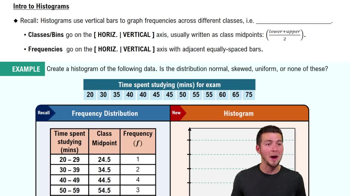
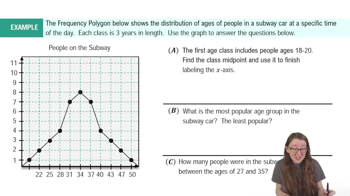
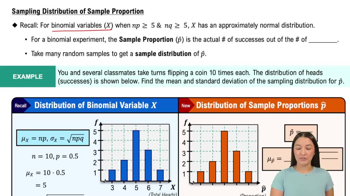
In Exercises 9–18, construct the histograms and answer the given questions.
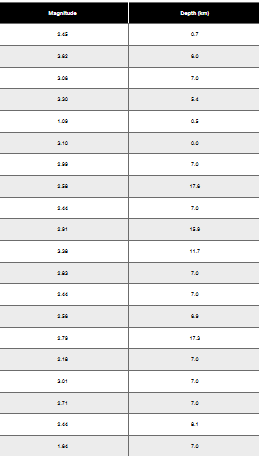
Old Faithful Use the frequency distribution from Exercise 15 in Section 2-1 to construct a histogram. Does it appear to be the graph of data from a population with a normal distribution?