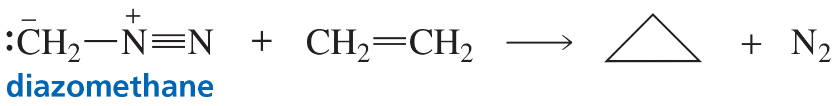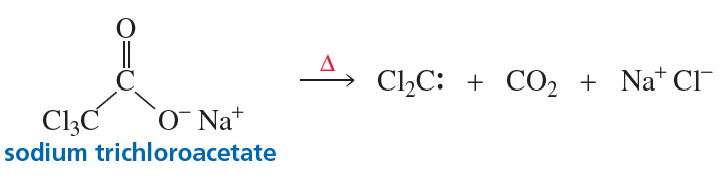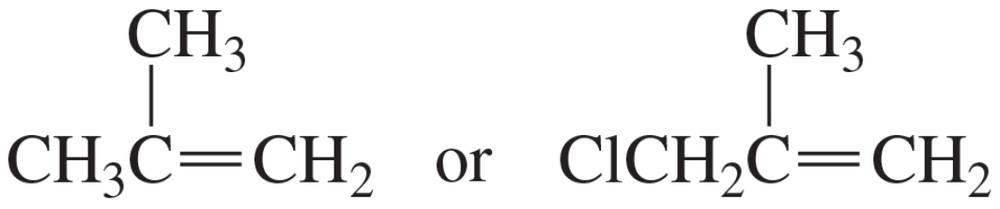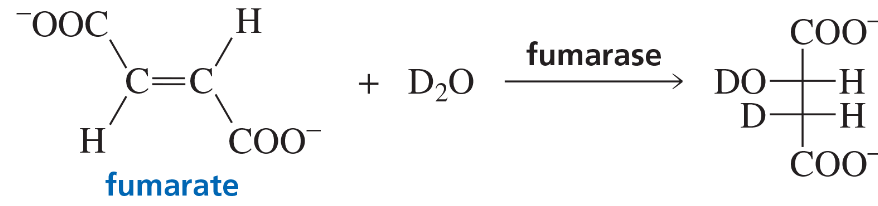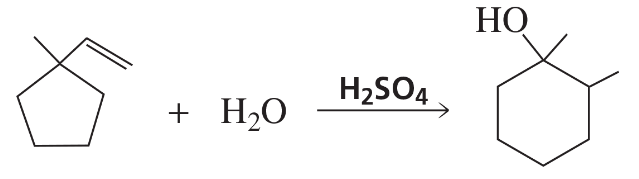Back
Back Bruice 8th Edition
Bruice 8th Edition Ch.6 - The Reactions of Alkenes The Stereochemistry of Addition Reactions
Ch.6 - The Reactions of Alkenes The Stereochemistry of Addition ReactionsProblem 87g
Draw the products of the following reactions. If the products can exist as stereoisomers show what stereoisomers are formed.
g. 3,3-dimethyl-1-pentene + HBr
Problem 87h
Draw the products of the following reactions. If the products can exist as stereoisomers show what stereoisomers are formed.
h. cis-2-butene + HBr
Problem 87i
Draw the products of the following reactions. If the products can exist as stereoisomers show what stereoisomers are formed.
i. (Z)-2,3-dichloro-2-butene + H2, Pd/C
Problem 87j
Draw the products of the following reactions. If the products can exist as stereoisomers show what stereoisomers are formed.
j. (E)-2,3-dichloro-2-butene + H2, Pd/C
Problem 87k,l
Draw the products of the following reactions. If the products can exist as stereoisomers show what stereoisomers are formed.
k. (Z)-3,4-dimethyl-3-hexene + H2, Pd/C
l. (E)-3,4-dimethyl-3-hexene + H2, Pd/C
Problem 88
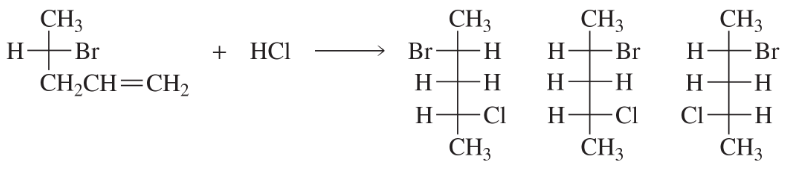
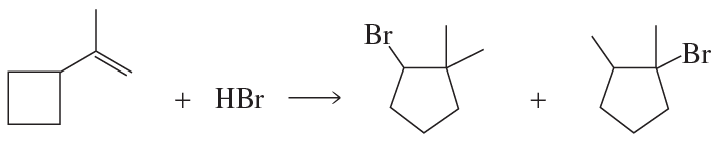
Of the possible products shown for the following reaction, are there any that will not be formed?
Problem 89
A, a compound with molecular formula C6H10, contains three methylene units. A reacts with one equivalent of H2 over Pd/C to yield B. A reacts with aqueous acid to form a single product, C, and undergoes hydroboration/oxidation to form a pair of enantiomers, D and E. Ozonolysis of A followed by reaction with dimethyl sulfide forms F with molecular formula C6H10O2. Provide structures for A–F.
Problem 90
The reaction of an alkene with diazomethane forms a cyclopropane ring. Propose a mechanism for the reaction. (Hint: It is a concerted reaction.)
Problem 91
Two chemists at Dupont found that ICH2ZnI is better than diazomethane at converting a C=C bond to a cylcopropane ring. Propose a mechanism for the reaction, now known as the Simmons–Smith reaction in their honor.
Problem 92b
Dichlorocarbene can also be generated by heating sodium trichloroacetate. Propose a mechanism for the reaction.
Problem 94a
What alkene gives the product shown after reaction first with ozone and then with dimethyl sulfide?
a.
Problem 94b
What alkene gives the product shown after reaction first with ozone and then with dimethyl sulfide?
b.
Problem 94c
What alkene gives the product shown after reaction first with ozone and then with dimethyl sulfide?
c.
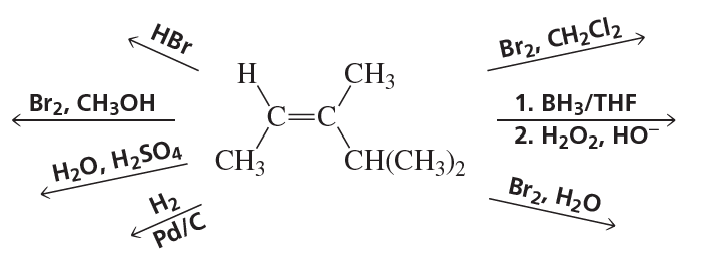
Problem 95a
Draw the products of the following reactions, including their configurations:
Problem 95b
Draw the products of the following reactions, including their configurations:
Problem 95c
Draw the products of the following reactions, including their configurations:
Problem 96
a. Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:
b. Is the initially formed carbocation primary, secondary, or tertiary?
c. Is the rearranged carbocation primary, secondary, or tertiary?
d. Why does the rearrangement occur?
Problem 97
Which compound is hydrated more rapidly?
Problem 98
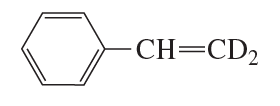
When the following compound is hydrated in the presence of acid, the unreacted alkene is found to have retained the deuterium atoms. What does this tell you about the mechanism for hydration?
Problem 99
When fumarate reacts with D2O in the presence of the enzyme fumarase, only one isomer of the product is formed, as shown here. Is the enzyme catalyzing a syn or an anti addition of D2O?
Problem 100
What stereoisomers are obtained when (S)-3-methyl-1-pentene reacts with Cl2?
Problem 101
Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:
Problem 102
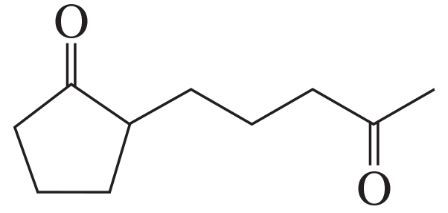
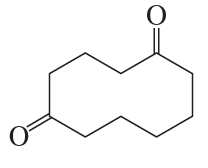
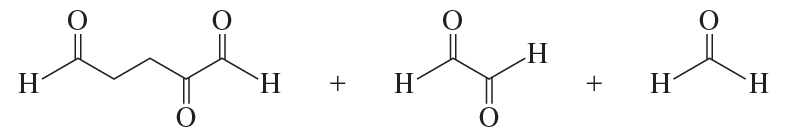
What hydrocarbon forms the following products after reaction first with ozone and then with dimethyl sulfide?
Problem 103a
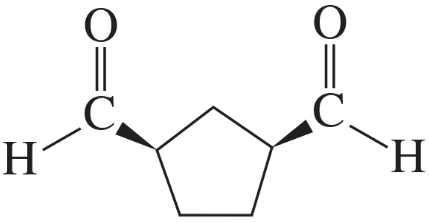
Ozonolysis of an alkene, followed by treatment with dimethyl sulfide, forms the following product(s). Identify the alkene in each case.
a.
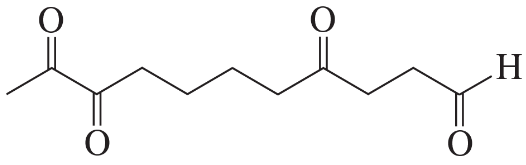
Problem 103b
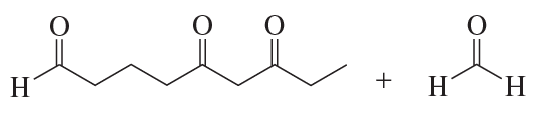
Ozonolysis of an alkene, followed by treatment with dimethyl sulfide, forms the following product(s). Identify the alkene in each case.
b.