Blue Eyes Assume that 35% of us have blue eyes (based on a study by Dr. P. Soria at Indiana University).
b. Find the value of P(B_bar).
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem: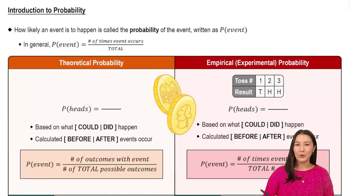
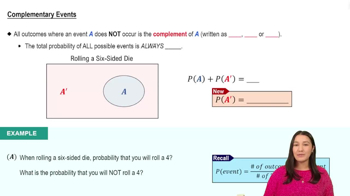
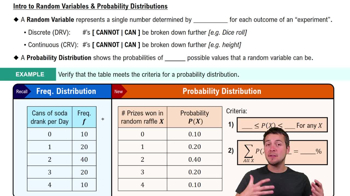

 4:23m
4:23mMaster Complementary Events with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning