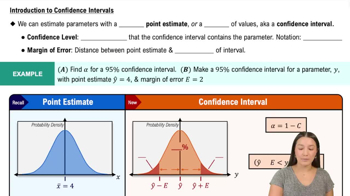
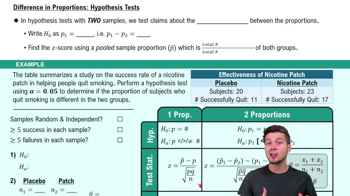
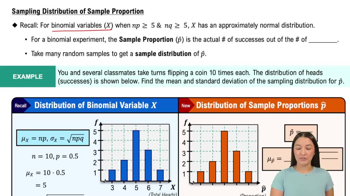
Voting Survey In a survey of 1002 people, 70% said that they voted in a recent presidential election (based on data from ICR Research Group). Voting records show that 61% of eligible voters actually did vote.
a. Among the 1002 people surveyed, what is the actual number of people who said that they voted?