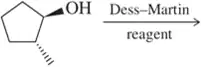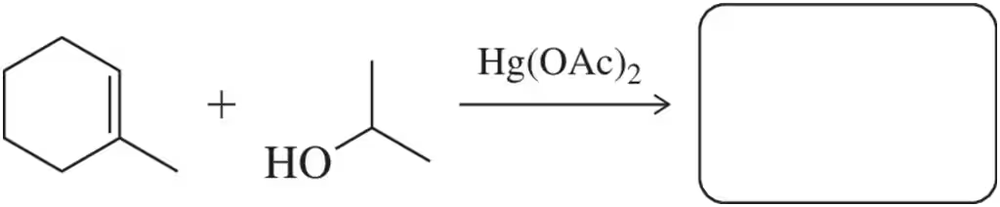Back
Back Mullins 1st Edition
Mullins 1st Edition Ch. 13 - Alcohols, Ethers and Related Compounds: Substitution and Elimination
Ch. 13 - Alcohols, Ethers and Related Compounds: Substitution and EliminationProblem 56
If there is no water present, the hydrate of an aldehyde cannot form. Could an aldehyde itself (not the hydrate) be oxidized to a carboxylic acid? Why?
Problem 57a
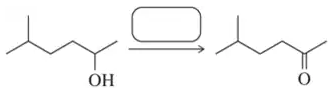
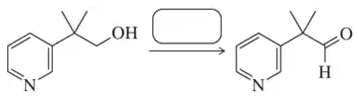
Fill in the missing reactant, reagent, or product for each of the following oxidation reactions.
(a)
Problem 57b
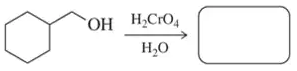
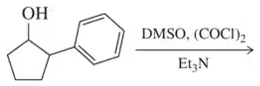
Fill in the missing reactant, reagent, or product for each of the following oxidation reactions.
(b)
Problem 57c
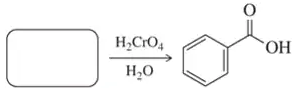
Fill in the missing reactant, reagent, or product for each of the following oxidation reactions.
(c)
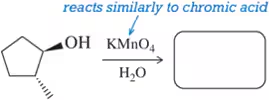
Problem 57d
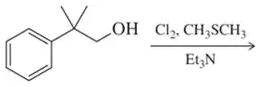
Fill in the missing reactant, reagent, or product for each of the following oxidation reactions. react similarly to chromic acid
(d)
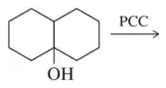
Problem 57f
Fill in the missing reactant, reagent, or product for each of the following oxidation reactions.
(f)
Problem 58
In Hinkley, the cleanup continues today. In one process PG&E is using to mitigate the chromium(VI) toxicity, ethanol is injected into the soil. How would this reduce the chromium(VI) contamination?
Problem 59a
Predict the product of the following oxidation reactions.
(a)
Problem 59b
Predict the product of the following oxidation reactions.
(b)
Problem 59c
Predict the product of the following oxidation reactions.
(c)
Problem 59d
Predict the product of the following oxidation reactions.
(d)
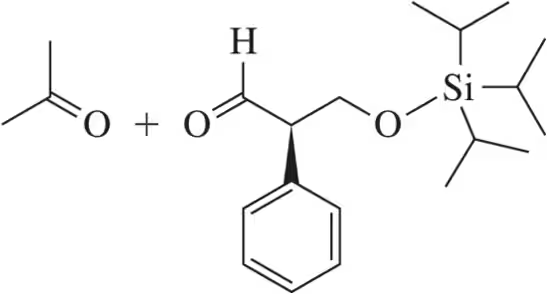
Problem 60
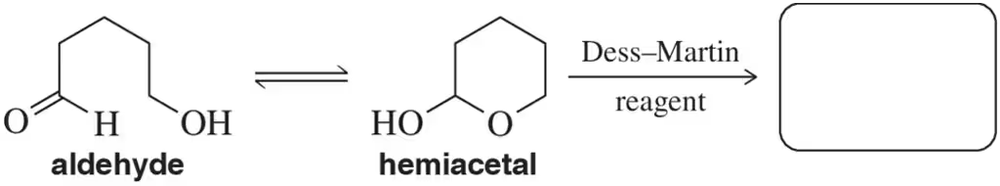
δ-Hydroxyaldehydes are in equilibrium with their hemiacetal form. Predict the product that would form upon treatment of the hemiacetal with Dess–Martin periodinane.
Problem 61a
Predict the product of the following reactions.
(a)
Problem 61b
Predict the product of the following reactions.
(b)
Problem 62
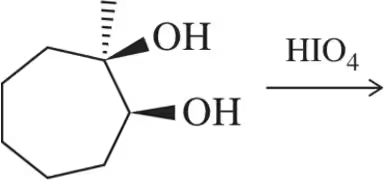
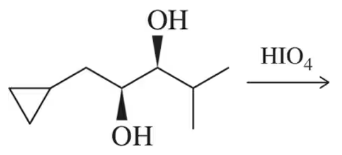
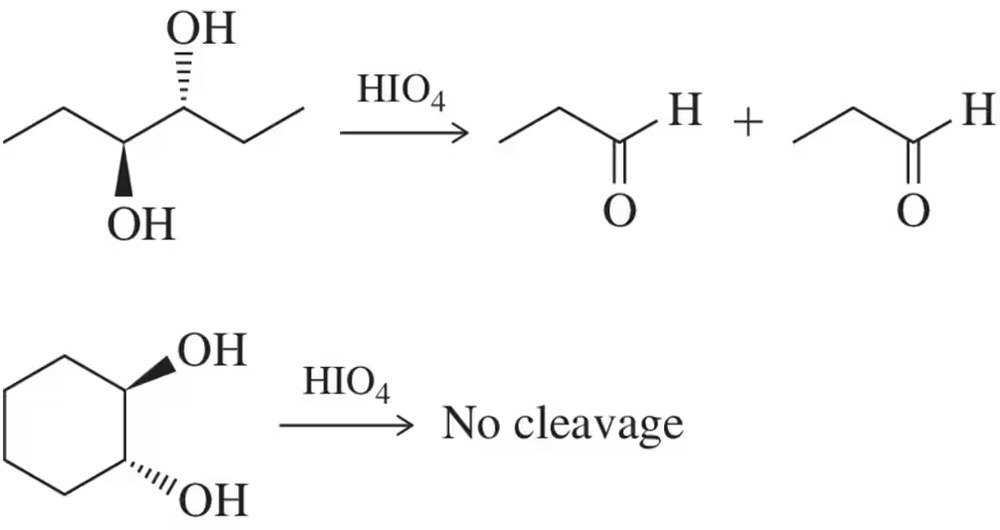
Although trans-diols in rings cannot be cleaved using HIO₄ acyclic trans-diols can. Explain this discrepancy.
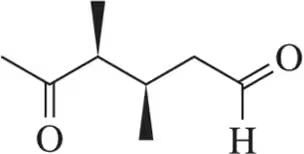
Problem 63a(i)
Propose a synthesis of the carbonyl(s) using the (i) ozonolysis pathways.
(a)
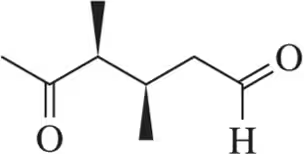
Problem 63a(ii)
Propose a synthesis of the carbonyl(s) using the (ii) dihydroxylation/periodic acid cleavage pathways.
(a)
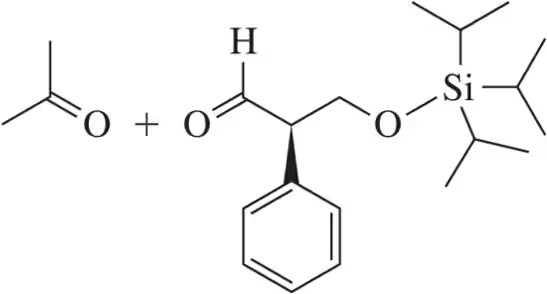
Problem 63b(i)
Propose a synthesis of the carbonyl(s) using the (i) ozonolysis pathways.
(b)
Problem 63b(ii)
Propose a synthesis of the carbonyl(s) using the (ii) dihydroxylation/periodic acid cleavage pathways.
(b)
Problem 64
Unfortunately, the use of NMO creates an additional green chemistry problem. What is the problem and how might it be solved?
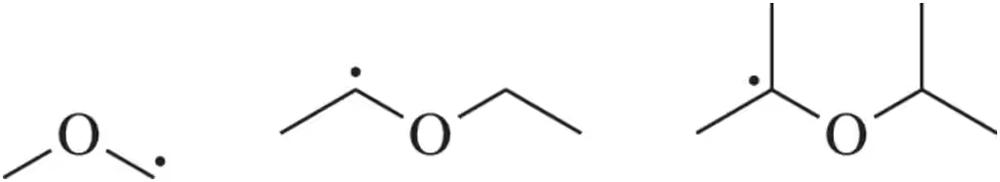
Problem 65
Ethers can be converted into radicals, some more easily than others. Which of the following radicals is more stable, and thus, more likely to form?
Problem 66a
Predict the product of the following reactions. [Two of them are Williamson ether syntheses. Why isn't the other?].
(a)
Problem 66b
Predict the product of the following reactions. [Two of them are Williamson ether syntheses. Why isn't the other?].
(b)
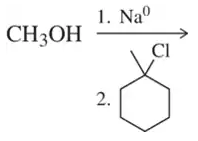
Problem 66c
Predict the product of the following reactions. [Two of them are Williamson ether syntheses. Why isn't the other?].
(c)
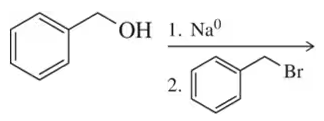
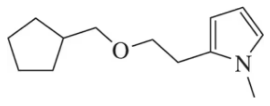
Problem 67a
Two different Williamson ether syntheses can be used to make the compound in (a). Show them. The compound in (b), however, can only be made one way. Show it and explain why a second Williamson ether synthesis is not possible.
(a)
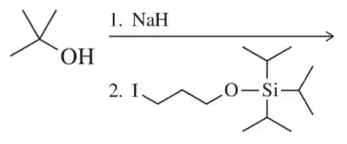
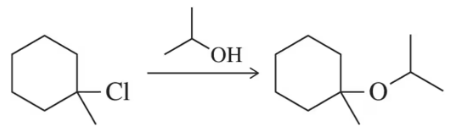
Problem 68
Why is the SN1 reaction shown an inefficient way of synthesizing ethers?
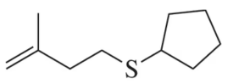
Problem 69
Starting with hydrogen sulfide, suggest a synthesis of the following thioether that makes use of two different haloalkanes.
Problem 70
How could the reaction in Figure 13.67(b) be modified to produce the following ether?
Problem 71
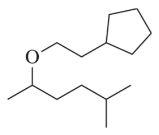
Predict the product and show an arrow-pushing mechanism for the first step of the alkoxymercuration reaction.
Problem 72
Draw a reaction coordinate diagram for the acid-catalyzed addition of an alcohol to an alkene. Which step is rate-determining?