Back
BackProblem 5
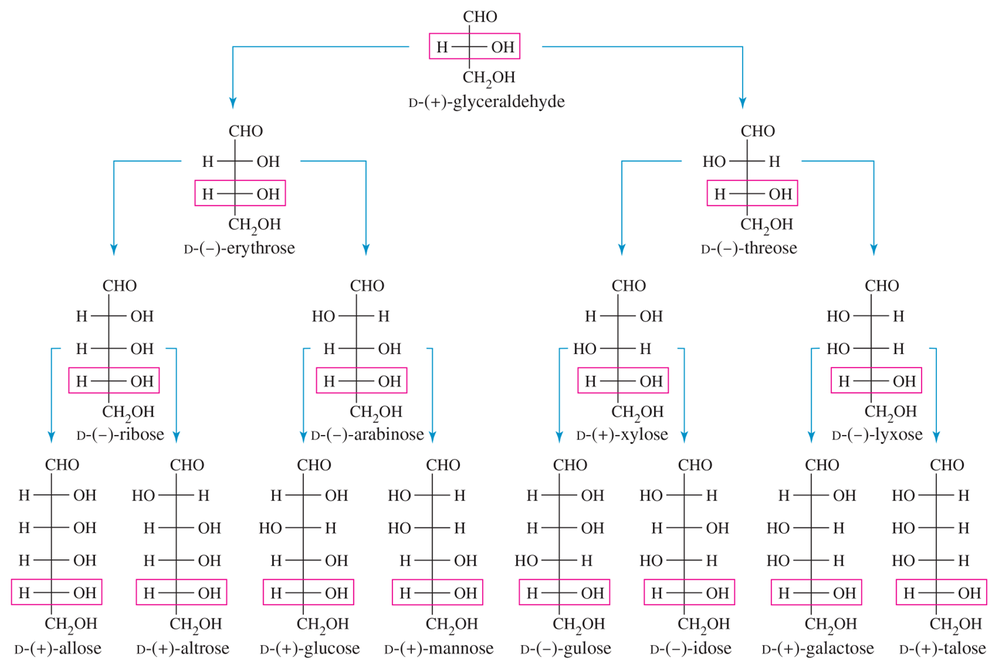
Which configuration (R or S) does the bottom asymmetric carbon have for the D series of sugars? Which configuration for the L series?
Problem 6a,b
a. Draw D-allose, the C3 epimer of glucose.
b. Draw D-talose, the C2 epimer of d-galactose
Problem 6c,d
c. Draw d-idose, the C3 epimer of D-talose. Now compare your answers with Figure 23-3.
d. Draw the C4 “epimer” of D-xylose. Notice that this “epimer” is actually an L-series sugar, and we have seen its enantiomer. Give the correct name for this L-series sugar.
Problem 7
Draw the Haworth projection for the cyclic structure of D-mannose by laying down the Fischer projection.
Problem 8
Allose is the C3 epimer of glucose. Draw the cyclic hemiacetal form of D-allose, first in the chair conformation and then in the Haworth projection.
Problem 9
Talose is the C4 epimer of mannose. Draw the chair conformation of D-talopyranose.
Problem 10a
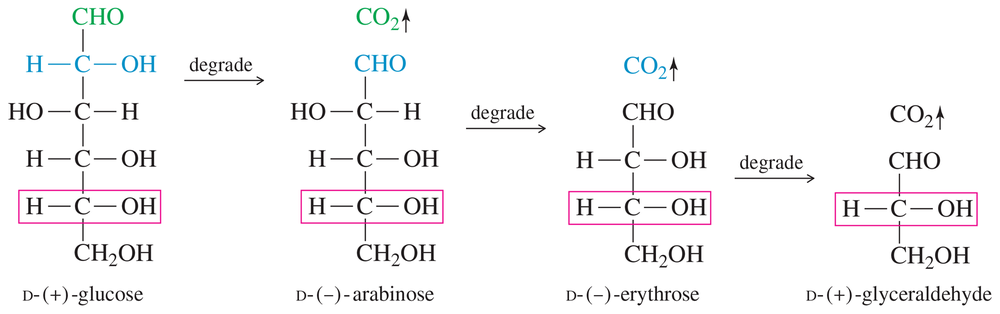
Figure 23-2 shows that the degradation of D-glucose gives D-arabinose, an aldopentose. Arabinose is most stable in its furanose form. Draw D-arabinofuranose.
Problem 10b
Ribose, the C2 epimer of arabinose, is most stable in its furanose form. Draw D-ribofuranose.
Problem 11
The carbonyl group in D-galactose may be isomerized from C1 to C2 by brief treatment with dilute base (by the enediol rearrangement). The product is the C4 epimer of fructose. Draw the furanose structure of the product.
Problem 13
Like glucose, galactose mutarotates when it dissolves in water. The specific rotation of α-D-galactopyranose is +150.7°, and that of the β anomer is +52.8°. When either of the pure anomers dissolves in water, the specific rotation gradually changes to +80.2°. Determine the percentages of the two anomers present at equilibrium.
Problem 14
When D-glucose is reduced with sodium borohydride, optically active glucitol results. When optically active D-galactose is reduced, however, the product is optically inactive. Explain this loss of optical activity.
Problem 16
Draw and name the products of bromine water oxidation of
(a) D-mannose
(b) D-galactose
(c) D-fructose
Problem 17
Draw and name the products of nitric acid oxidation of
(a) D-mannose
(b) D-galactose
Problem 18
Two sugars, A and B, are known to be glucose and galactose, but it is not certain which one is which. On treatment with nitric acid, A gives an optically inactive aldaric acid, while B gives an optically active aldaric acid. Which sugar is glucose, and which is galactose?
Problem 19a
Except for the Tollens test, basic aqueous conditions are generally avoided with sugars because they lead to fast isomerizations.
(a) Under basic conditions, the proton alpha to the aldehyde (or ketone) carbonyl group is reversibly removed, and the resulting enolate ion is no longer asymmetric. Reprotonation can occur on either face of the enolate, giving either the original structure or its epimer. Because a mixture of epimers results, this process is called epimerization. Propose a mechanism for the base-catalyzed equilibration of glucose to a mixture of glucose and its C2 epimer, mannose.
Problem 19b
Except for the Tollens test, basic aqueous conditions are generally avoided with sugars because they lead to fast isomerizations.
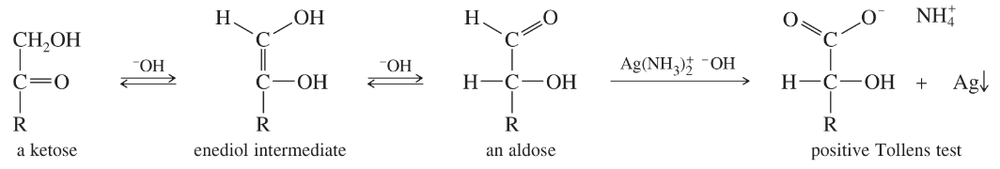
(b) Propose a mechanism for the isomerization of a ketose to an aldose, via the enediol intermediate, shown immediately above. Note that the enediol has two –OH protons, and removing one or the other gives two different enolate ions.
Problem 20c,d
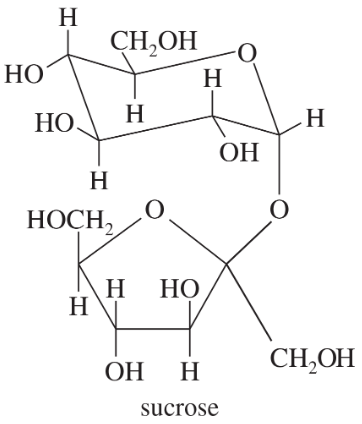
Which of the following are reducing sugars? Comment on the common name sucrose for table sugar.
(c) α-D-allopyranose
(d) ethyl β-D-ribofuranoside
Problem 20e,f
Which of the following are reducing sugars? Comment on the common name sucrose for table sugar.
(e)
(f)
Problem 21a
Draw the structures of the compound methyl α-D-galactopyranoside.
Allose is the C3 epimer of glucose, and ribose is the C2 epimer of arabinose.
Problem 21b
Draw the structures of the compound α-D-allopyranose.
Allose is the C3 epimer of glucose, and ribose is the C2 epimer of arabinose.
Problem 21c
Draw the structures of the compound ethyl β-D-ribofuranoside.
Allose is the C3 epimer of glucose, and ribose is the C2 epimer of arabinose.
Problem 22
The mechanism of glycoside formation is the same as the second part of the mechanism for acetal formation. Propose a mechanism for the formation of methyl β-D-glucopyranoside.
- Predict the products obtained when d-galactose reacts with each reagent. (a) Br2 and H2O
Problem 23
Problem 23a
Show the products that result from hydrolysis of amygdalin in dilute acid. Can you suggest why amygdalin might be toxic to tumor (and possibly other) cells?
Problem 24
Treatment of either anomer of fructose with excess ethanol in the presence of a trace of HCl gives a mixture of the α and β anomers of ethyl-D-fructofuranoside. Draw the starting materials, reagents, and products for this reaction. Circle the aglycone in each product.
Problem 25a
Show the product that results when fructose is treated with an excess of methyl iodide and silver oxide.
Problem 25b
Show what happens when the product of part (a) is hydrolyzed using dilute acid.
Problem 25c
What do the results of parts (a) and (b) imply about the hemiacetal structure of fructose?
Problem 26
Propose a mechanism for methylation of any one of the hydroxy groups of methyl α-D-glucopyranoside, using NaOH and dimethyl sulfate.
Problem 27a
Draw the expected product of the reaction of the following sugars with excess methyl iodide and silver oxide.
(a) α-D-fructofuranose