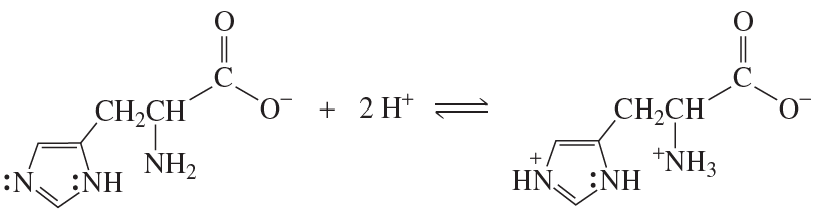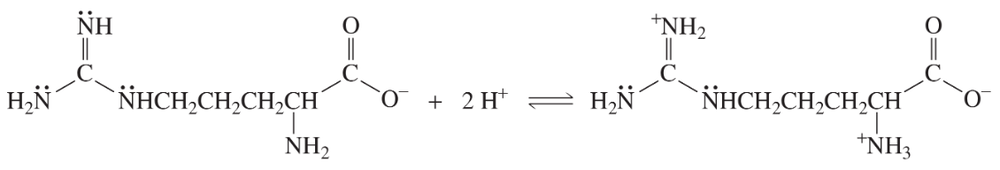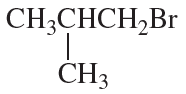Back
BackProblem 1a
Explain why, when the imidazole ring of histidine is protonated, the double-bonded nitrogen is the nitrogen that accepts the proton.
Problem 1b
Explain why, when the guanidino group of arginine is protonated, the double-bonded nitrogen is the nitrogen that accepts the proton.
Problem 5
Alanine has pKa values of 2.34 and 9.69. Therefore, alanine exists predominately as a zwitterion in an aqueous solution with pH >____ and pH <____.
Problem 8a
Draw the predominant form for glutamate in a solution with the following pH:
a. 0
Problem 8b
Draw the predominant form for glutamate in a solution with the following
pH: b. 3
Problem 9b
Why is the pKa of the arginine side chain greater than the pKa of the lysine side chain?
Problem 11a,b
a. Which amino acid has the lowest pI value?
b. Which amino acid has the highest pI value?
Problem 11c
c. Which amino acid has the greatest amount of negative charge at pH = 6.20?
Problem 11d
d. Which amino acid has a greater negative charge at pH = 6.20, glycine or methionine?
Problem 13
a. What percentage of the a-amino group of lysine will be protonated at its pI?
<25%, 50%, >75%
b. Answer the same question for the e-amino group of lysine
Problem 14
Explain why the pI of lysine is the average of the pKa values of its two protonated amino groups.
Problem 16
A mixture of seven amino acids (glycine, glutamate, leucine, lysine, alanine, isoleucine, and aspartate) is separated by chromatography. Explain why only six spots show up when the chromatographic plate is coated with ninhydrin and heated.
Problem 18a
Explain the order of elution (with a buffer of pH 4) of the following pairs of amino acids through a column packed with Dowex 50:
a. aspartate before serine
Problem 18b
Explain the order of elution (with a buffer of pH 4) of the following pairs of amino acids through a column packed with Dowex 50:
b. serine before alanine
Problem 20
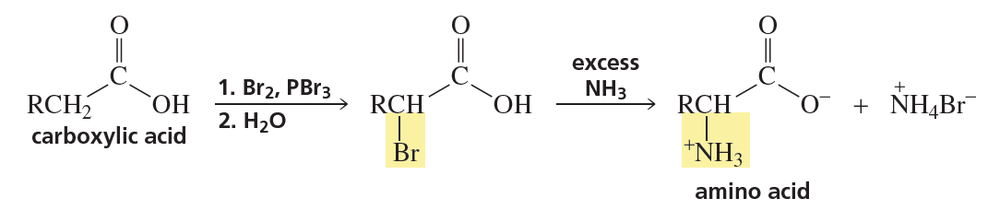
Why is excess ammonia used in the preceding reaction?
Problem 22a
What amino acid is formed using the N-phthalimidomalonic ester synthesis when the following alkyl halides are used in the third step?
a.
Problem 22b
What amino acid is formed using the N-phthalimidomalonic ester synthesis when the following alkyl halides are used in the third step?
b. CH3SCH2CH2Br
Problem 23a
What alkyl halide is used in the acetamidomalonic ester synthesis to prepare
a. lysine?
Problem 23b
What alkyl halide is used in the acetamidomalonic ester synthesis to prepare
b. phenylalanine?
Problem 24b
What amino acid is formed when the aldehyde used in the Strecker synthesis is
b. 2-methylbutanal?
Problem 25
Esterase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of esters. It hydrolyzes esters of l-amino acids more rapidly than esters of D-amino acids. How can this enzyme be used to separate a racemic mixture of amino acids?
Problem 26
Draw the tetrapeptide Ala-Thr-Asp-Asn and indicate the peptide bonds.
Problem 27
Draw the resonance contributors of the peptide bond in the less stable configuration.
Problem 28
Which bonds in the backbone of a peptide can rotate freely?
Problem 29
An opioid pentapeptide has the following structure: Tyr-Cys-Gly-Phe-Cys
a. Draw the structure of the pentapeptide including all the side chains.
b. Write its structure following mild oxidation.
Problem 30
What is the configuration about each of the asymmetric centers in aspartame?
Problem 32
What dipeptides would be formed by heating a mixture of valine and N-protected leucine?
Problem 34
Show the steps in the synthesis of the tetrapeptide Leu-Phe-Ala-Val.
Problem 35
a. Calculate the overall yield of bradykinin when the yield for the addition of each amino acid to the chain is 70%.
b. What would be the overall yield of a peptide containing 15 amino acids if the yield for the incorporation of each is 80%
Problem 36
Show the steps in the synthesis of the tetrapeptide in Problem 34, using Merrifield's method.