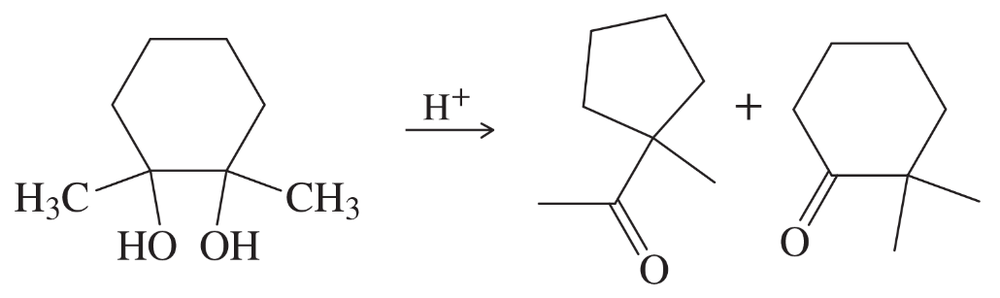
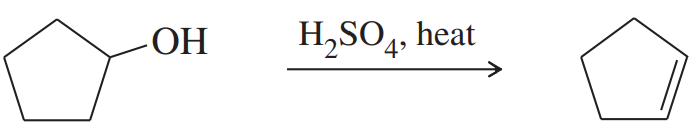Back
BackProblem 5a,b,c
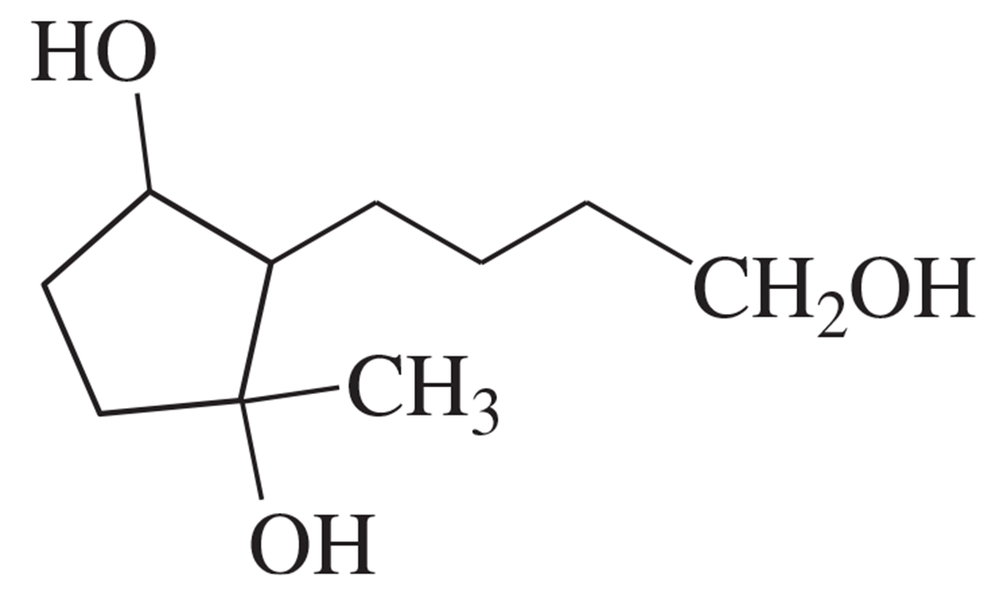
Predict the products you expect when the following starting material undergoes oxidation with an excess of each of the reagents shown below.
a. chromic acid
b. PCC (pyridinium chlorochromate)
c. sodium hypochlorite/acetic acid
Problem 5d,e
Predict the products you expect when the following starting material undergoes oxidation with an excess of each of the reagents shown below.
d. DMSO and oxalyl chloride
e. DMP (periodinane) reagent
Problem 6a,b,c
Suggest the most appropriate method for each of the following laboratory syntheses. In each case, suggest both a chromium reagent and a chromium-free reagent.
(a) butan-1-ol → butanal, CH3CH2CH2CHO
(b) but-2-en-1-ol → but-2-enoic acid, CH3CH=CH–COOH
(c) butan-2-ol → butan-2-one, CH3COCH2CH3
Problem 6d,e
Suggest the most appropriate method for each of the following laboratory syntheses. In each case, suggest both a chromium reagent and a chromium-free reagent.
(d) cyclopentanol → 1-ethylcyclopentanol (two steps)
(e) cyclopentylmethanol → 1-cyclopentylpropan-1-ol (two steps)
Problem 6f
Suggest the most appropriate method for each of the following laboratory syntheses. In each case, suggest both a chromium reagent and a chromium-free reagent.
(f) 1-methylcyclohexanol → 2-methylcyclohexanone (several steps)
Problem 7
A chronic alcoholic requires a much larger dose of ethanol as an antidote to methanol poisoning than does a nonalcoholic patient. Suggest a reason why a larger dose of the competitive inhibitor is required for an alcoholic.
Problem 9a,b,c
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(a) ethyl tosylate + potassium tert-butoxide
(b) isobutyl tosylate + NaI
(c) (R)-2-hexyl tosylate + NaCN
Problem 9d,e
Predict the major products of the following reactions.
(d) the tosylate of cyclohexylmethanol + excess NH3
(e) n-butyl tosylate + sodium acetylide, H–C≡C:– +Na
Problem 10a,b
Show how you would convert propan-1-ol to the following compounds using tosylate intermediates. You may use whatever additional reagents are needed.
a. 1-bromopropane
b. propan-1-amine, CH3CH2CH2NH2
Problem 10c,d
Show how you would convert propan-1-ol to the following compounds using tosylate intermediates. You may use whatever additional reagents are needed.
c. CH3CH2CH2OCH2CH3, ethyl proyl ether
d. CH3CH2CH2CN, butyronitrile
Problem 11a,b
Predict the products of the following reactions.
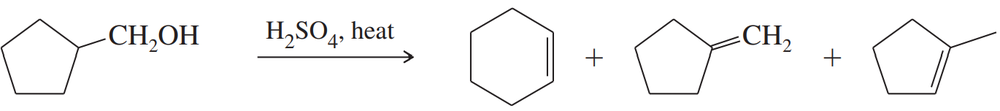
(a) cyclohexylmethanol + TsCl/pyridine
(b) product of (a) + LiAlH4
Problem 11c,d
Predict the products of the following reactions.
(c) 1-methylcyclohexanol + H2SO4, heat
(d) product of (c) + H2, Pt
Problem 12a
Propose a mechanism for the reaction of
(a) 1-methylcyclohexanol with HBr to form 1-bromo-1-methylcyclohexane.
Problem 13
The reaction of tert-butyl alcohol with concentrated HCl goes by the SN1 mechanism. Write a mechanism for this reaction.
Problem 14d,e
Show how you would use a simple chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds. Tell what you would observe with each compound.
(d) allyl alcohol and propan-1-ol
(e) butan-2-one and tert-butyl alcohol
Problem 15
Neopentyl alcohol, (CH3)3CCH2OH, reacts with concentrated HBr to give 2-bromo-2-methylbutane, a rearranged product. Propose a mechanism for the formation of this product.
Problem 16
Explain the products observed in the following reaction of an alcohol with the Lucas reagent.
Problem 17
When cis-2-methylcyclohexanol reacts with the Lucas reagent, the major product is 1-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane. Propose a mechanism to explain the formation of this product.
Problem 18
Write balanced equations for the three preceding reactions.
Problem 19
Suggest how you would convert trans-4-methylcyclohexanol to
a. trans-1-chloro-4-methylcyclohexane.
b. cis-1-chloro-4-methylcyclohexane.
Problem 20a,b
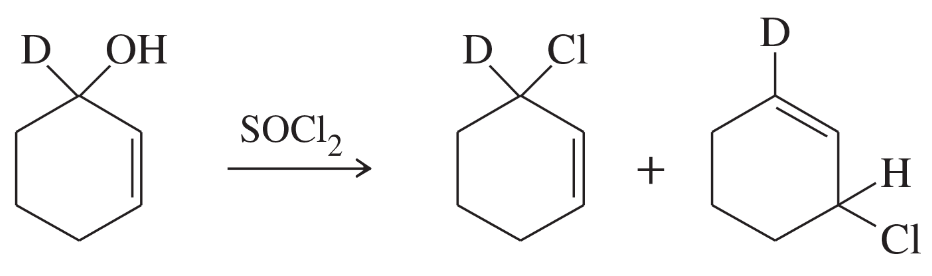
Two products are observed in the following reaction.
a. Suggest a mechanism to explain how these two products are formed.
b. Your mechanism for part (a) should be different from the usual mechanism of the reaction of SOCl2 with alcohols. Explain why the reaction follows a different mechanism in this case.
Problem 21a,b
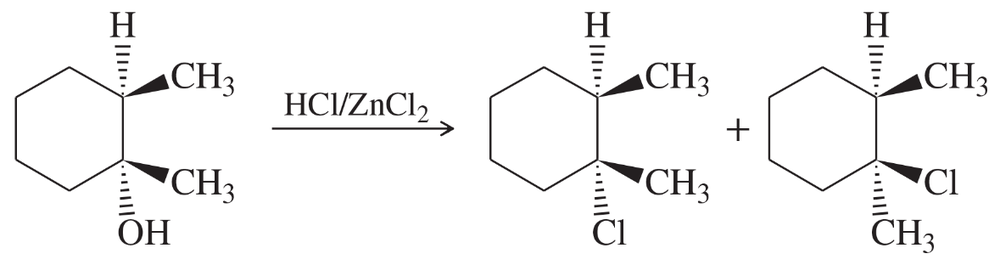
Give the structures of the products you would expect when each alcohol reacts with (1) HCl, ZnCl2; (2) HBr; (3) PBr3; (4) P/I2; and (5) SOCl2.
(a) butan-1-ol
(b) 2-methylbutan-2-ol
Problem 22d,e
Predict the products of the sulfuric acid-catalyzed dehydration of the following alcohols. When more than one product is expected, label the major and minor products.
(d) 1-isopropylcyclohexanol
(e) 2-methylcyclohexanol
Problem 23
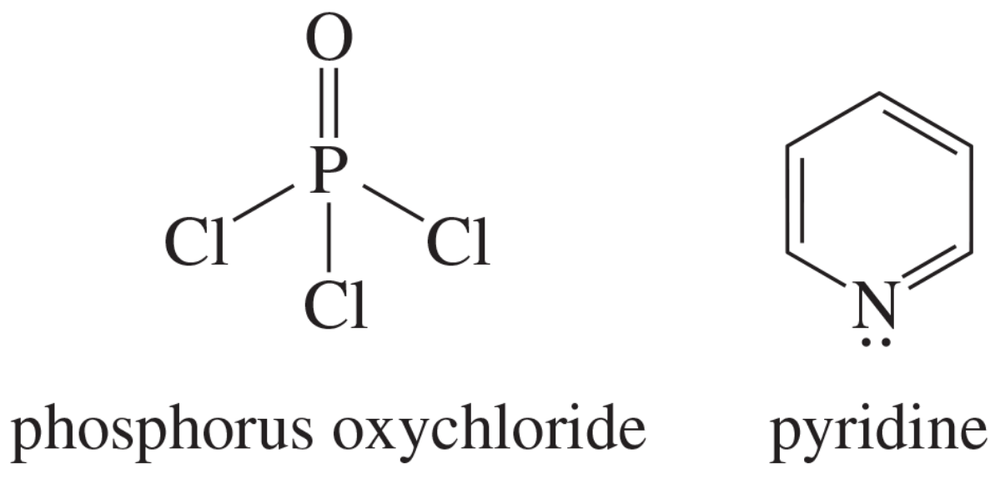
Some alcohols undergo rearrangement or other unwanted side reactions when they dehydrate in acid. Alcohols may be dehydrated under mildly basic conditions using phosphorus oxy-chloride (POCl3) in pyridine. The alcohol reacts with phosphorus oxychloride much like it reacts with tosyl chloride (Section 11-5), displacing a chloride ion from phosphorus to give an alkyl dichlorophosphate ester. The dichlorophosphate group is an outstanding leaving group. Pyridine reacts as a base with the dichlorophosphate ester to give an E2 elimination. Propose a mechanism for the dehydration of cyclohexanol by POCl3 in pyridine.
Problem 24a
Contrast the mechanisms of the two preceding reactions, the dehydration and condensation of ethanol.
Problem 25
Explain why the acid-catalyzed condensation is a poor method for the synthesis of an unsymmetrical ether such as ethyl methyl ether, CH3CH2-O-CH3.
Problem 26a
Propose a mechanism for each reaction.
(a)
Problem 26c
Propose a mechanism for each reaction.
(c)
Problem 27
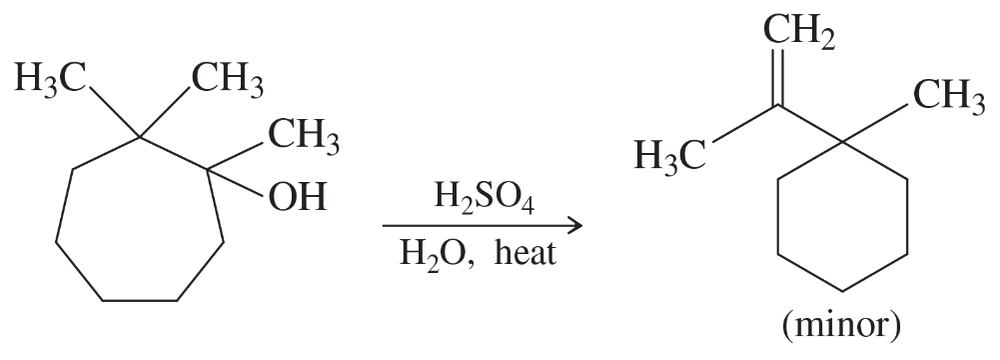
When the following substituted cycloheptanol undergoes dehydration, one of the minor products has undergone a ring contraction. Propose a mechanism to show how this ring contraction occurs.
Problem 28
Propose a mechanism for each reaction.
(a)
(b)