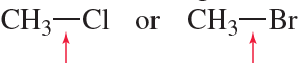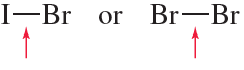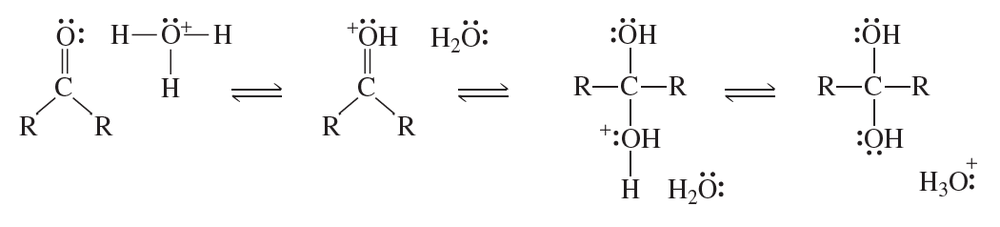Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch.5 - Alkenes:Structure, Nomenclature, and an Introduction to Reactivity Thermodynamics and Kinetics
Ch.5 - Alkenes:Structure, Nomenclature, and an Introduction to Reactivity Thermodynamics and KineticsProblem 47
a. Which is the most stable: 3,4-dimethyl-2-hexene, 2,3-dimethyl-2-hexene, or 4,5-dimethyl-2-hexene?
b. Which compound has the largest heat of hydrogenation?
c. Which compound has the smallest heat of hydrogenation?
Problem 49
Draw the skeletal structure of 3,3-dimethyl-7-(1-methylethyl)-6-(1-methylpropyl)decane.
Problem 50a,b
In a reaction in which reactant A is in equilibrium with product B at 25 °C, what relative amounts of A and B are present at equilibrium if ∆G° at 25 °C is
a. 2.72 kcal/mol?
b. 0.65 kcal/mol?
Problem 50c,d
In a reaction in which reactant A is in equilibrium with product B at 25 °C, what relative amounts of A and B are present at equilibrium if ∆G° at 25 °C is
c. -2.72 kcal/mol?
d. -0.65 kcal/mol?
Problem 51a
Which bond is stronger? Briefly explain why.
a.
Problem 51b
Which bond is stronger? Briefly explain why.
b.
Problem 53a
For each of the following compounds, draw the possible geometric isomers and name each isomer:
a. 2-methyl-2,4-hexadiene
Problem 53b
For each of the following compounds, draw the possible geometric isomers and name each isomer:
b. 1,5-heptadiene
Problem 53c
For each of the following compounds, draw the possible geometric isomers and name each isomer:
c. 1,4-pentadiene
Problem 53d
For each of the following compounds, draw the possible geometric isomers and name each isomer:
d. 3-methyl-2,4-hexadiene
Problem 55a,b,c
How many of the following names are correct? Correct the incorrect names.
a. 3-pentene
b. 2-octene
c. 2-vinylpentane
Problem 55d,e,f
How many of the following names are correct? Correct the incorrect names.
d. 1-ethyl-1-pentene
e. 5-ethylcyclohexene
f. 5-chloro-3-hexene
Problem 55g,h,i
How many of the following names are correct? Correct the incorrect names.
g. 2-ethyl-2-butene
h. (E)-2-methyl-1-hexene
i. 2-methylcyclopentene
Problem 56
a. How many alkenes could you treat with H2, Pd/C to prepare methylcyclopentane?
b. Which of the alkenes is the most stable?
c. Which of the alkenes has the smallest heat of hydrogenation?
Problem 57c,d
Draw structures for the following:
c. (3Z,5Z)-4,5-dimethyl-3,5-nonadiene
d. (3E,5E)-2,5-dibromo-3,5-octadiene
Problem 58a-f
Given the reaction coordinate diagram for the reaction of A to form G, answer the following questions:
<IMAGE>
a. How many intermediates are formed in the reaction?
b. Which letters represent transition states?
c. What is the fastest step in the reaction?
d. Which is more stable: A or G?
e. Does A or E form faster from C?
f. Which is the more stable intermediate?
Problem 59
a. Which of the following reactions has the larger ∆S° value?
b. Is the ∆S° value positive or negative?
Problem 60
Draw the structure of a compound with molecular C8H14 that reacts with one equivalent of H2 over Pd/C to form a meso compound
Problem 61
a. What is the equilibrium constant for a reaction that is carried out at 25 °C (298 K) with ∆H° = 20 kcal/mol and ∆S° = 5.0 × 10-2 kcal mol-1 K-1?
b. What is the equilibrium constant for the same reaction carried out at 125 °C?
Problem 62
Using curved arrows, show the mechanism of the following reaction:
Problem 63
For a reaction carried out at 25 °C with an equilibrium constant of 1 × 10-3, to increase the equilibrium constant by a factor of 10:
a. how much must ∆G° change?
b. how much must ∆H° change if ∆S° = 0 kcal mol-1 K-1?
c. how much must ∆S° change if ∆H° = 0 kcal mol-1?
Problem 64
Given that the free energy of the twist-boat conformer of cyclohexane is 5.3 kcal/mol greater than that of the chair conformer, calculate the percentage of twist-boat conformers present in a sample of cyclohexane at 25 °C. Does your answer agree with the statement made in Section 3.13 about the relative number of molecules in these two conformations?
Problem 65
From the following rate constants, determined at five temperatures, calculate the experimental energy of activation and ∆G‡, ∆H‡, and ∆S‡ for the reaction at 30 °C:
<IMAGE>