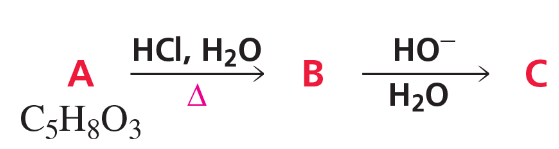Back
BackProblem 36b
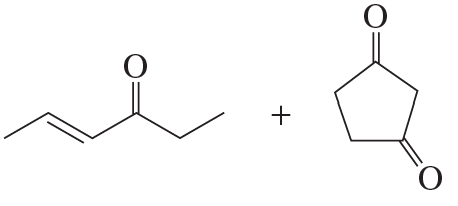
Draw the product obtained by heating each pair of ketones in a basic solution.
b.
Problem 37a
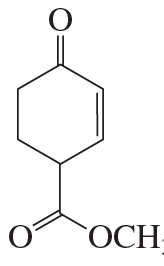
What two carbonyl compounds are needed to synthesize each of the following compounds, using a Robinson annulation?
a.
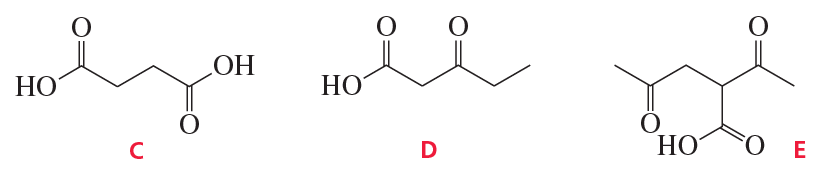
Problem 38a,b
Which of the following compounds will decarboxylate when heated?
a.
b.
Problem 38c,d,e
Which of the following compounds will decarboxylate when heated?
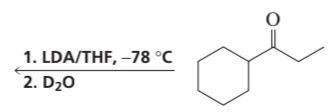
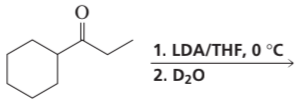
Problem 39a,b
What alkyl bromide(s) should be used in the malonic ester synthesis of each of the following carboxylic acids?
a. propanoic acid
b. 2-methylpropanoic acid
Problem 40c
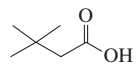
Explain why the following carboxylic acids cannot be prepared by a malonic ester synthesis:
c.
Problem 41a
What alkyl bromide should be used in the acetoacetic ester synthesis of each of the following methyl ketones? a. 2-pentanone
Problem 41b
What alkyl bromide should be used in the acetoacetic ester synthesis of each of the following methyl ketones? b. 2-octanone
Problem 41c
What alkyl bromide should be used in the acetoacetic ester synthesis of each of the following methyl ketones? c. 4-phenyl-2-butanone
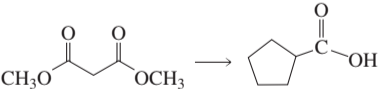
Problem 43b
Design a synthesis for each of the following compounds using the given starting material:
b.
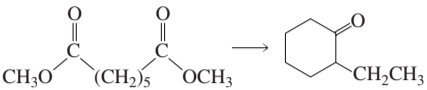
Problem 43d
Design a synthesis for each of the following compounds using the given starting material:
d.
Problem 48a
Draw a structure for each of the following:
a. ethyl acetoacetate
Problem 48b
Draw a structure for each of the following:
b. a-methylmalonic acid
Problem 48c
Draw a structure for each of the following:
c. a β-keto ester
Problem 48d
Draw a structure for each of the following: d. the enol tautomer of cyclopentanone
Problem 49a
Draw the products of the following reactions:
a. diethyl heptanedioate: (1) sodium ethoxide; (2) HCl
Problem 49b
Draw the products of the following reactions: b. pentanoic acid + PBr3 + Br2, followed by hydrolysis
Problem 49c
Draw the products of the following reactions:
c. acetone + LDA/THF: (1) slow addition of ethyl acetate; (2) HCl
Problem 49e
Draw the products of the following reactions: e. diethyl malonate: (1) sodium ethoxide; (2) isobutyl bromide; (3) HCl, H2O + heat
Problem 51
The 1H NMR chemical shifts of nitromethane, dinitromethane, and trinitromethane are at δ6.10, δ4.33, and δ7.52. Match each chemical shift with the compound. Explain how chemical shift correlates with pKa.
Problem 52
Which of the following compounds decarboxylates when heated?
Problem 53d
Draw the products of the following reactions:
d. diethyl 1,2-benzenedicarboxylate + sodium ethoxide: (1) slow addition of ethyl acetate; (2) HCl
Problem 55a
Draw the products of the following reactions:
a.
Problem 55b
Draw the products of the following reactions:
b.
Problem 57
An aldol addition can be catalyzed by acids as well as by bases. Propose a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed aldol addition of propanal.
Problem 58
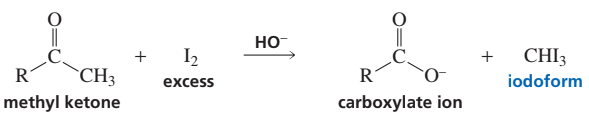
In the presence of excess base and excess halogen, a methyl ketone is converted to a carboxylate ion. The reaction is known as the haloform reaction because one of the products is haloform (chloroform, bromoform, or iodoform). Before spectroscopy became a routine analytical tool, the haloform reaction served as a test for methyl ketones: the formation of iodoform, a bright yellow compound, signaled that a methyl ketone was present. Why do only methyl ketones form a haloform?
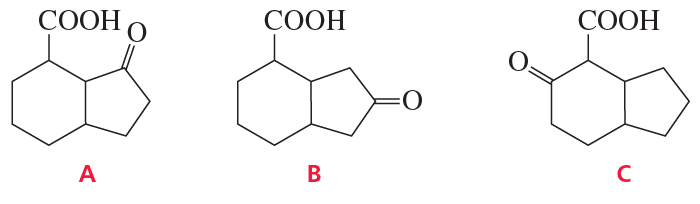
Problem 59a,b,c
Identify A–C. (Hint: A shows three singlets in its 1H NMR spectrum with integral ratios 3 : 2 : 3 and gives a positive iodoform test; see Problem 58.)
Problem 60a
Using cyclopentanone as the reactant, show the product of a. acid-catalyzed keto–enol interconversion.
Problem 60a,b
Using cyclopentanone as the reactant, show the product of
b. an aldol addition.
c. an aldol condensation.
Problem 61
Show how 4-methyl-3-hexanol can be synthesized from 3-pentanone.