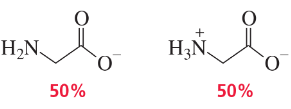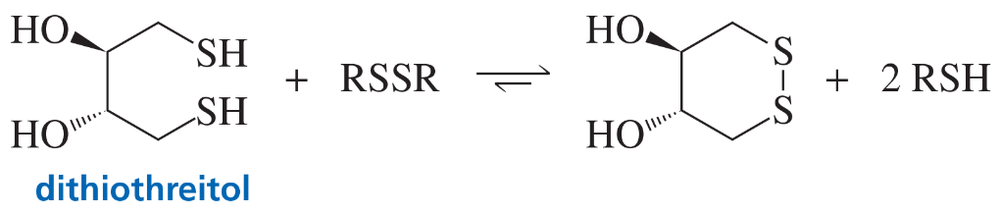Back
BackProblem 37
Write the mechanism for the reaction of a cysteine side chain with iodoacetic acid.
Problem 39
A decapeptide undergoes partial hydrolysis to give peptides whose amino acid compositions are shown. Reaction of the intact decapeptide with Edman's reagent releases PTH-Gly. What is the sequence of the decapeptide?
1. Ala, Trp
2. Val, Pro, Asp
3. Pro, Val
4. Ala, Glu
5. Trp, Ala, Arg
6. Arg, Gly
7. Glu, Ala, Leu
8. Met, Pro, Leu, Glu
Problem 41
Indicate the peptides produced from cleavage by the indicated reagent:
a. His-Lys-Leu-Val-Glu-Pro-Arg-Ala-Gly-Ala by trypsin
b. Leu-Gly-Ser-Met-Phe-Pro-Tyr-Gly-Val by chymotrypsin
Problem 44a
Three peptides were obtained from a trypsin digestion of two different polypeptides. In each case, indicate the possible sequences from the given data and tell what further experiment should be carried out in order to determine the primary structure of the polypeptide.
a. polypeptide I:
1. Val-Gly-Asp-Lys
2. Leu-Glu-Pro-Ala-Arg
3. Ala-Leu-Gly-Asp
Problem 46
How would a protein that resides in the nonpolar interior of a membrane fold compared with the water-soluble protein just discussed?
Problem 49a
Glycine has pKa values of 2.34 and 9.60. At what pH does glycine exist in the forms shown?
a.
Problem 50
Show the peptides that would result from cleavage by the indicated reagent:
a. Val-Arg-Gly-Met-Arg-Ala-Ser by carboxypeptidase A
b. Ser-Phe-Lys-Met-Pro-Ser-Ala-Asp by cyanogen bromide
c. Arg-Ser-Pro-Lys-Lys-Ser-Glu-Gly by trypsin
Problem 52
Which has a higher percentage of negative charge at physiological pH (7.4), leucine with pI = 5.98 or asparagine with pI = 5.43?
Problem 54c
Draw the form of aspartate that predominates at the following pH values: c. pH=6.0
Problem 54d
Draw the form of aspartate that predominates at the following pH values:
d. pH=11.0
Problem 57b,c
What aldehydes are formed when the following amino acids are treated with ninhydrin?
b. leucine
c. arginine
Problem 60
Explain why amino acids, unlike most amines and carboxylic acids, are insoluble in diethyl ether.
Problem 61
Explain the difference in the pKa values of the carboxyl groups of alanine, serine, and cysteine
Problem 63c
Identify the location and type of charge on the hexapeptide Lys-Ser-Asp-Cys-His-Tyr at each of the following pH values:
c. pH=7
Problem 63d
Identify the location and type of charge on the hexapeptide Lys-Ser-Asp-Cys-His-Tyr at each of the following pH values:
d. pH=12
Problem 64
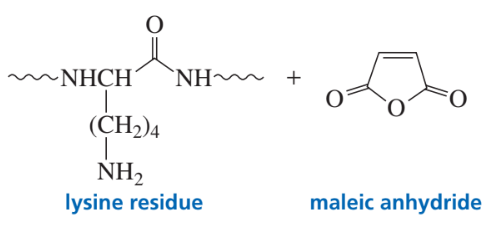
Draw the product obtained when a lysine side chain in a polypeptide reacts with maleic anhydride.
Problem 65a,b
After the polypeptide shown below was treated with maleic anhydride, it was hydrolyzed by trypsin. (After a polypeptide is treated with maleic anhy- dride, trypsin will cleave the polypeptide only on the C-side of arginine.)
Gly-Ala-Asp-Ala-Leu-Pro-Gly-Ile-Leu-Val-Arg-Asp-Val-Gly-Lys-Val-Glu-Val-Phe-Glu-Ala-Gly- Arg-Ala-Glu-Phe-Lys-Glu-Pro-Arg-Leu-Val-Met-Lys-Val-Glu-Gly-Arg-Pro-Val-Gly-Ala-Gly-Leu-Trp
a. After a polypeptide is treated with maleic anhydride, why does trypsin no longer cleave it on the C-side of lysine?
b. How many fragments are obtained from the polypeptide?
Problem 68a
α-Amino acids can be prepared by treating an aldehyde with ammonia/trace acid, followed by hydrogen cyanide, followed by acid-catalyzed hydrolysis.
a. Draw the structures of the two intermediates formed in this reaction.
Problem 68b,c
α-Amino acids can be prepared by treating an aldehyde with ammonia/trace acid, followed by hydrogen cyanide, followed by acid-catalyzed hydrolysis.
b. What amino acid is formed when the aldehyde that is used is 3-methylbutanal?
c. What aldehyde is needed to prepare isoleucine?
Problem 69
Reaction of a polypeptide with carboxypeptidase A releases Met. The polypeptide undergoes partial hydrolysis to give the following peptides. What is the sequence of the polypeptide?
1. Ser, Lys, Trp
2. Gly, His, Ala
3. Glu, Val, Ser
4. Leu, Glu, Ser
5. Met, Ala, Gly
6. Ser, Lys, Val
7. Glu, His
8. Leu, Lys, Trp
9. Lys, Ser
10. Glu, His, Val
11. Trp, Leu, Glu
12. Ala, Met
Problem 71
Glycine has pKa values of 2.3 and 9.6. Do you expect the pKa values of glycylglycine to be higher or lower than these values?
Problem 73
Write the mechanism for the reaction of an amino acid with di-tert-butyl dicarbonate.
Problem 74
Dithiothreitol reacts with disulfide bridges in the same way that 2-mercaptoethanol does. With dithiothreitol, however, the equilibrium lies much more to the right. Explain.
Problem 75a
Show how valine can be prepared by
a. a Hell–Volhard–Zelinski reaction.
Problem 75c
Show how valine can be prepared by
c. a reductive amination.
Problem 75d
Show how valine can be prepared by
d. a N-phthalimidomalonic ester synthesis.
Problem 78
Propose a mechanism for the rearrangement of the thiazoline obtained from the reaction of Edman's reagent with a peptide to a PTH-amino acid. (Hint: Thioesters are very reactive toward nucleophiles.)