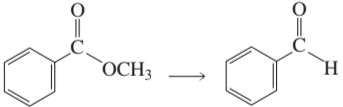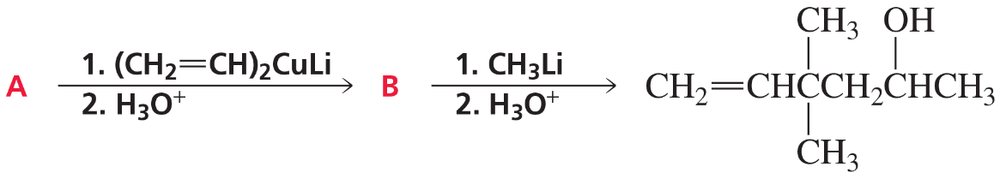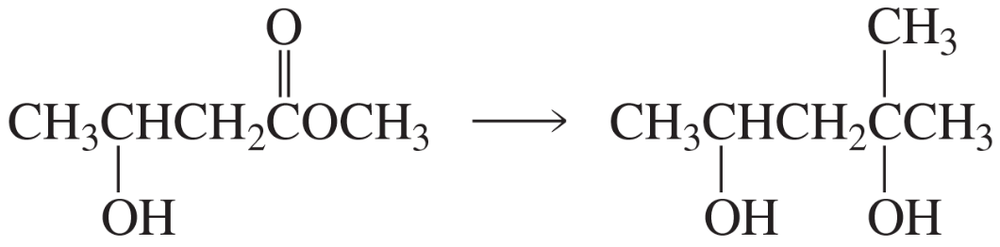Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch. 16 - Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones More Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Ch. 16 - Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones More Reactions of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesProblem 80
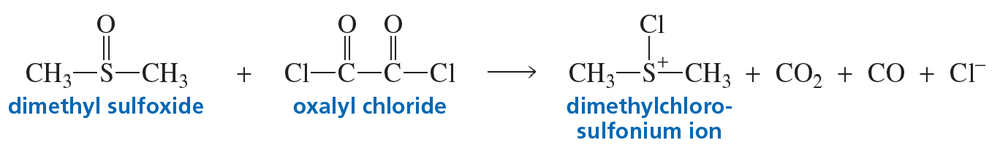
Propose a mechanism to explain how dimethyl sulfoxide and oxalyl chloride react to form the dimethylchlorosulfonium ion used as the oxidizing agent in the Swern oxidation.
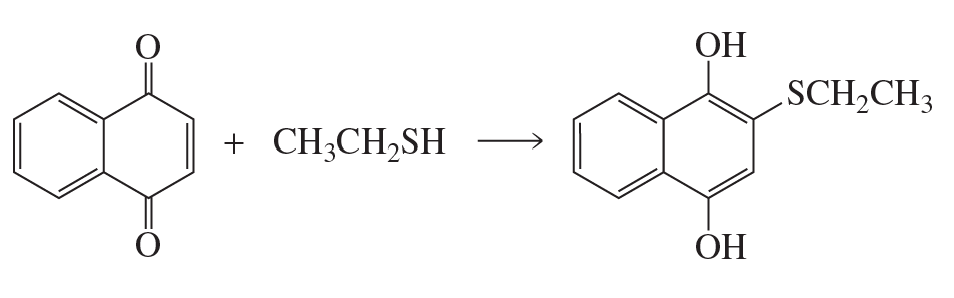
Problem 81a
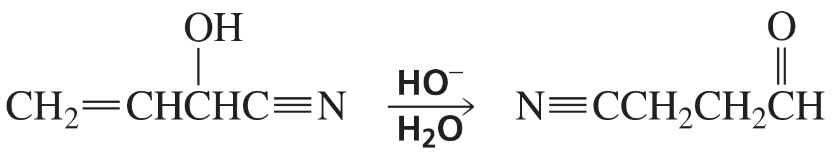
a. Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:
Problem 82
Unlike a phosphonium ylide that reacts with an aldehyde or a ketone to form an alkene, a sulfonium ylide reacts with an aldehyde or a ketone to form an epoxide. Explain why one ylide forms an alkene, whereas the other forms an epoxide.
Problem 83
A compound gives the following IR spectrum. Upon reaction with sodium borohydride followed by acidification, it forms the product with the 1H NMR spectrum shown below. Identify the starting material and the product.
<IMAGE>
Problem 84a
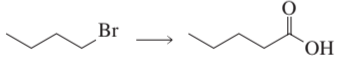
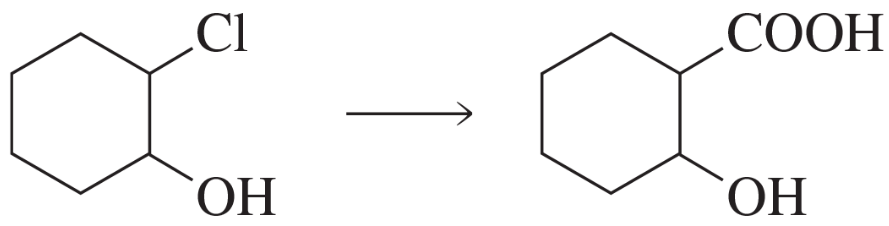
How can the following compounds be prepared from the given starting materials?
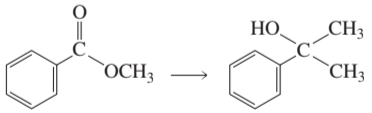
a.
Problem 84b
How can the following compounds be prepared from the given starting materials?
b.
Problem 84c
How can the following compounds be prepared from the given starting materials?
c.
Problem 84d
How can the following compounds be prepared from the given starting materials?
d.
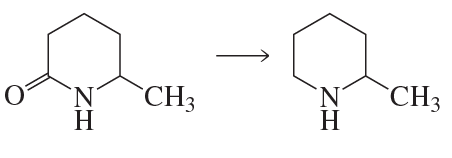
Problem 85a
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
a.
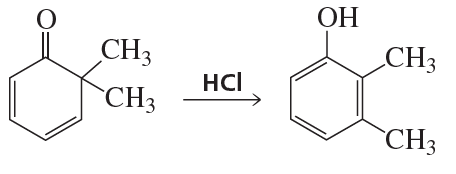
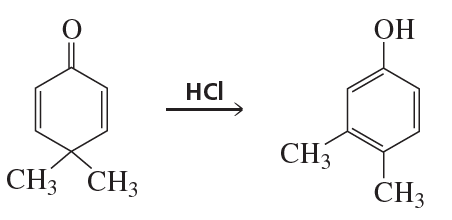
Problem 85b
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
b.
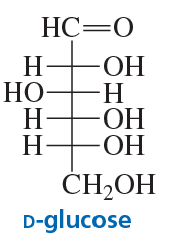
Problem 86a
In an aqueous solution, D-glucose exists in equilibrium with two six-membered ring compounds. Draw the structures of these compounds.
Problem 87
Shown below is the 1H NMR spectrum of the alkyl bromide used to make the phosphonium ylide that reacts with a ketone in a Wittig reaction to form a compound with molecular formula C11H14. What product is obtained from the Wittig reaction?
<IMAGE>
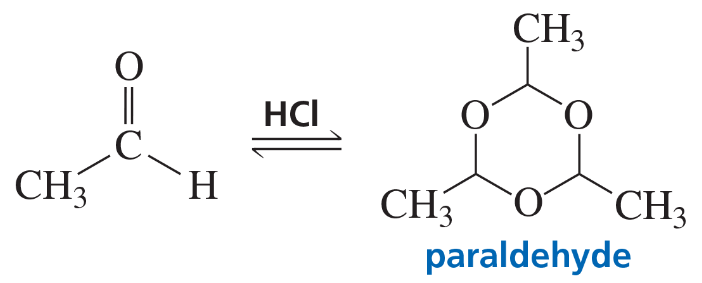
Problem 88
In the presence of an acid catalyst, acetaldehyde forms a trimer known as paraldehyde. Because it induces sleep when it is administered to animals in large doses, paraldehyde is used as a sedative or hypnotic. Propose a mechanism for the formation of paraldehyde.
Problem 89b
What carbonyl compound and what phosphonium ylide are needed to synthesize the following compounds?
b.
Problem 90
Identify compounds A and B:
Problem 91
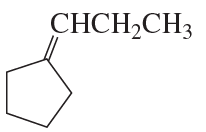
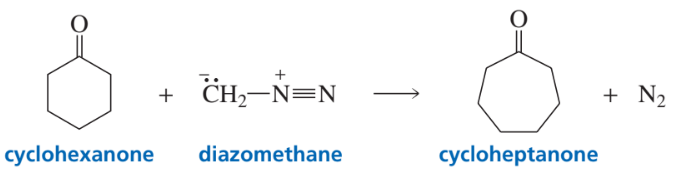
When a cyclic ketone reacts with diazomethane, the next larger cyclic ketone is formed. This is called a ring-expansion reaction. Draw a mechanism for the following ring-expansion reaction.
Problem 93a,b
Show how each of the following compounds can be prepared from the given starting material. In each case, you will need to use a protecting group.
a.
b.
Problem 95b
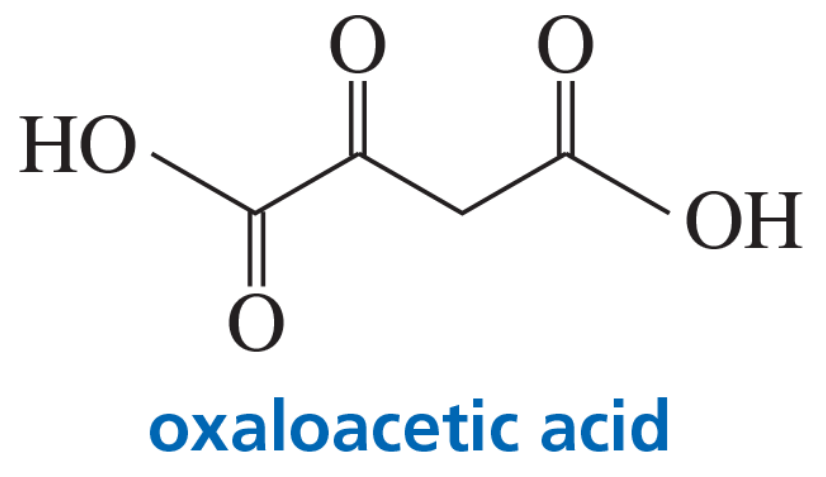
The pKa values of the carboxylic acid groups of oxaloacetic acid are 2.22 and 3.98.
b. The amount of hydrate present in an aqueous solution of oxaloacetic acid depends on the pH of the solution: 95% at pH 0, 81% at pH 1.3, 35% at pH 3.1, 13% at pH 4.7, 6% at pH 6.7, and 6% at pH 12.7. Explain this pH dependence.
Problem 96
The Baylis-Hillman reaction is a DABCO (1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane) catalyzed reaction of an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound with an aldehyde to form an allylic alcohol. Propose a mechanism for the reaction. (Hint: DABCO serves as both a nucleophile and as a base in the reaction.)
Problem 97b
To solve this problem, you need to read the description of the Hammett , treatment given in [Chapter 15, Problem 92]. When the rate constants for the hydrolysis of several morpholine enamines of para-substituted propiophenones are determined at pH 4.7, the value is positive; however, when the rates of hydrolysis are determined at pH 10.4, the value is negative.
b. What is the rate-determining step of the hydrolysis reaction when it is carried out in an acidic solution?
<IMAGE>
Problem 98b
Propose a mechanism for each of the following reactions:
b.