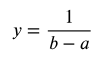Back
BackProblem 5.2.9c
Finding Probabilities for Normal Distributions In Exercises 7–12, find the indicated probabilities. If convenient, use technology to find the probabilities.
MCAT Scores In a recent year, the MCAT total scores were normally distributed, with a mean of 500.9 and a standard deviation of 10.6. Find the probability that a randomly selected medical student who took the MCAT has a total score that is (c) more than 515. Identify any unusual events in parts (a)–(c). Explain your reasoning. (Source: Association of American Medical Colleges)
Problem 5.1.60d
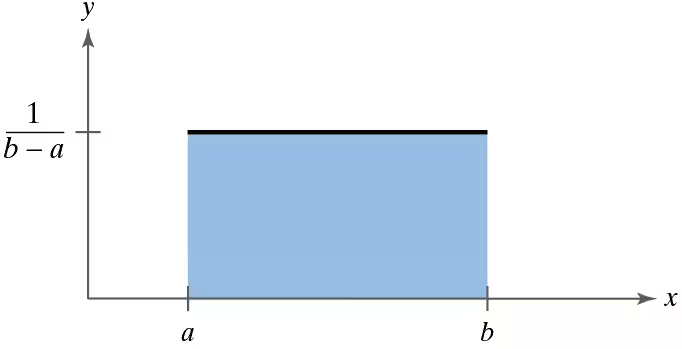
Uniform Distribution A uniform distribution is a continuous probability distribution for a random variable x between two values a and b (a<b), where (a ≤ x ≤ b) and all of the values of x are equally likely to occur. The graph of a uniform distribution is shown below.
The probability density function of a uniform distribution is
on the interval from (x=a) to (x=b). For any value of x less than a or greater than b, y=0 . In Exercises 59 and 60, use this information.
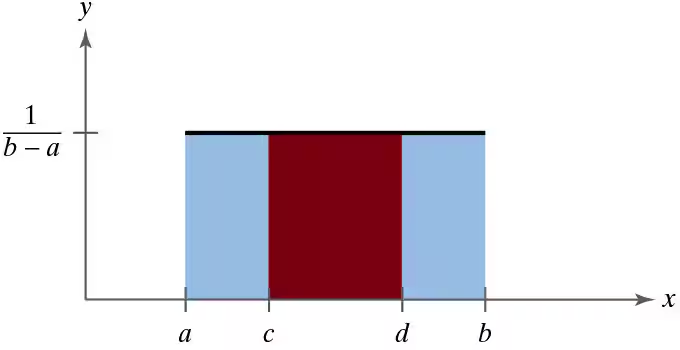
For two values c and d, where a ≤ c < d ≤ b, the probability that x lies between c and d is equal to the area under the curve between c and d, as shown below.
So, the area of the red region equals the probability that x lies between c and d. For a uniform distribution from (a=1) to (b=25) , find the probability that
d. x lies between 8 and 14.
Problem 5.3.42e
History Grades In a history class, the grades for various assessments are all positive numbers and have different distributions. Determine whether the grades for each assessment could be normally distributed. Explain your reasoning.
e. an extra credit assignment with a mean of 2.25 and a standard deviation of 2.49