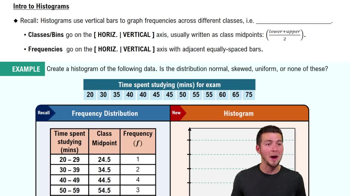
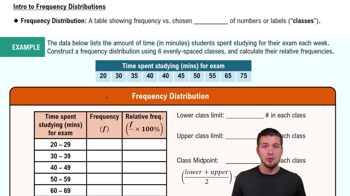
In Exercises 5–8, answer the questions by referring to the following Minitab-generated histogram, which depicts the weights (grams) of all quarters listed in Data Set 40 “Coin Weights” in Appendix B. (Grams are actually units of mass and the values shown on the horizontal scale are rounded.)
Sample Size What is the approximate number of quarters depicted in the three bars farthest to the left?