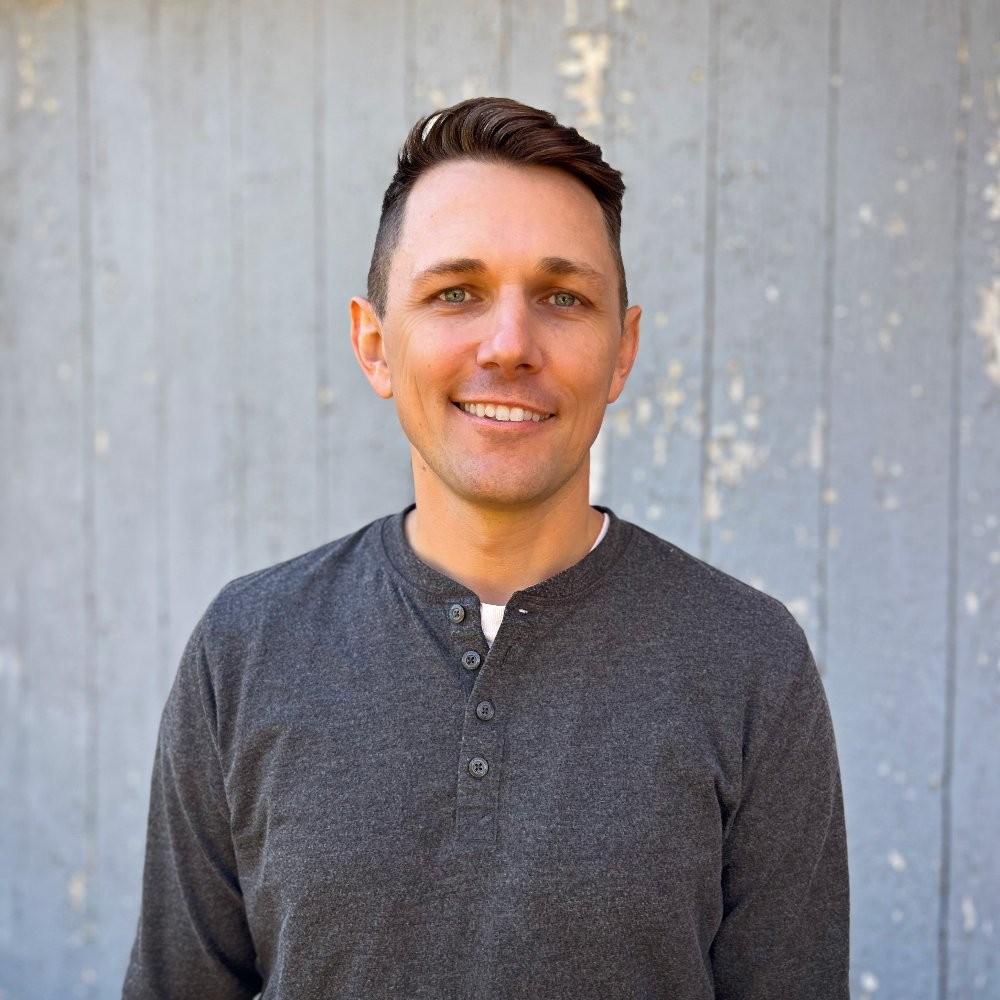
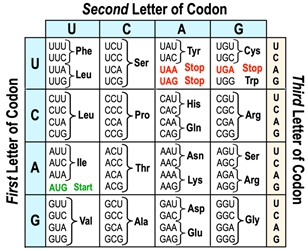
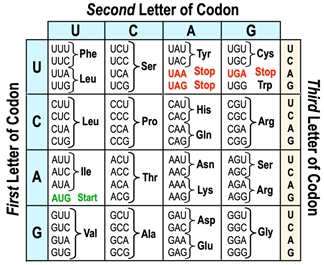
The genetic code serves as a crucial framework that connects nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, to the amino acids that form proteins. Essentially, it is a table that outlines how sequences of nucleotides are translated into the corresponding amino acid sequences in proteins. This code is largely universal among different organisms, although some variations can occur between species.
At the heart of the genetic code is the concept of the codon, which is a sequence of three nucleotides found in messenger RNA (mRNA). Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, making it possible to decode the genetic information into functional proteins. The process of translation involves analyzing one codon at a time, allowing for the sequential assembly of amino acids into a polypeptide chain.
Understanding how to read and interpret the genetic code is essential for grasping the mechanisms of protein synthesis. In future discussions, we will delve deeper into the practical applications of the genetic code and how it facilitates the translation process.