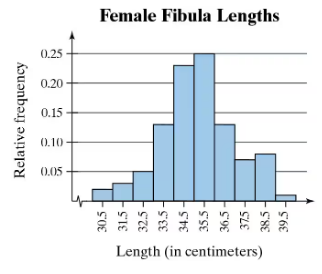
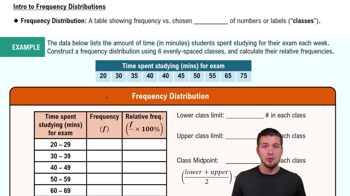
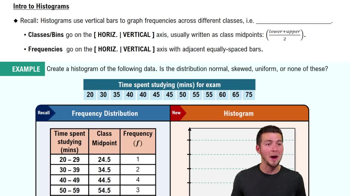
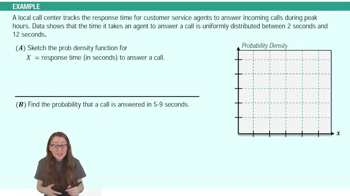
Song Lengths Side-by-side box-and-whisker plots can be used to compare two or more different data sets. Each box-and-whisker plot is drawn on the same number line to compare the data sets more easily. The lengths (in seconds) of songs played at two different concerts are shown.
d. Can you determine which concert lasted longer? Explain.