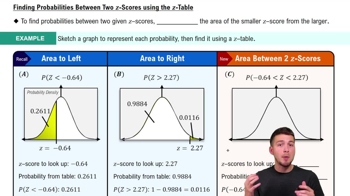
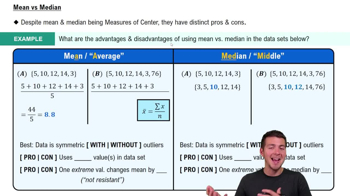
In Exercises 5–16, use analysis of variance for the indicated test.
Triathlon Times Jeff Parent is a statistics instructor who participates in triathlons. Listed below are times (in minutes and seconds) he recorded while riding a bicycle for five stages through each mile of a 3-mile loop. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that it takes the same time to ride each of the miles. Does one of the miles appear to have a hill?