Back
BackProblem 7.1.49
Writing Hypotheses: Medicine A medical research team is investigating the mean cost of a 30-day supply of a heart medication. A pharmaceutical company thinks that the mean cost is less than $60. You want to support this claim. How would you write the null and alternative hypotheses?
Problem 7.4.17
use the figure at the left, which suggests what adults think about protecting the environment.
[Image]
Are People Concerned About Protecting the Environment? You interview a random sample of 100 adults. The results of the survey show that 58% of the adults said they live in ways that help protect the environment some of the time. At α=0.05, can you reject the claim that at least 64% of adults make an effort to live in ways that help protect the environment some of the time?
Problem 7.5.2
Can a critical value for the chi-square test be negative? Explain.
Problem 7.4.12
Hypothesis Testing Using Rejection Regions In Exercises 7–12, (a) identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, (b) find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), (c) find the standardized test statistic z, (d) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
Changing Jobs A researcher claims that 40% of U.S. adults would consider changing jobs. In a random sample of 50 U.S. adults, 25 say they would consider changing jobs. At α=0.10, is there enough evidence to reject the researcher’s claim?
Problem 7.1.5
True or False? In Exercises 5–10, determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is false, rewrite it as a true statement.
In a hypothesis test, you assume the alternative hypothesis is true.
Problem 7.3.8
In Exercises 3–8, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance alpha and sample size n.
Left-tailed test, α=0.10, n=38
Problem 7.4.7
In Exercises 3–8, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance alpha and sample size n.
Two-tailed test, α=0.05, n=27
Problem 7.3.17
In Exercises 13–18, test the claim about the population mean μ at the level of significance α. Assume the population is normally distributed.
Claim: μ=4915; α=0.01. Sample statistics: x_bar=5017, s=5613, n=51
Problem 7.2.43
Hypothesis Testing Using Rejection Region(s) In Exercises 39–44, (a) identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, (b) find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), (c) find the standardized test statistic z, (d) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
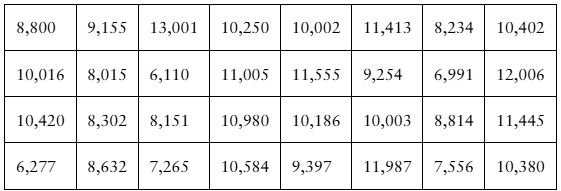
[APPLET] Fluorescent Lamps A compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) bulb manufacturer guarantees that the mean life of a CFL bulb is at least 10,000 hours. You want to test this guarantee. To do so, you record the lives of a random sample of 32 CFL bulbs. The results (in hours) are listed. Assume the population standard deviation is 1850 hours. At alpha=0.11, do you have enough evidence to reject the manufacturer’s claim?
Problem 7.2.10
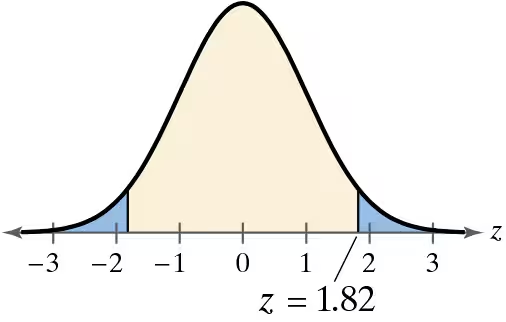
Graphical Analysis In Exercises 9–12, match the P-value or z-statistic with the graph that represents the corresponding area. Explain your reasoning.
P= 0.2802
Problem 7.2.42
Hypothesis Testing Using Rejection Region(s) In Exercises 39–44, (a) identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, (b) find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), (c) find the standardized test statistic z, (d) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
Light Bulbs A light bulb manufacturer guarantees that the mean life of a certain type of light bulb is at least 750 hours. A random sample of 25 light bulbs has a mean life of 745 hours. Assume the population is normally distributed and the population standard deviation is 60 hours. At alpha= 0.02, do you have enough evidence to reject the manufacturer’s claim?
Problem 7.4.8
Hypothesis Testing Using Rejection Regions In Exercises 7–12, (a) identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, (b) find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), (c) find the standardized test statistic z, (d) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
Vaccinations In 2021, a reporter claims that at least 55% of U.S. adults feel that COVID-19 vaccinations should be required for high school students to attend school in the fall. In a random sample of 200 U.S. adults, 56% feel that COVID-19 vaccinations should be required for high school students to attend school in the fall. At α=0.10, is there enough evidence to reject the reporter’s claim?
Problem 7.5.8
In Exercises 7–12, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance α.
Right-tailed test, n=10,α=0.10
Problem 7.3.3
In Exercises 3–8, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance alpha and sample size n.
Left-tailed test, α=0.10, n=20
Problem 7.5.3
How do the critical values for a two-tailed test change as alpha decreases?
Problem 7.5.30
Hypothesis Testing Using Rejection Regions In Exercises 23–30, (a) identify the claim and state H0 and Ha, (b) find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s), (c) find the standardized test statistic X^2, (d) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and (e) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Assume the population is normally distributed.
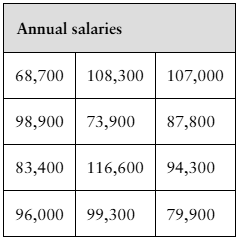
Salaries The annual salaries (in dollars) of 12 randomly chosen nursing supervisors are shown in the table at the left. At α=0.10, is there enough evidence to reject the claim that the standard deviation of the annual salaries is $18,630?
Problem 7.3.32
Deciding on a Distribution In Exercises 31 and 32, decide whether you should use the standard normal sampling distribution or a t-sampling distribution to perform the hypothesis test. Justify your decision. Then use the distribution to test the claim. Write a short paragraph about the results of the test and what you can conclude about the claim.
Tuition and Fees An education publication claims that the mean in-state tuition and fees at public four-year institutions by state is more than $10,500 per year. A random sample of 30 states has a mean in-state tuition and fees at public four-year institutions of $10,931 per year. Assume the population standard deviation is $2380. At α=0.01, test the publication’s claim.
Problem 7.3.1
Explain how to find critical values for a t-distribution.
Problem 7.1.30
Stating the Null and Alternative Hypotheses In Exercises 25–30, write the claim as a mathematical statement. State the null and alternative hypotheses, and identify which represents the claim.
College Debt According to a recent survey, 14% of adults currently carry student loan debt.
Problem 7.1.41
Identifying the Nature of a Hypothesis Test In Exercises 37–42, state and in words and in symbols. Then determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed. Explain your reasoning. Sketch a normal sampling distribution and shade the area for the P-value.
Survey A polling organization reports that the number of responses to a survey mailed to 100,000 U.S. residents is not 100,000.
Problem 7.3.33
Writing You are testing a claim and incorrectly use the standard normal sampling distribution instead of the t-sampling distribution, mistaking the sample standard deviation for the population standard deviation. Does this make it more or less likely to reject the null hypothesis? Is this result the same no matter whether the test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed? Explain your reasoning.
Problem 7.1.25
Stating the Null and Alternative Hypotheses In Exercises 25–30, write the claim as a mathematical statement. State the null and alternative hypotheses, and identify which represents the claim.
Tablets A tablet manufacturer claims that the mean life of the battery for a certain model of tablet is more than 8 hours.
Problem 7.5.12
In Exercises 7–12, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance α.
Two-tailed test, n=61,α=0.01
Problem 7.3.4
In Exercises 3–8, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance alpha and sample size n.
Left-tailed test, α=0.01, n=35
Problem 7.4.3
In Exercises 3–6, determine whether a normal sampling distribution can be used. If it can be used, test the claim.
Claim: p <0.12, α=0.01. Sample statistics: p_hat = 0.10, n=40
Problem 7.1.40
Identifying the Nature of a Hypothesis Test In Exercises 37–42, state and in words and in symbols. Then determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed. Explain your reasoning. Sketch a normal sampling distribution and shade the area for the P-value.
Lung Cancer A report claims that lung cancer accounts for 25% of all cancer diagnoses.
Problem 7.1.16
Stating Hypotheses In Exercises 11–16, the statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha.
p = 0.21
Problem 7.1.31
Identifying Type I and Type II Errors In Exercises 31–36, describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the indicated claim.
Repeat Customers A used textbook selling website claims that at least 60% of its new customers will return to buy their next textbook.
Problem 7.5.7
In Exercises 7–12, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance α.
Right-tailed test, n=27,α=0.05
Problem 7.1.23
Identifying a Test In Exercises 21–24, determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed.
Ha: σ^2 = 142
H0: σ ≠ 142