Back
BackProblem 7.RE.9d
In Exercises 7–10, explain how you should interpret a decision that rejects the null hypothesis.
A nonprofit consumer organization says that the standard deviation of the starting prices of its top-rated vehicles for a recent year is no more than $2900.
Problem 7.RE.9e
In Exercises 7–10, explain how you should interpret a decision that fails to reject the null hypothesis.
A nonprofit consumer organization says that the standard deviation of the starting prices of its top-rated vehicles for a recent year is no more than $2900.
Problem 7.RE.10a
In Exercises 7–10, state the null and alternative hypotheses and identify which represents the claim,
An energy bar maker claims that the mean number of grams of carbohydrates in one bar is less than 25.
Problem 7.RE.10b
In Exercises 7–10, describe type I and type II errors for a hypothesis test of the claim.
An energy bar maker claims that the mean number of grams of carbohydrates in one bar is less than 25.
Problem 7.RE.10c
In Exercises 7–10, (c) explain whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed.
An energy bar maker claims that the mean number of grams of carbohydrates in one bar is less than 25.
Problem 7.RE.10d
In Exercises 7–10, (d) explain how you should interpret a decision that rejects the null hypothesis.
An energy bar maker claims that the mean number of grams of carbohydrates in one bar is less than 25.
Problem 7.RE.11
In Exercises 11 and 12, find the P-value for the hypothesis test with the standardized test statistic z. Decide whether to reject H0 for the level of significance α.
Left-tailed test, z = -0.94, α = 0.05
Problem 7.RE.12
In Exercises 11 and 12, find the P-value for the hypothesis test with the standardized test statistic z. Decide whether to reject H0 for the level of significance α.
Two-tailed test, z = 2.57, α = 0.10
Problem 7.RE.13
In Exercises 13 –16, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance . Include a graph with your answer.
Left-tailed test, α=0.02
Problem 7.RE.15
In Exercises 13 –16, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance . Include a graph with your answer.
Right-tailed test, α=0.025
Problem 7.RE.16
In Exercises 13 –16, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance . Include a graph with your answer.
Two-tailed test, α=0.03
Problem 7.RS.3
You want your test to support a positive claim about your college, not just fail to reject one. Should you state your claim so that the null hypothesis contains the claim or the alternate hypothesis contains the claim? Explain.
Problem 7.T.3
When you reject a true claim with a level of significance that is virtually zero, what can you infer about the randomness of your sampling process?
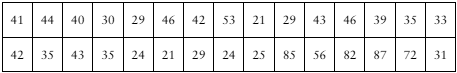
Problem 7.T.7
[APPLET] A researcher claims that the mean age of the residents of a small town is more than 38 years. The ages (in years) of a random sample of 30 residents are listed below. At α=0.10, is there enough evidence to support the researcher’s claim? Assume the population standard deviation is 9 years.
Problem 7.T.5
A nutrition bar manufacturer claims that the standard deviation of the number of grams of carbohydrates in a bar is 1.11 grams. A random sample of 26 bars has a standard deviation of 1.19 grams. At α=0.05, is there enough evidence to reject the manufacturer’s claim? Assume the population is normally distributed.
Problem 7.T.3
A travel analyst says that the mean price of a meal for a family of 4 in a resort restaurant is at most $100. A random sample of 33 meal prices for families of 4 has a mean of $110 and a standard deviation of $19. At α=0.01, is there enough evidence to reject the analyst’s claim?
Problem 7.RE.55
In Exercises 55–58, test the claim about the population variance or standard deviation at the level of significance . Assume the population is normally distributed.
Claim: σ^2 > 2; α=0.10. Sample statistics: s^2 = 2.95, n=18
Problem 7.RE.54
In Exercises 51–54, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of chi-square test with sample size n and level of significance.
Left-tailed test, n=6, α=0.05
Problem 7.RE.34
In Exercises 29 –34, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n.
Two-tailed test, α=0.02, n=12
Problem 7.RE.29
In Exercises 29 –34, find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of t-test with level of significance α and sample size n.
Two-tailed test, α=0.05, n=20
Problem 7.RE.5
n Exercises 1–6, the statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha.
σ > 1.9
Problem 7.RE.3
n Exercises 1–6, the statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha.
p < 0.205
Problem 7.RE.1
n Exercises 1–6, the statement represents a claim. Write its complement and state which is H0 and which is Ha.
μ ≤ 375
Problem 7.1.51a
Writing Hypotheses: Backpack Manufacturer A backpack manufacturer claims that the mean life of its competitor’s backpacks is less than 5 years. You are asked to perform a hypothesis test to test this claim. How would you write the null and alternative hypotheses when
a. you represent the manufacturer and want to support the claim?
Problem 7.1.1
What are the two types of hypotheses used in a hypothesis test? How are they related?
Problem 7.1.4
Does failing to reject the null hypothesis mean that the null hypothesis is true? Explain.
Problem 7.1.5
True or False? In Exercises 5–10, determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is false, rewrite it as a true statement.
In a hypothesis test, you assume the alternative hypothesis is true.
Problem 7.1.6
True or False? In Exercises 5–10, determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is false, rewrite it as a true statement.
A statistical hypothesis is a statement about a sample.
Problem 7.1.8
True or False? In Exercises 5–10, determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is false, rewrite it as a true statement.
The level of significance is the maximum probability you allow for rejecting a null hypothesis when it is actually true.
Problem 7.1.9
True or False? In Exercises 5–10, determine whether the statement is true or false. If it is false, rewrite it as a true statement.
A large P-value in a test will favor rejection of the null hypothesis.