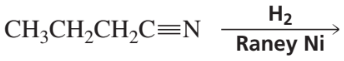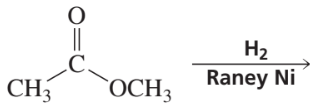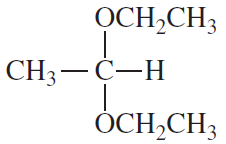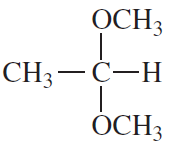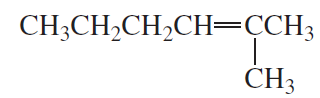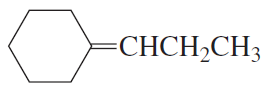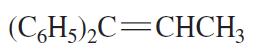Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch. 16 - Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones More Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Ch. 16 - Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones More Reactions of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesProblem 23a
How would you make the following compounds from N-benzylbenzamide?
a. dibenzylamine
Problem 23b
How would you make the following compounds from N-benzylbenzamide?
b. benzoic acid
Problem 23c
How would you make the following compounds from N-benzylbenzamide?
c. benzyl alcohol
Problem 24
What are the products of the following reactions?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Problem 27
A ketone can be prepared from the reaction of a nitrile with a Grignard reagent. Describe the intermediate formed in this reaction, and show how it can be converted to a ketone.
Problem 28
Why is the pKa value of protonated hydroxylamine (6.0) so much lower than the value of a protonated primary amine such as protonated methylamine (10.7)?
Problem 30a
The pKa of protonated acetone is about –7.5 and the pKa of protonated hydroxylamine is 6.0.
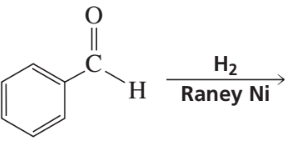
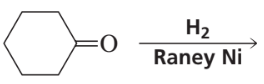
a. In a reaction with hydroxylamine at pH 4.5 (Figure 16.2), what fraction of acetone is present in its acidic, protonated form?
<IMAGE>
Problem 31
Imines can exist as stereoisomers. The isomers are named using the E,Z system of nomenclature (Section 4.2 ). The lone pair has the lowest priority.
<IMAGE>
Draw the structure of each of the following compounds:
a. the (E)-hydrazone of benzaldehyde
b. the (Z)-oxime of propiophenone
Problem 33a,b
What are the products of the following reactions? (A trace amount of acid is present in each case.)
a. cyclopentanone + ethylamine
b. cyclopentanone + diethylamine
Problem 34
Excess ammonia must be used when a primary amine is synthesized by reductive amination. What product will be obtained if the reaction is carried out with excess carbonyl compound?
Problem 35a
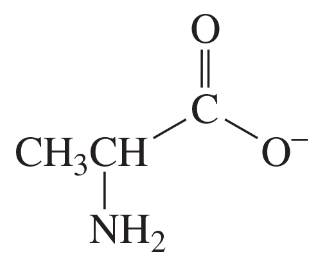
The compounds commonly known as 'amino acids' are actually α-aminocarboxylic-aminocarboxylic acids. What carbonyl compounds should be used to synthesize the two amino acids shown here?
a.
Problem 35b
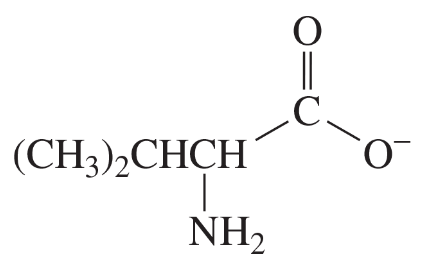
The compounds commonly known as 'amino acids' are actually α-aminocarboxylic-aminocarboxylic acids. What carbonyl compounds should be used to synthesize the two amino acids shown here?
b.
Problem 36
Hydration of an aldehyde is also catalyzed by hydroxide ion. Propose a mechanism for the reaction.
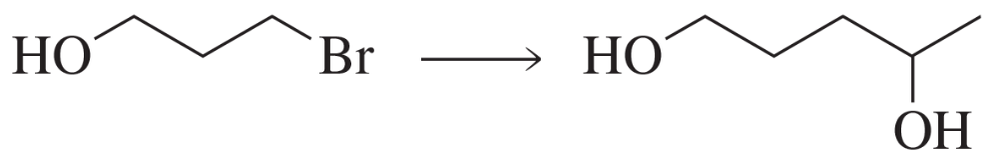
Problem 37
Which ketone forms the most hydrate in an aqueous solution?
Problem 39(1)
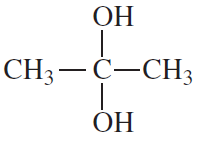
Which of the following are a. hemiacetals? b. acetals? c. hydrates?
1.
Problem 39(2)
Which of the following are a. hemiacetals? b. acetals? c. hydrates?
2.
Problem 39(3)
Which of the following are a. hemiacetals? b. acetals? c. hydrates?
3.
Problem 39(4)
Which of the following are a. hemiacetals? b. acetals? c. hydrates?
4.
Problem 40c
Can the rate of hydrate formation be increased by hydroxide ion as well as by acid? Explain.
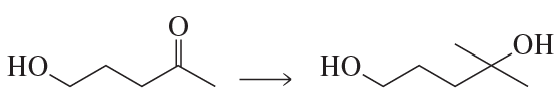
Problem 42a
What would have been the product of the preceding reaction with LiAlH4 if the keto group had not been protected?
<IMAGE>
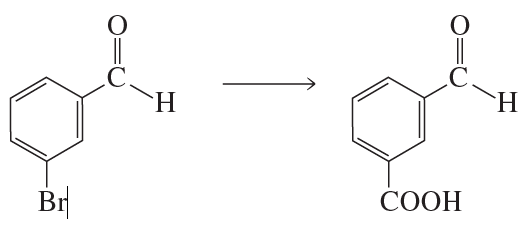
Problem 42b
What reagent could you use to reduce only the keto group?
<IMAGE>
Problem 43
Explain why acetals do not react with nucleophiles.
Problem 45b
What would the yield be if two more steps (each with an 80% yield) were added to the synthesis?
Problem 46a
Show how each of the following compounds could be prepared from the given starting material. Each requires a protecting group.
a.
Problem 46b
Show how each of the following compounds could be prepared from the given starting material. Each requires a protecting group.
b.
Problem 46c
Show how each of the following compounds could be prepared from the given starting material. Each requires a protecting group.
c.
Problem 47c,d
What is the product of each of the following reactions?
c.
d.
Problem 48c
What is the best set of reagents to use for the synthesis?
Problem 49a(1)
What two sets of reagents (each consisting of a carbonyl compound and phosphonium ylide) can be used for the synthesis of the following alkene?
1.
Problem 49c(2)
What is the best set of reagents to use for the synthesis?
2.