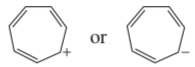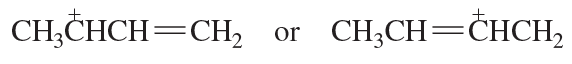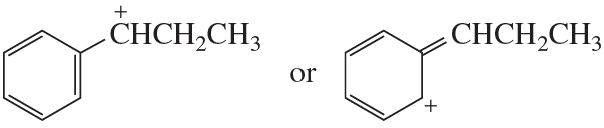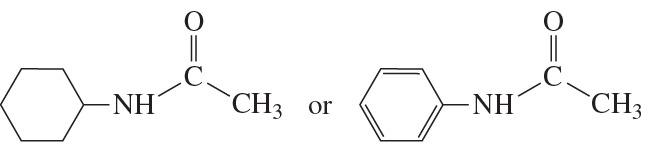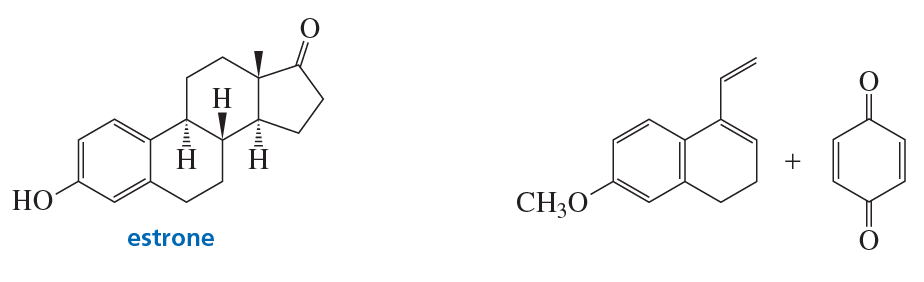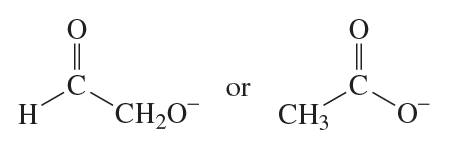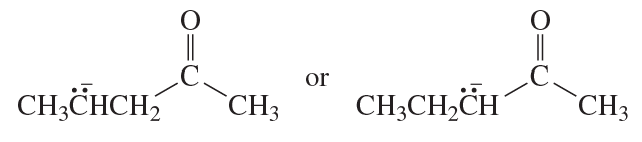Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch.8 - Delocalized Electrons:Their Effect on Stability, pKa, and the Products of a Reaction Aromaticity and Electronic Effects:An Introduction to the Reactions of Benzene
Ch.8 - Delocalized Electrons:Their Effect on Stability, pKa, and the Products of a Reaction Aromaticity and Electronic Effects:An Introduction to the Reactions of BenzeneProblem 69b
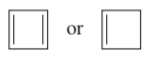
Which ion in each of the following pairs is more stable?
b.
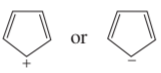
Problem 69c
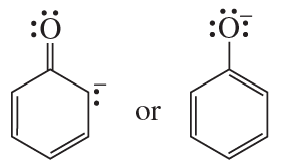
Which ion in each of the following pairs is more stable?
c.
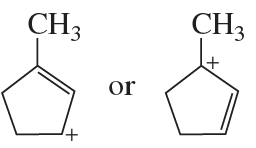
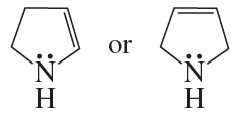
Problem 69d
Which ion in each of the following pairs is more stable?
d.
Problem 71a,b
Which resonance contributor in each pair makes the greater contribution to the resonance hybrid?
a.
b.
Problem 71c
Which resonance contributor in each pair makes the greater contribution to the resonance hybrid?
c.
Problem 71d
Which resonance contributor in each pair makes the greater contribution to the resonance hybrid?
d.
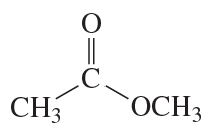
Problem 73a
Which oxygen atom has the greater electron density?
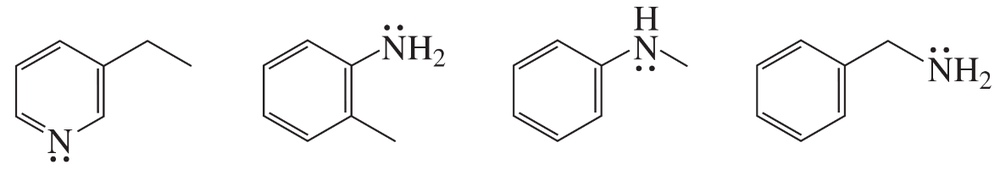
Problem 73b
Which compound has the greater electron density on its nitrogen atom?
Problem 73c
Which compound has the greater electron density on its oxygen atom?
Problem 74
Which compound is the strongest base?
Problem 75
Which loses a proton more readily: a methyl group bonded to cyclohexane or a methyl group bonded to benzene?
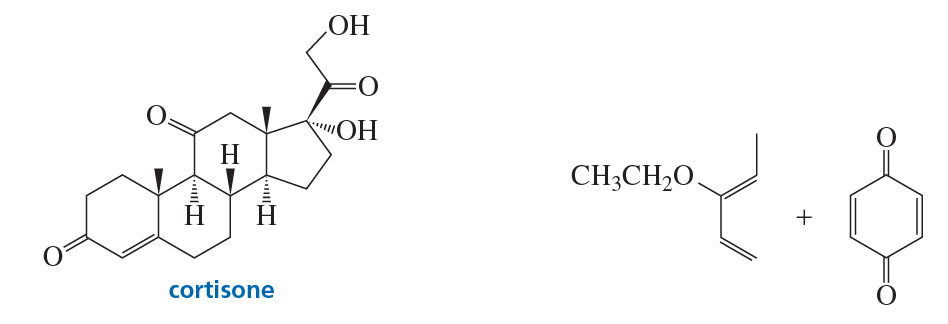
Problem 77a
The A ring of cortisone (a steroid) is formed by a Diels–Alder reaction using the two reactants shown here. What is the product of this reaction?
Problem 77b
The C ring of estrone (a steroid) is formed by a Diels–Alder reaction using the two reactants shown here. What is the product of this reaction?
Problem 79
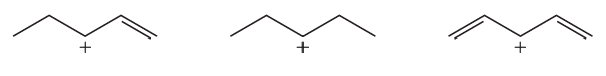
Rank the following carbocations from most stable to least stable:
Problem 81a,b
Which species in each of the pairs in Problem 80 is the stronger base?
a.
b.
Problem 82
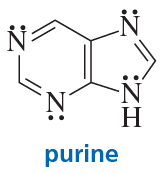
Purine is a heterocyclic compound with four nitrogen atoms.
a. Which nitrogen is most apt to be protonated?
b. Which nitrogen is least apt to be protonated?
Problem 85
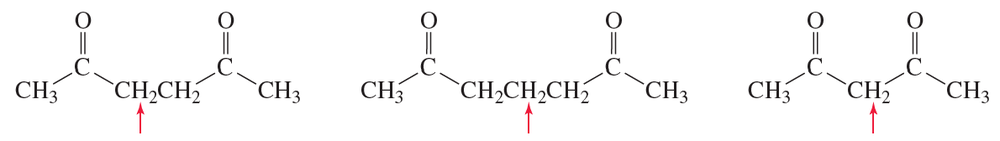
Rank the indicated hydrogen in the following compounds from most acidic to least acidic:
Problem 86a
Answer the following questions for the molecular orbitals (MOs) of 1,3,5,7-octatetraene:
a. How many MOs does the compound have?
Problem 86b
Answer the following questions for the molecular orbitals (MOs) of 1,3,5,7-octatetraene:
b. Which are the bonding MOs, and which are the antibonding MOs?
Problem 86c
Answer the following questions for the molecular orbitals (MOs) of 1,3,5,7-octatetraene:
c. Which MOs are symmetric, and which are antisymmetric?
Problem 86d
Answer the following questions for the molecular orbitals (MOs) of 1,3,5,7-octatetraene:
d. Which MO is the HOMO and which is the LUMO in the ground state?
Problem 86e
Answer the following questions for the molecular orbitals (MOs) of 1,3,5,7-octatetraene:
e. Which MO is the HOMO and which is the LUMO in the excited state?
Problem 86f
Answer the following questions for the molecular orbitals (MOs) of 1,3,5,7-octatetraene:
f. What is the relationship between HOMO and LUMO and symmetric and antisymmetric orbitals?
Problem 86g
Answer the following questions for the molecular orbitals (MOs) of 1,3,5,7-octatetraene:
g. How many nodes does the highest-energy MO of 1,3,5,7-octatetraene have between the nuclei?
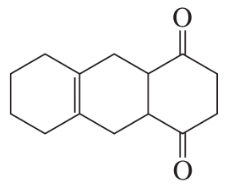
Problem 87
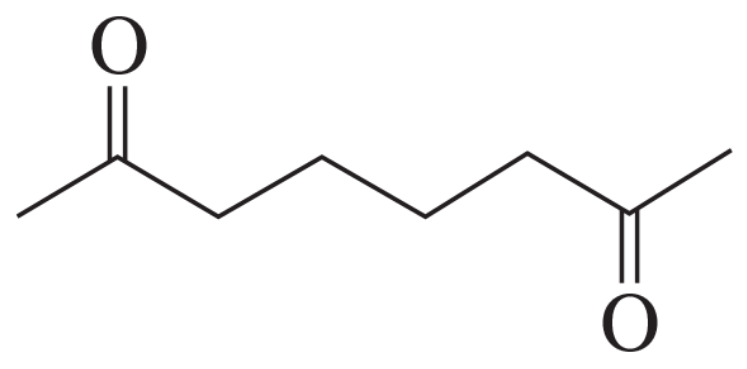
How could you synthesize the following compound from starting materials containing no more than six carbons?
Problem 88
A student obtained two products from the reaction of 1,3-cyclohexadiene with Br2 (disregarding stereoisomers). His lab partner was surprised when he obtained only one product from the reaction of 1,3-cyclohexadiene with HBr (disregarding stereoisomers). Account for these results.
Problem 89a
How could the following compounds be synthesized using a Diels–Alder reaction?
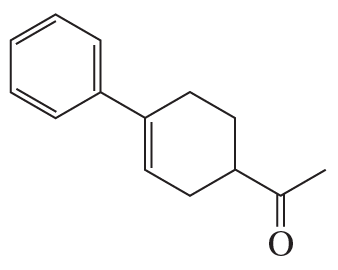
a.
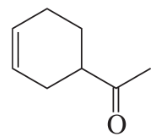
Problem 89b
How could the following compounds be synthesized using a Diels–Alder reaction?
b.
Problem 89c
How could the following compounds be synthesized using a Diels–Alder reaction?
c.
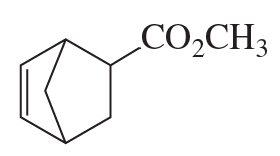
Problem 89d
How could the following compounds be synthesized using a Diels–Alder reaction?
d.