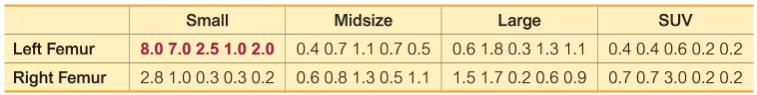
Transformations of Data Example 1 illustrated the use of two-way ANOVA to analyze the sample data in Table 12-3. How are the results affected in each of the following cases?
b. Each sample value is multiplied by the same nonzero constant.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:


 6:21m
6:21mMaster Step 1: Write Hypotheses with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning