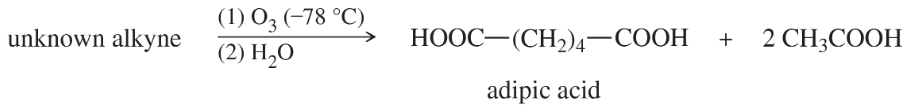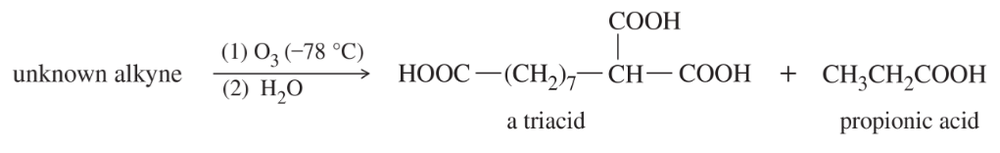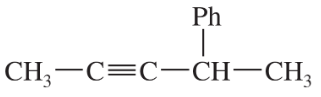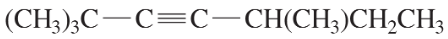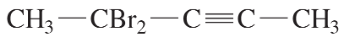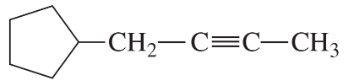Back
BackProblem 20b
The hydroboration–oxidation of internal alkynes produces ketones.
b. When hydroboration–oxidation is applied to pent-2-yne, two products are obtained. Show why a mixture of products should be expected with any unsymmetrical internal alkyne.
Problem 21a
For each compound, give the product(s) expected from (1) HgSO4/H2SO4 - catalyzed hydration and (2) hydroboration–oxidation.
a. hex-1-yne
Problem 21b
For each compound, give the product(s) expected from (1) HgSO4/H2SO4 - catalyzed hydration and (2) hydroboration–oxidation.
b. hex-2-yne
Problem 21c
For each compound, give the product(s) expected from (1) HgSO4/H2SO4 - catalyzed hydration and (2) hydroboration–oxidation.
c. hex-3-yne
Problem 21d
For each compound, give the product(s) expected from (1) HgSO4/H2SO4 - catalyzed hydration and (2) hydroboration–oxidation.
d. cyclodecyne
Problem 22
Disiamylborane adds only once to alkynes by virtue of its two bulky secondary isoamyl groups. Disiamylborane is prepared by the reaction of BH3·THF with an alkene.
a. Draw the structural formulas of the reagents and the products in the preparation of disiamylborane.
b. Explain why the reaction in part (a) goes only as far as the dialkylborane. Why is Sia3B not formed?
Problem 23a
Predict the product(s) you would expect from treatment of each compound with (1) dilute, neutral KMnO4 and (2) warm basic KMnO4, then dilute acid.
(a) hex-1-yne
Problem 23b
Predict the product(s) you would expect from treatment of each compound with (1) dilute, neutral KMnO4 and (2) warm basic KMnO4, then dilute acid.
(b) hex-2-yne
Problem 23c
Predict the product(s) you would expect from treatment of each compound with (1) dilute, neutral KMnO4 and (2) warm basic KMnO4, then dilute acid.
(c) hex-3-yne
Problem 23d
Predict the product(s) you would expect from treatment of each compound with (1) dilute, neutral KMnO4 and (2) warm basic KMnO4, then dilute acid.
(d) 2-methylhex-3-yne
Problem 23e
Predict the product(s) you would expect from treatment of each compound with (1) dilute, neutral KMnO4 and (2) warm basic KMnO4, then dilute acid.
(e) cyclodecyne
Problem 24a
Oxidative cleavages can help to determine the positions of the triple bonds in alkynes.
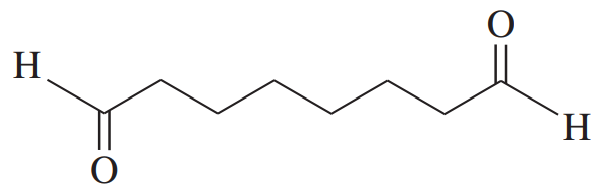
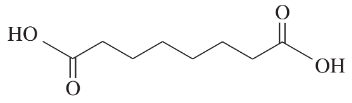
(a) An unknown alkyne undergoes oxidative cleavage to give adipic acid and two equivalents of acetic acid. Propose a structure for the alkyne.
Problem 24b
Oxidative cleavages can help to determine the positions of the triple bonds in alkynes.
(b) An unknown alkyne undergoes oxidative cleavage to give the following triacid plus one equivalent of propionic acid. Propose a structure for the alkyne.
Problem 25a
Develop syntheses for the following compounds, using acetylene and compounds containing no more than four carbon atoms as your organic starting materials.
(a) 3-methylnon-4-yn-3-ol (“3-ol” means there is an OH group on C3.)
Problem 25b
Develop syntheses for the following compounds, using acetylene and compounds containing no more than four carbon atoms as your organic starting materials.
(b) cis-1-ethyl-2-methylcyclopropane
Problem 26a,b,c
Write structural formulas for the following compounds (includes both old- and new-style names).
(a) 2-octyne
(b) ethylisopentylacetylene
(c) ethynylbenzene
Problem 26d,e,f
Write structural formulas for the following compounds (includes both old- and new-style names).
(d) cyclohexylacetylene
(e) 5-methyl-3-octyne
(f) trans-3,5-dibromocyclodecyne
Problem 26g,h,i
Write structural formulas for the following compounds (includes both old- and new-style names).
g. 5,5-dibromo-4-phenylcyclooct-1-yne
h. (E)-6-ethyloct-2-en-4-yne
i.1,4-heptadiyne
Problem 26j,k
Write structural formulas for the following compounds (includes both old- and new-style names).
(j) vinylacetylene
(k) (S)-3-methyl-1-penten-4-yne
Problem 27a,b
Give common names for the following compounds.
(a) CH3–C≡C–CH2CH3
(b) Ph–C≡C–H
Problem 27c,d
Give common names for the following compounds.
(c) 3-methyloct-4-yne
(d) (CH3)3C–C≡C–CH(CH3)CH2CH3
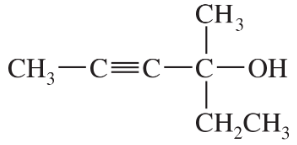
Problem 28a,b,c
Give IUPAC names for the following compounds.
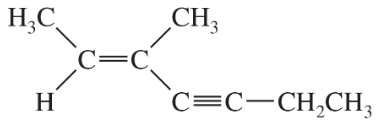
(a)
(b)
(c)
Problem 28d,e,f
Give IUPAC names for the following compounds.
(d)
(e)
(f)
Problem 29a,b,c
Using hex-1-ene as your starting material, show how you would synthesize the following compounds. (Once you have shown how to synthesize a compound, you may use it as the starting material in any later parts of this problem.)
a. 1,2-dibromohexane
b. hex-1-yne
c. 2,2-dibromohexane
Problem 29d,e,f
Using hex-1-ene as your starting material, show how you would synthesize the following compounds. (Once you have shown how to synthesize a compound, you may use it as the starting material in any later parts of this problem.)
d. hex-2-yne
e. hexan-2-one
f. hexanal
Problem 29g,h,i
Using hex-1-ene as your starting material, show how you would synthesize the following compounds. (Once you have shown how to synthesize a compound, you may use it as the starting material in any later parts of this problem.)
g. pentanoic acid
h. pentanal
i. undec-6-yn-5-ol
Problem 30a,b,c
Using cyclooctyne as your starting material, show how you would synthesize the following compounds. (Once you have shown how to synthesize a compound, you may use it as the starting material in any later parts of this problem.)
(a) cis-cyclooctene
(b) cyclooctane
(c) trans-1,2-dibromocyclooctane
Problem 30g
Using cyclooctyne as your starting material, show how you would synthesize the following compounds. (Once you have shown how to synthesize a compound, you may use it as the starting material in any later parts of this problem.)
(g) cyclooctane-1,2-dione
Problem 30h
Using cyclooctyne as your starting material, show how you would synthesize the following compounds. (Once you have shown how to synthesize a compound, you may use it as the starting material in any later parts of this problem.)
(h)
Problem 30i
Using cyclooctyne as your starting material, show how you would synthesize the following compounds. (Once you have shown how to synthesize a compound, you may use it as the starting material in any later parts of this problem.)
(i)