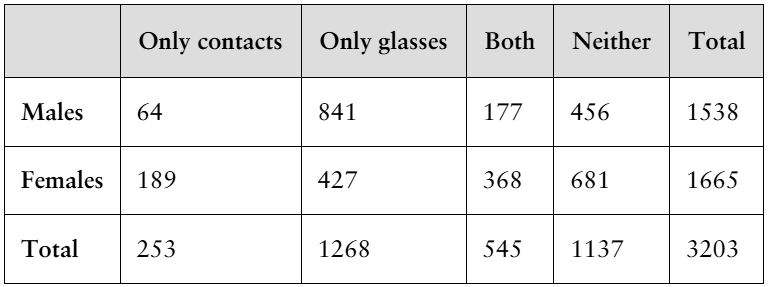
18. Rolling a Die You roll a die. Find the probability of each event.
b. Rolling a 2 or an odd number
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

 5:14m
5:14mMaster Probability of Mutually Exclusive Events with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learning