrahydrofuran can solvate a positively charged species better than diethyl ether can.
Problem 123
The reaction of an alkyl chloride with potassium iodide is generally carried out in acetone to maximize the amount of alkyl iodide that is formed. Why does the solvent increase the yield of alkyl iodide? (Hint: Potassium iodide is soluble in acetone, but potassium chloride is not.)
Problem 124a
Propose a mechanism for the following reaction.
Problem 125
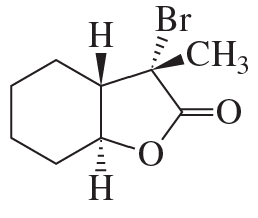
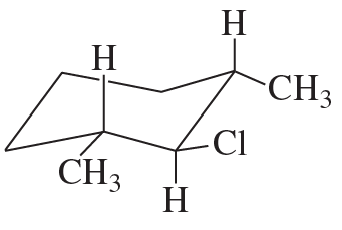
What products are formed when the following stereoisomer of 2-chloro-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane reacts with methoxide ion?
Problem 126
Predict the product for the following reaction and write a mechanism to explain how it is formed.
Problem 127a
For each of the following compounds, draw the product that forms in an E2 reaction and indicate its configuration:
a. (1S,2S)-1-bromo-1,2-diphenylpropane
Problem 127b
For each of the following compounds, draw the product that forms in an E2 reaction and indicate its configuration:
b. (1S,2R)-1-bromo-1,2-diphenylpropane
Problem 129
When equivalent amounts of methyl bromide and sodium iodide are dissolved in methanol, the concentration of iodide ion quickly decreases and then slowly returns to its original concentration. Account for this observation.