Are Nuclear Plants Safe? Using the survey results from Exercise 2 and ignoring those respondents with no opinion, is the following graph somehow misleading? If so, how?
Table of contents
- 1. Intro to Stats and Collecting Data1h 14m
- 2. Describing Data with Tables and Graphs1h 56m
- 3. Describing Data Numerically2h 5m
- 4. Probability2h 16m
- 5. Binomial Distribution & Discrete Random Variables3h 6m
- 6. Normal Distribution and Continuous Random Variables2h 11m
- 7. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Mean3h 23m
- Sampling Distribution of the Sample Mean and Central Limit Theorem19m
- Distribution of Sample Mean - Excel23m
- Introduction to Confidence Intervals15m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Mean1h 18m
- Determining the Minimum Sample Size Required12m
- Finding Probabilities and T Critical Values - Excel28m
- Confidence Intervals for Population Means - Excel25m
- 8. Sampling Distributions & Confidence Intervals: Proportion2h 10m
- 9. Hypothesis Testing for One Sample5h 8m
- Steps in Hypothesis Testing1h 6m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Means1h 4m
- Hypothesis Testing: Means - Excel42m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Proportions37m
- Hypothesis Testing: Proportions - Excel27m
- Performing Hypothesis Tests: Variance12m
- Critical Values and Rejection Regions28m
- Link Between Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Testing12m
- Type I & Type II Errors16m
- 10. Hypothesis Testing for Two Samples5h 37m
- Two Proportions1h 13m
- Two Proportions Hypothesis Test - Excel28m
- Two Means - Unknown, Unequal Variance1h 3m
- Two Means - Unknown Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variance15m
- Two Means - Unknown, Equal Variances Hypothesis Test - Excel9m
- Two Means - Known Variance12m
- Two Means - Sigma Known Hypothesis Test - Excel21m
- Two Means - Matched Pairs (Dependent Samples)42m
- Matched Pairs Hypothesis Test - Excel12m
- Two Variances and F Distribution29m
- Two Variances - Graphing Calculator16m
- 11. Correlation1h 24m
- 12. Regression3h 33m
- Linear Regression & Least Squares Method26m
- Residuals12m
- Coefficient of Determination12m
- Regression Line Equation and Coefficient of Determination - Excel8m
- Finding Residuals and Creating Residual Plots - Excel11m
- Inferences for Slope31m
- Enabling Data Analysis Toolpak1m
- Regression Readout of the Data Analysis Toolpak - Excel21m
- Prediction Intervals13m
- Prediction Intervals - Excel19m
- Multiple Regression - Excel29m
- Quadratic Regression15m
- Quadratic Regression - Excel10m
- 13. Chi-Square Tests & Goodness of Fit2h 21m
- 14. ANOVA2h 28m
2. Describing Data with Tables and Graphs
Visualizing Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data
Problem 2.3.3
Textbook Question
Ethics There are data showing that smoking is detrimental to good health. Given that people could be helped and lives could be saved by reducing smoking, is it ethical to graph the data in a way that is misleading by exaggerating the health risks of smoking?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the ethical implications of presenting data: In statistics, it is crucial to present data accurately and without bias. Misleading graphs can distort the interpretation of data, which may lead to unethical outcomes, even if the intention is to promote a positive cause.
Consider the principles of ethical data representation: Ethical data representation involves honesty, transparency, and clarity. Misleading graphs, such as those with manipulated scales or omitted context, violate these principles and can undermine trust in statistical findings.
Evaluate the potential consequences of exaggerating risks: While the goal of reducing smoking is beneficial, exaggerating health risks through misleading graphs could lead to public mistrust in health campaigns or statistical data in general, potentially harming future efforts to promote public health.
Explore alternative approaches: Instead of exaggerating risks, focus on presenting the data accurately and effectively. Use clear and well-designed graphs that highlight the true health risks of smoking without distortion, ensuring the message is both impactful and ethical.
Reflect on professional responsibility: As statisticians or data communicators, it is our responsibility to uphold ethical standards in data presentation. Misleading graphs, even with good intentions, compromise the integrity of the field and the trust of the audience.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ethical Considerations in Data Presentation
Ethical considerations in data presentation involve the responsibility of researchers and communicators to present data honestly and transparently. Misleading representations can distort public understanding and lead to harmful consequences. In the context of health data, exaggerating risks may induce unnecessary fear or anxiety, while downplaying risks can lead to complacency.
Recommended video:
Guided course
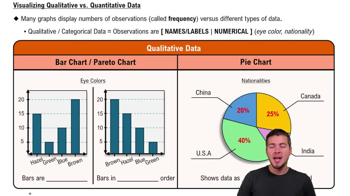
Visualizing Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data
Statistical Misrepresentation
Statistical misrepresentation occurs when data is presented in a way that misleads the audience about the true nature of the information. This can include using inappropriate scales, cherry-picking data, or employing misleading visuals. Understanding how to accurately represent data is crucial for ensuring that the audience receives a truthful interpretation of the findings.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Parameters vs. Statistics
Public Health Implications
Public health implications refer to the potential effects that data presentation can have on community health behaviors and policies. Accurate data can inform effective interventions and promote healthier choices, while misleading data can hinder public health efforts. It is essential to balance the urgency of health messages with ethical data representation to foster informed decision-making.
Recommended video:
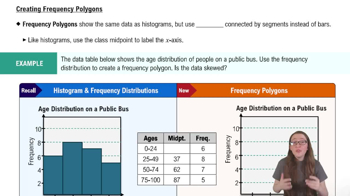
Creating Frequency Polygons

 4:39m
4:39mWatch next
Master Visualizing Qualitative vs. Quantitative Data with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
