Back
BackProblem 8.3.12c
Testing the Difference Between Two Means (c) calculate d̄ and Sd, Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed.
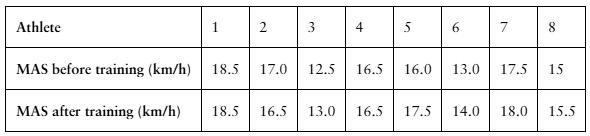
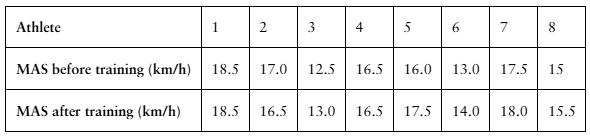
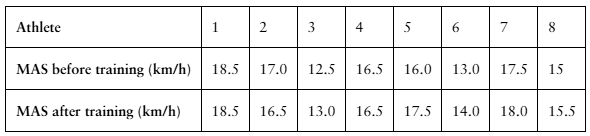
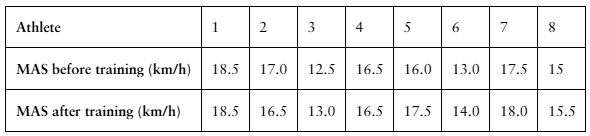
Interval Training
A researcher claims that sprint interval training improves running performance in trained athletes. The table shows the maximum aerobic speed (MAS), in kilometers per hour, of trained athletes before and after six sessions of sprint interval training. At , α=0.10 is there enough evidence to support the researcher’s claim? (Adapted from National Strength and Conditioning Association)
Problem 8.2.14c
Testing the Difference Between Two Means, (c) find the standardized test statistic t,
Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
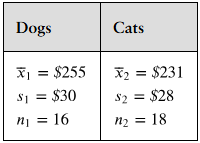
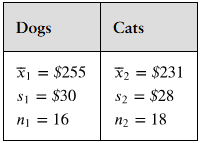
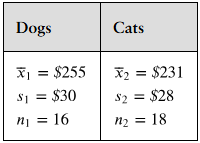
Transactions
A magazine claims that the mean amount spent by a customer at Burger Stop is greater than the mean amount spent by a customer at Fry World. The results for samples of customer transactions for the two fast food restaurants are shown at the left. At , α=0.05 can you support the magazine’s claim? Assume the population variances are equal.
Problem 8.3.9c
Testing the Difference Between Two Means (c) calculate d̄ and Sd, Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed.
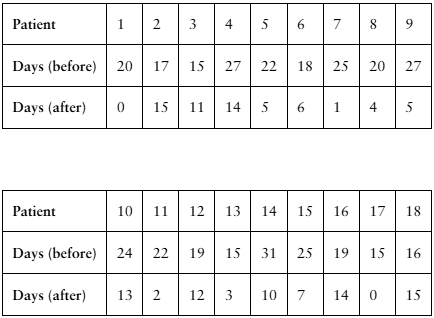
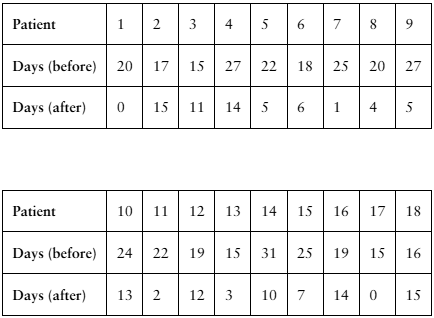
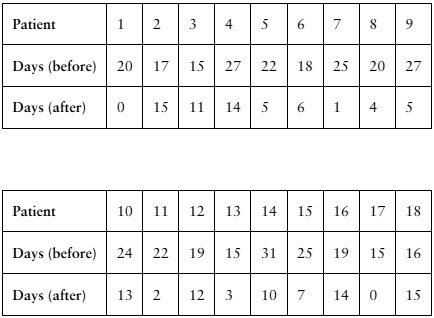
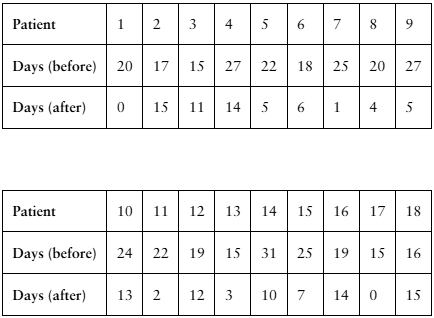
[APPLET] Migraines
A researcher claims that injections of onabotulinumtoxinA reduce the number of days per month that chronic migraine sufferers have headaches. The table shows the number of days chronic migraine sufferers suffered migraines before and after using the treatment. At , α= 0.01 is there enough evidence to support the researcher’s claim? (Adapted from Journal of Headache and Pain)
Problem 8.3.12d
Testing the Difference Between Two Means (d) find the standardized test statistic t, Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Interval Training
A researcher claims that sprint interval training improves running performance in trained athletes. The table shows the maximum aerobic speed (MAS), in kilometers per hour, of trained athletes before and after six sessions of sprint interval training. At , α=0.10 is there enough evidence to support the researcher’s claim? (Adapted from National Strength and Conditioning Association)
Problem 8.2.14d
Testing the Difference Between Two Means,
(d) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Transactions
A magazine claims that the mean amount spent by a customer at Burger Stop is greater than the mean amount spent by a customer at Fry World. The results for samples of customer transactions for the two fast food restaurants are shown at the left. At , α=0.05 can you support the magazine’s claim? Assume the population variances are equal.
Problem 8.3.18d
Testing the Difference Between Two Means (d) find the standardized test statistic t, Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed.
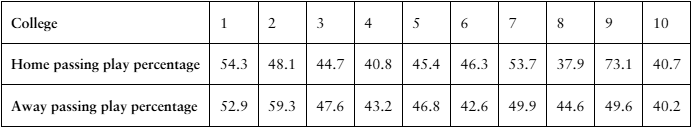
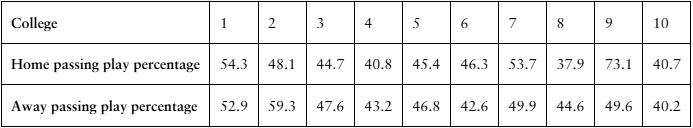
[APPLET] Passing Play Percentages The passing play percentages of 10 randomly selected NCAA Division 1A college football teams for home and away games in the 2020–2021 season are shown in the table. At , α=0.20 is there enough evidence to support the claim that passing play percentage is different for home and away games? (Source: TeamRankings)
Problem 8.3.9d
Testing the Difference Between Two Means (d) find the standardized test statistic t, Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed.
[APPLET] Migraines
A researcher claims that injections of onabotulinumtoxinA reduce the number of days per month that chronic migraine sufferers have headaches. The table shows the number of days chronic migraine sufferers suffered migraines before and after using the treatment. At , α= 0.01 is there enough evidence to support the researcher’s claim? (Adapted from Journal of Headache and Pain)
Problem 8.3.12e
Testing the Difference Between Two Means (e) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Interval Training
A researcher claims that sprint interval training improves running performance in trained athletes. The table shows the maximum aerobic speed (MAS), in kilometers per hour, of trained athletes before and after six sessions of sprint interval training. At , α=0.10 is there enough evidence to support the researcher’s claim? (Adapted from National Strength and Conditioning Association)
Problem 8.3.9e
Testing the Difference Between Two Means (e) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed.
[APPLET] Migraines
A researcher claims that injections of onabotulinumtoxinA reduce the number of days per month that chronic migraine sufferers have headaches. The table shows the number of days chronic migraine sufferers suffered migraines before and after using the treatment. At , α= 0.01 is there enough evidence to support the researcher’s claim? (Adapted from Journal of Headache and Pain)
Problem 8.3.18e
Testing the Difference Between Two Means (e) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed.
[APPLET] Passing Play Percentages The passing play percentages of 10 randomly selected NCAA Division 1A college football teams for home and away games in the 2020–2021 season are shown in the table. At , α=0.20 is there enough evidence to support the claim that passing play percentage is different for home and away games? (Source: TeamRankings)
Problem 8.2.14e
Testing the Difference Between Two Means, (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Transactions
A magazine claims that the mean amount spent by a customer at Burger Stop is greater than the mean amount spent by a customer at Fry World. The results for samples of customer transactions for the two fast food restaurants are shown at the left. At , α=0.05 can you support the magazine’s claim? Assume the population variances are equal.
Problem 8.3.18f
Testing the Difference Between Two Means (f ) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed.
[APPLET] Passing Play Percentages The passing play percentages of 10 randomly selected NCAA Division 1A college football teams for home and away games in the 2020–2021 season are shown in the table. At , α=0.20 is there enough evidence to support the claim that passing play percentage is different for home and away games? (Source: TeamRankings)
Problem 8.3.9f
Testing the Difference Between Two Means (f ) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed.
[APPLET] Migraines
A researcher claims that injections of onabotulinumtoxinA reduce the number of days per month that chronic migraine sufferers have headaches. The table shows the number of days chronic migraine sufferers suffered migraines before and after using the treatment. At , α= 0.01 is there enough evidence to support the researcher’s claim? (Adapted from Journal of Headache and Pain)
Problem 8.3.12f
Testing the Difference Between Two Means (f ) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the samples are random and dependent, and the populations are normally distributed.
Interval Training
A researcher claims that sprint interval training improves running performance in trained athletes. The table shows the maximum aerobic speed (MAS), in kilometers per hour, of trained athletes before and after six sessions of sprint interval training. At , α=0.10 is there enough evidence to support the researcher’s claim? (Adapted from National Strength and Conditioning Association)