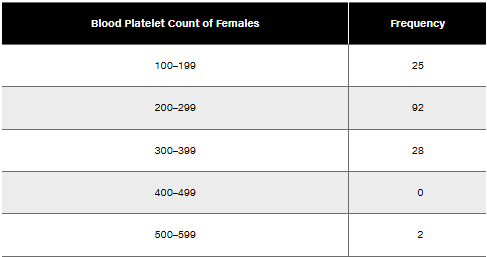
A data set has a minimum value of 16 and a maximum value of 71. Without constructing a table, find the class width if you organized this data into 7 classes. Write the lower and upper class limits.
min = 16; max = 71; 7 classes.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 6:38m
6:38mMaster Intro to Frequency Distributions with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning